原文链接: https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/maximum-depth-of-binary-tree
英文原文
Given the root of a binary tree, return its maximum depth.
A binary tree's maximum depth is the number of nodes along the longest path from the root node down to the farthest leaf node.
Example 1:

Input: root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7] Output: 3
Example 2:
Input: root = [1,null,2] Output: 2
Example 3:
Input: root = [] Output: 0
Example 4:
Input: root = [0] Output: 1
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[0, 104]. -100 <= Node.val <= 100
中文题目
给定一个二叉树,找出其最大深度。
二叉树的深度为根节点到最远叶子节点的最长路径上的节点数。
说明: 叶子节点是指没有子节点的节点。
示例:
给定二叉树 [3,9,20,null,null,15,7],
3
/ \
9 20
/ \
15 7
返回它的最大深度 3 。
通过代码
高赞题解
📺 视频题解
📖 文字题解
方法一:深度优先搜索
思路与算法
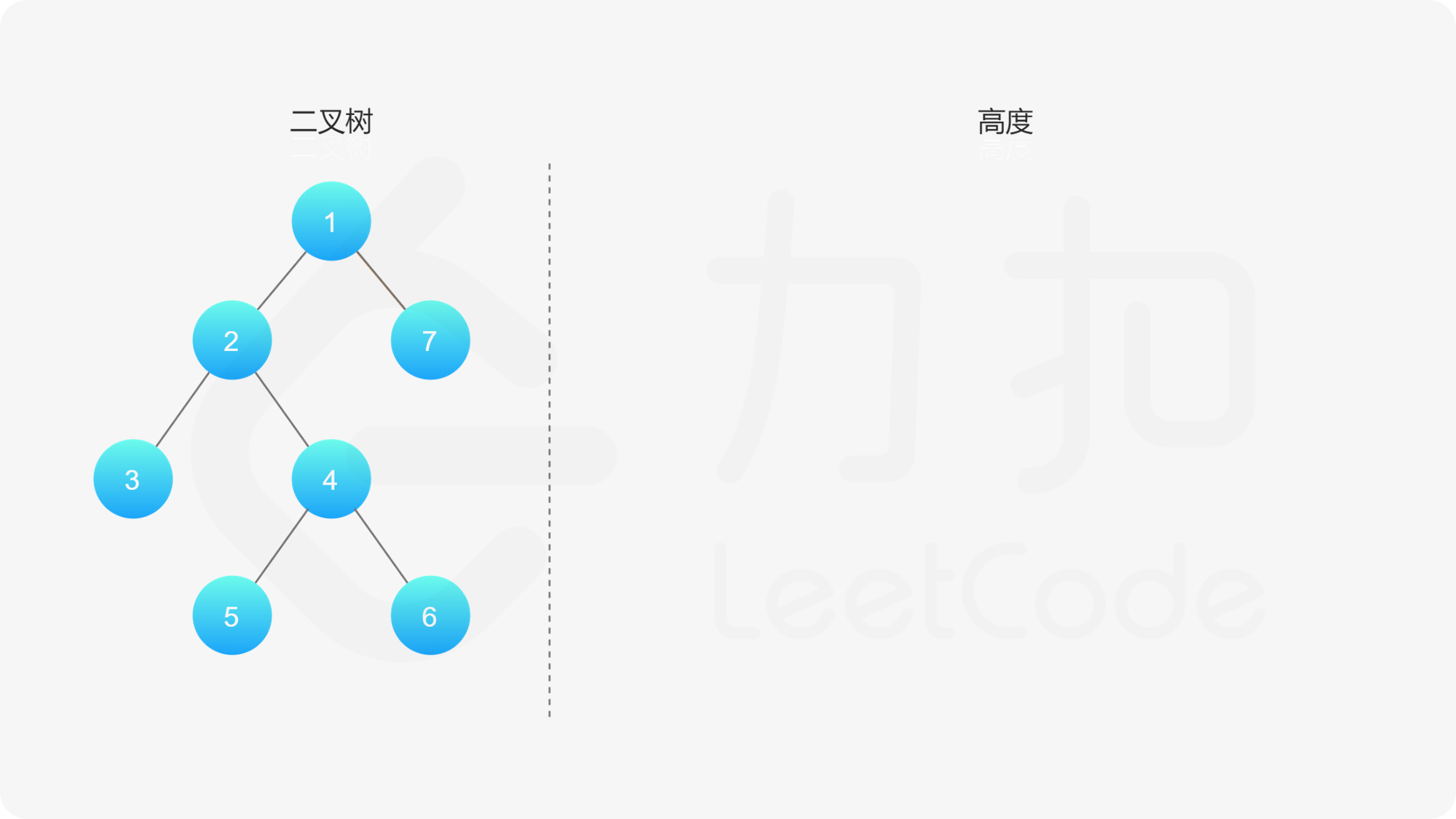
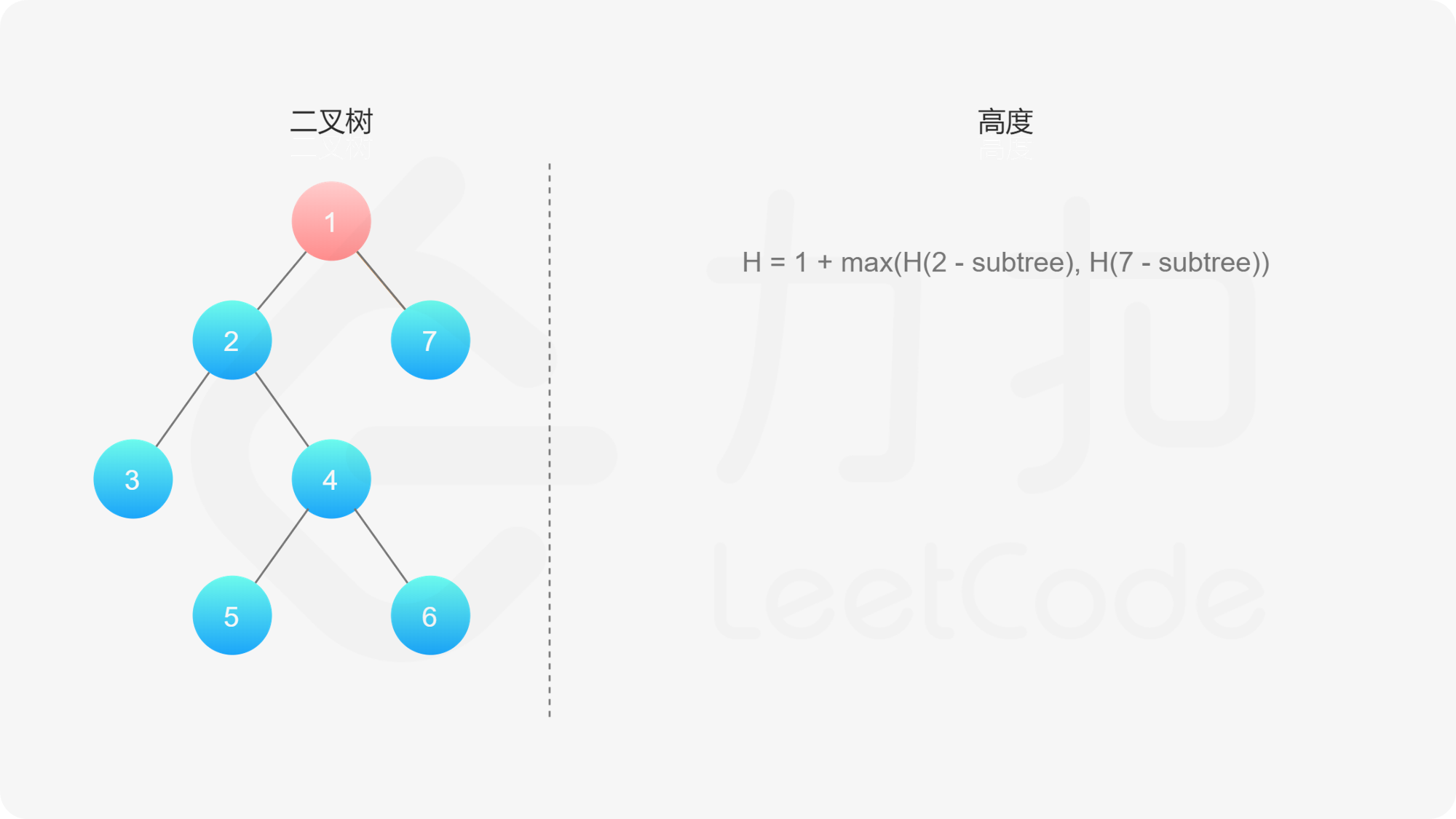
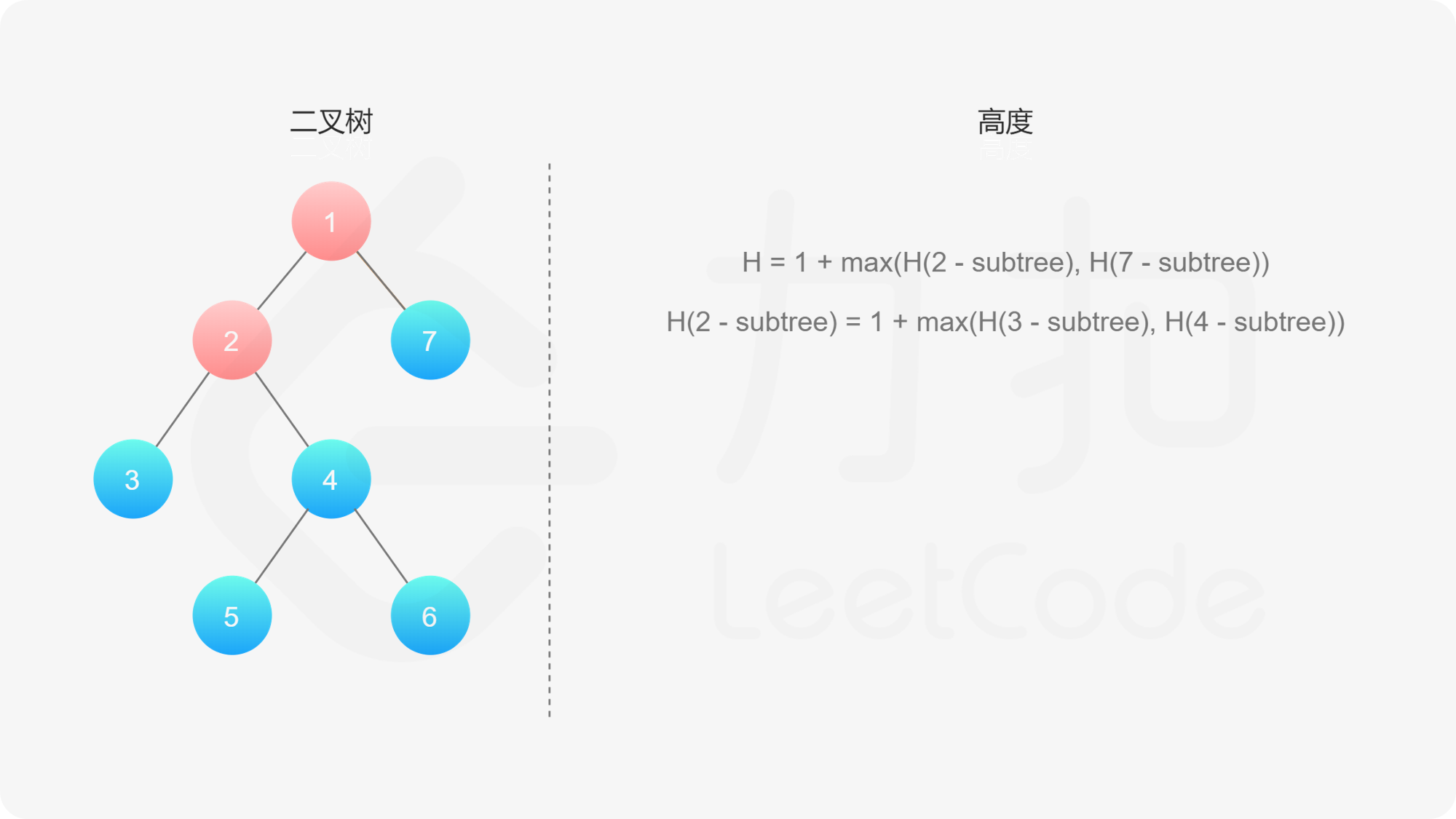
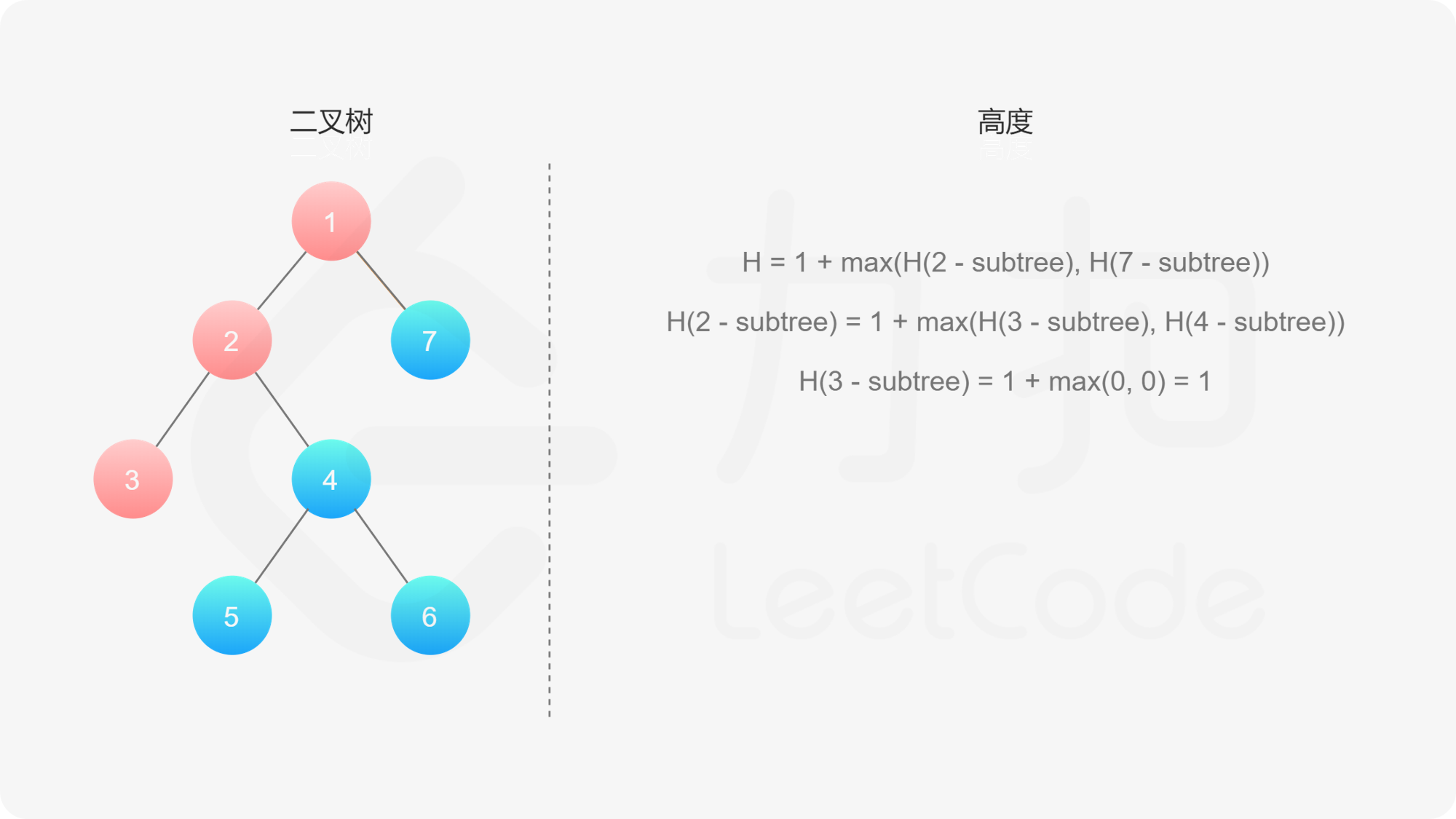
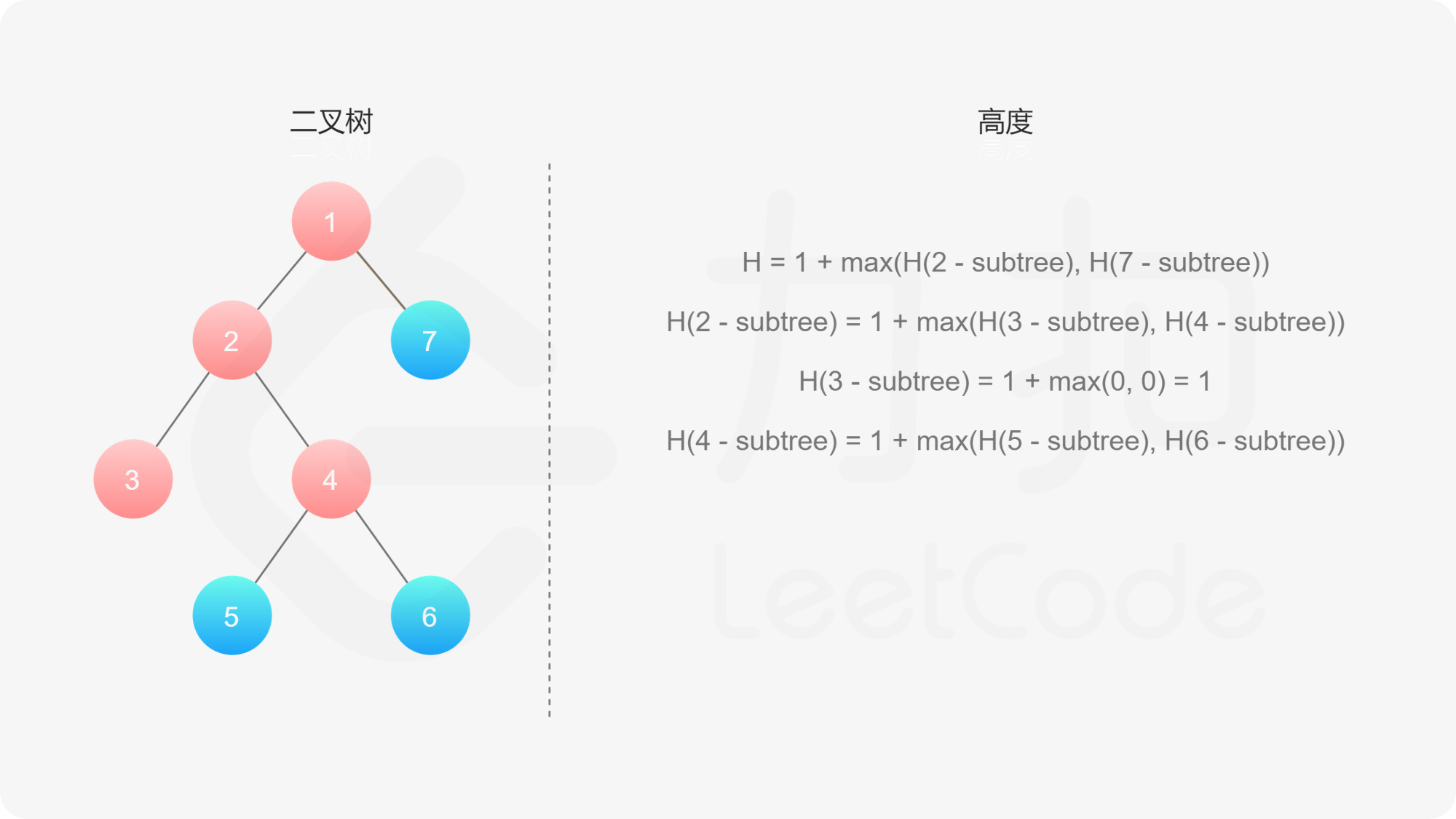
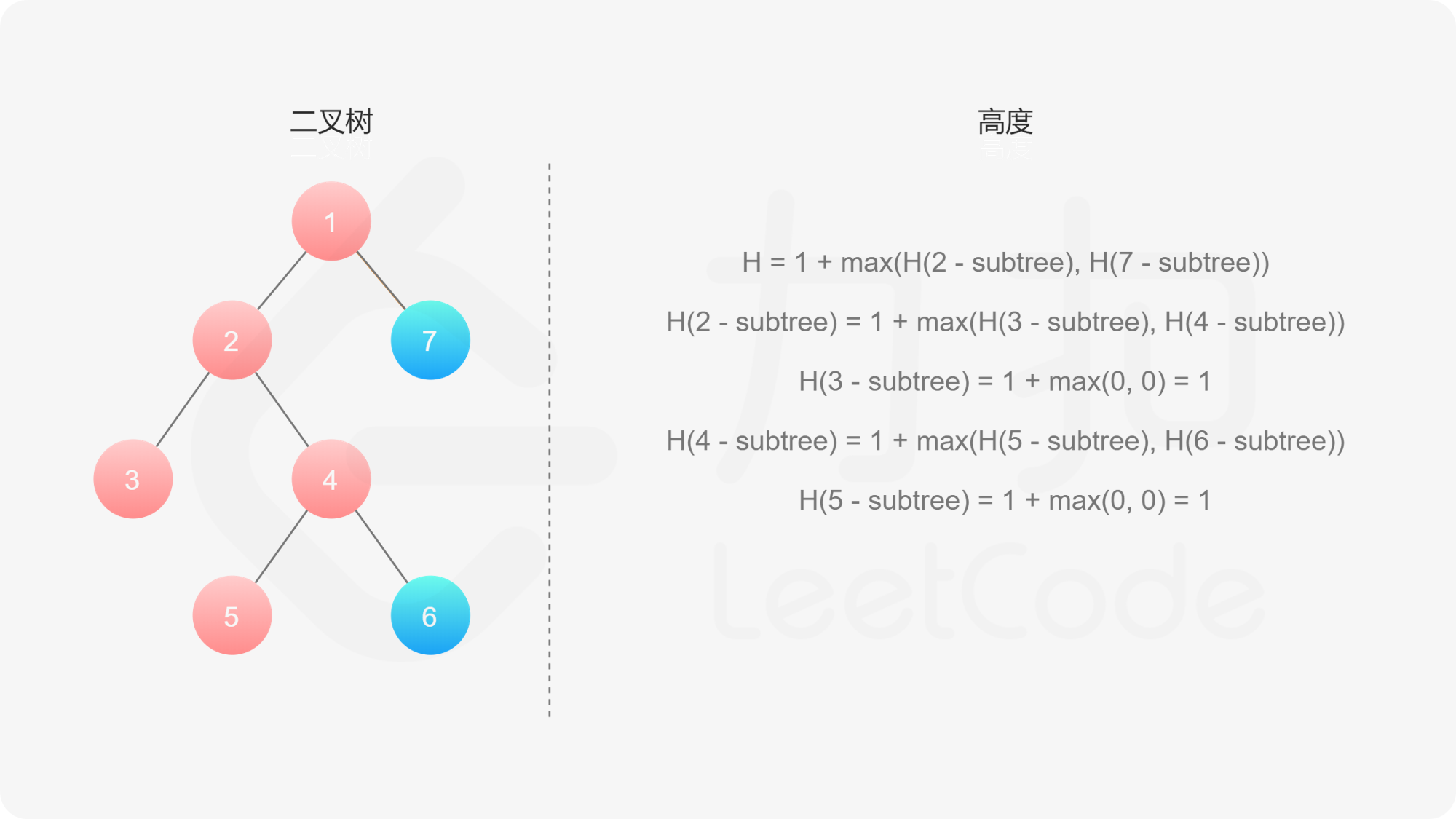
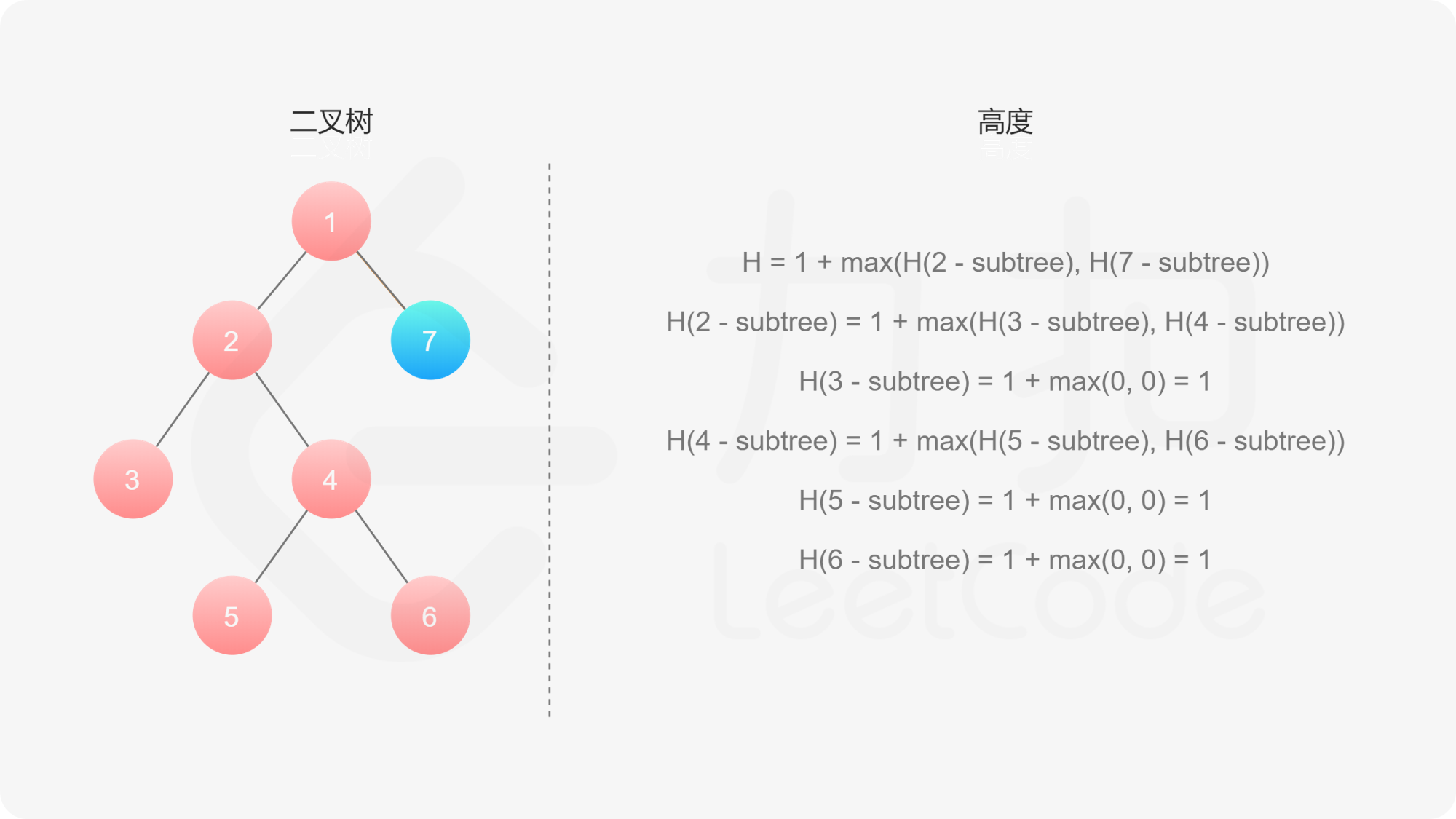
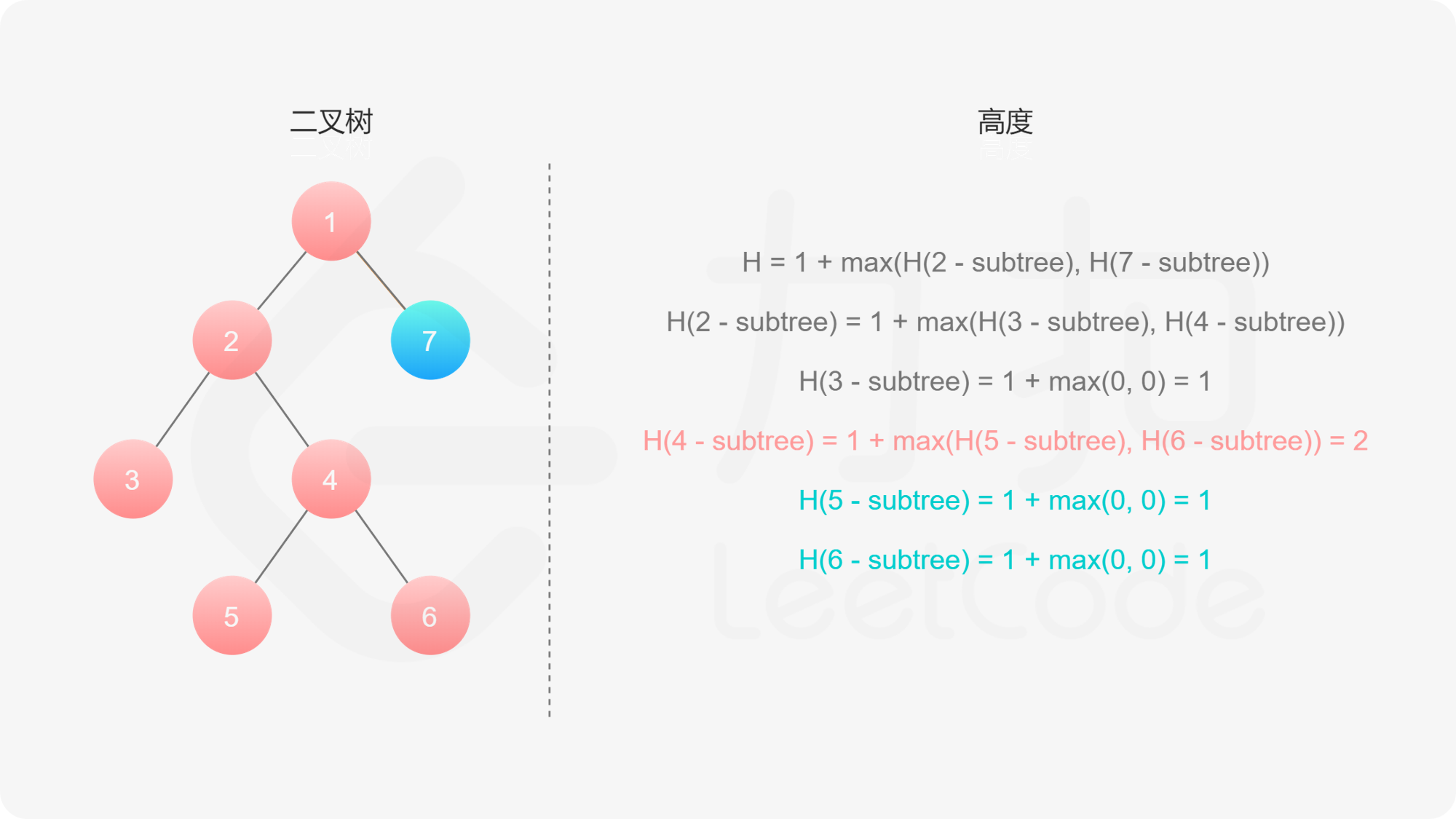
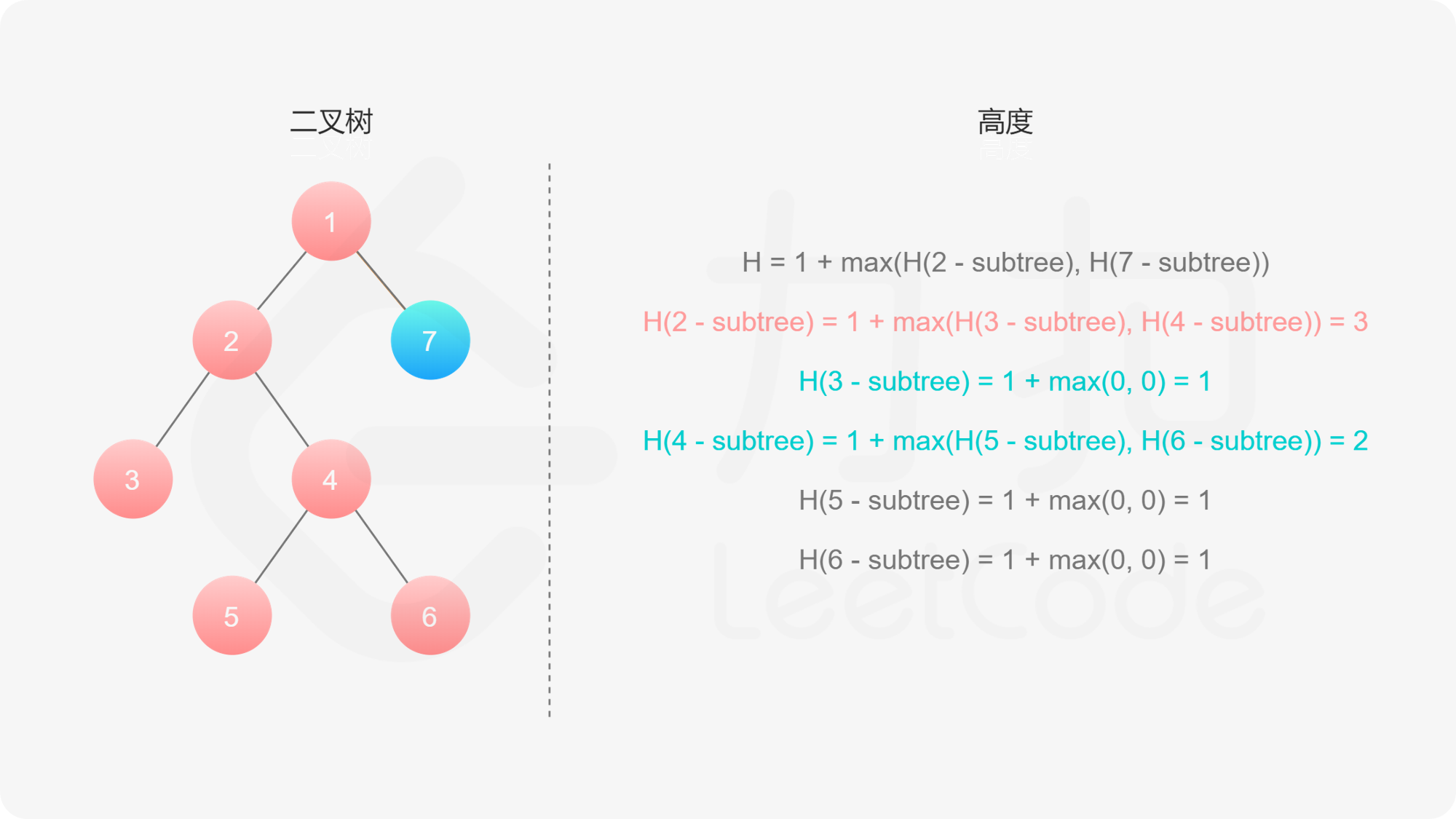
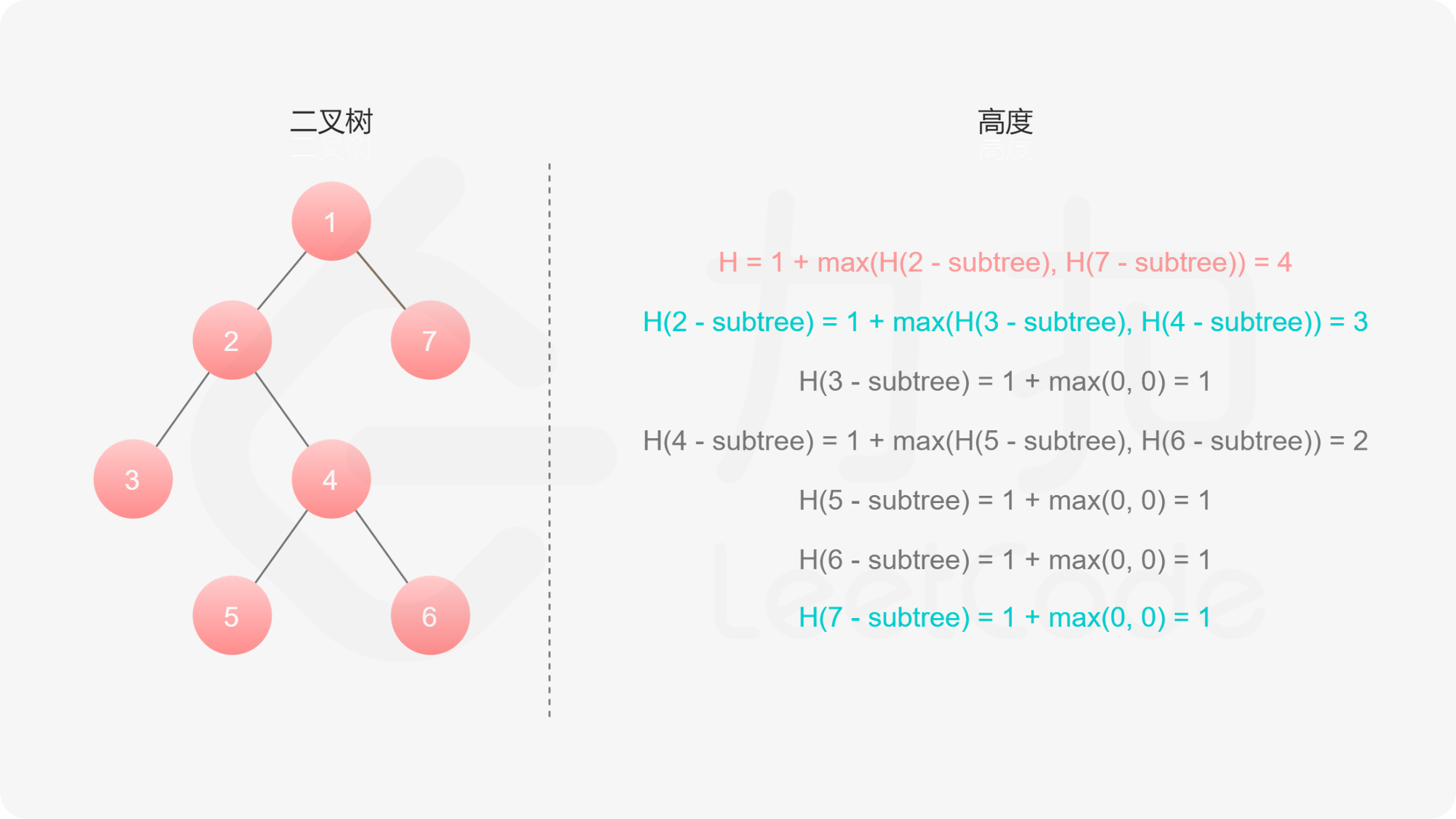
如果我们知道了左子树和右子树的最大深度 $l$ 和 $r$,那么该二叉树的最大深度即为
$$
\max(l,r) + 1
$$
