英文原文
Given a binary tree, determine if it is height-balanced.
For this problem, a height-balanced binary tree is defined as:
a binary tree in which the left and right subtrees of every node differ in height by no more than 1.
Example 1:
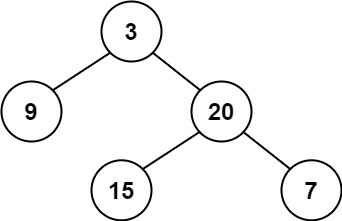
Input: root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7] Output: true
Example 2:
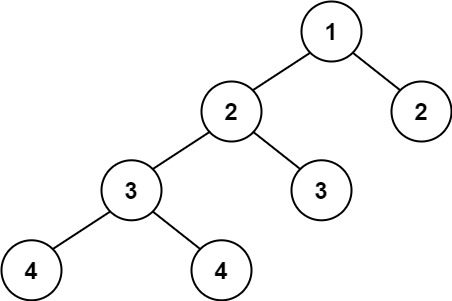
Input: root = [1,2,2,3,3,null,null,4,4] Output: false
Example 3:
Input: root = [] Output: true
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[0, 5000]. -104 <= Node.val <= 104
中文题目
给定一个二叉树,判断它是否是高度平衡的二叉树。
本题中,一棵高度平衡二叉树定义为:
一个二叉树每个节点 的左右两个子树的高度差的绝对值不超过 1 。
示例 1:

输入:root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7] 输出:true
示例 2:

输入:root = [1,2,2,3,3,null,null,4,4] 输出:false
示例 3:
输入:root = [] 输出:true
提示:
- 树中的节点数在范围
[0, 5000]内 -104 <= Node.val <= 104
通过代码
高赞题解
从底至顶(提前阻断)
此方法为本题的最优解法,但“从底至顶”的思路不易第一时间想到。
思路是对二叉树做先序遍历,从底至顶返回子树最大高度,若判定某子树不是平衡树则 “剪枝” ,直接向上返回。
算法流程:
recur(root):
- 递归返回值:
- 当节点
root左 / 右子树的高度差 $< 2$ :则返回以节点root为根节点的子树的最大高度,即节点root的左右子树中最大高度加 $1$ (max(left, right) + 1); - 当节点
root左 / 右子树的高度差 $\geq 2$ :则返回 $-1$ ,代表 此子树不是平衡树 。
- 当节点
- 递归终止条件:
- 当越过叶子节点时,返回高度 $0$ ;
- 当左(右)子树高度
left== -1时,代表此子树的 左(右)子树 不是平衡树,因此直接返回 $-1$ ;
isBalanced(root) :
- 返回值: 若
recur(root) != 1,则说明此树平衡,返回 $true$ ; 否则返回 $false$ 。
复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度 $O(N)$: $N$ 为树的节点数;最差情况下,需要递归遍历树的所有节点。
- 空间复杂度 $O(N)$: 最差情况下(树退化为链表时),系统递归需要使用 $O(N)$ 的栈空间。
[]class Solution: def isBalanced(self, root: TreeNode) -> bool: return self.recur(root) != -1 def recur(self, root): if not root: return 0 left = self.recur(root.left) if left == -1: return -1 right = self.recur(root.right) if right == -1: return -1 return max(left, right) + 1 if abs(left - right) < 2 else -1
[]