而左子树和右子树的最大深度又可以以同样的方式进行计算。因此我们可以用「深度优先搜索」的方法来计算二叉树的最大深度。具体而言,在计算当前二叉树的最大深度时,可以先递归计算出其左子树和右子树的最大深度,然后在 $O(1)$ 时间内计算出当前二叉树的最大深度。递归在访问到空节点时退出。
< ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, >
>
[sol1-C++]class Solution { public: int maxDepth(TreeNode* root) { if (root == nullptr) return 0; return max(maxDepth(root->left), maxDepth(root->right)) + 1; } };
[sol1-Java]class Solution { public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) { if (root == null) { return 0; } else { int leftHeight = maxDepth(root.left); int rightHeight = maxDepth(root.right); return Math.max(leftHeight, rightHeight) + 1; } } }
[sol1-Python]class Solution: def maxDepth(self, root): if root is None: return 0 else: left_height = self.maxDepth(root.left) right_height = self.maxDepth(root.right) return max(left_height, right_height) + 1
[sol1-Golang]func maxDepth(root *TreeNode) int { if root == nil { return 0 } return max(maxDepth(root.Left), maxDepth(root.Right)) + 1 } func max(a, b int) int { if a > b { return a } return b }
[sol1-C]int maxDepth(struct TreeNode *root) { if (root == NULL) return 0; return fmax(maxDepth(root->left), maxDepth(root->right)) + 1; }
复杂度分析
时间复杂度:$O(n)$,其中 $n$ 为二叉树节点的个数。每个节点在递归中只被遍历一次。
空间复杂度:$O(\textit{height})$,其中 $\textit{height}$ 表示二叉树的高度。递归函数需要栈空间,而栈空间取决于递归的深度,因此空间复杂度等价于二叉树的高度。
方法二:广度优先搜索
思路与算法
我们也可以用「广度优先搜索」的方法来解决这道题目,但我们需要对其进行一些修改,此时我们广度优先搜索的队列里存放的是「当前层的所有节点」。每次拓展下一层的时候,不同于广度优先搜索的每次只从队列里拿出一个节点,我们需要将队列里的所有节点都拿出来进行拓展,这样能保证每次拓展完的时候队列里存放的是当前层的所有节点,即我们是一层一层地进行拓展,最后我们用一个变量 $\textit{ans}$ 来维护拓展的次数,该二叉树的最大深度即为 $\textit{ans}$。
[sol2-C++]class Solution { public: int maxDepth(TreeNode* root) { if (root == nullptr) return 0; queue<TreeNode*> Q; Q.push(root); int ans = 0; while (!Q.empty()) { int sz = Q.size(); while (sz > 0) { TreeNode* node = Q.front();Q.pop(); if (node->left) Q.push(node->left); if (node->right) Q.push(node->right); sz -= 1; } ans += 1; } return ans; } };
[sol2-Java]class Solution { public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) { if (root == null) { return 0; } Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<TreeNode>(); queue.offer(root); int ans = 0; while (!queue.isEmpty()) { int size = queue.size(); while (size > 0) { TreeNode node = queue.poll(); if (node.left != null) { queue.offer(node.left); } if (node.right != null) { queue.offer(node.right); } size--; } ans++; } return ans; } }
[sol2-Golang]func maxDepth(root *TreeNode) int { if root == nil { return 0 } queue := []*TreeNode{} queue = append(queue, root) ans := 0 for len(queue) > 0 { sz := len(queue) for sz > 0 { node := queue[0] queue = queue[1:] if node.Left != nil { queue = append(queue, node.Left) } if node.Right != nil { queue = append(queue, node.Right) } sz-- } ans++ } return ans }
[sol2-C]struct QueNode { struct TreeNode *p; struct QueNode *next; }; void init(struct QueNode **p, struct TreeNode *t) { (*p) = (struct QueNode *)malloc(sizeof(struct QueNode)); (*p)->p = t; (*p)->next = NULL; } int maxDepth(struct TreeNode *root) { if (root == NULL) return 0; struct QueNode *left, *right; init(&left, root); right = left; int ans = 0, sz = 1, tmp = 0; while (left != NULL) { tmp = 0; while (sz > 0) { if (left->p->left != NULL) { init(&right->next, left->p->left); right = right->next; tmp++; } if (left->p->right != NULL) { init(&right->next, left->p->right); right = right->next; tmp++; } left = left->next; sz--; } sz += tmp; ans++; } return ans; }
复杂度分析
时间复杂度:$O(n)$,其中 $n$ 为二叉树的节点个数。与方法一同样的分析,每个节点只会被访问一次。
空间复杂度:此方法空间的消耗取决于队列存储的元素数量,其在最坏情况下会达到 $O(n)$。
统计信息
| 通过次数 | 提交次数 | AC比率 |
|---|---|---|
| 559456 | 729750 | 76.7% |
提交历史
| 提交时间 | 提交结果 | 执行时间 | 内存消耗 | 语言 |
|---|
相似题目
| 题目 | 难度 |
|---|---|
| 平衡二叉树 | 简单 |
| 二叉树的最小深度 | 简单 |
| N 叉树的最大深度 | 简单 |




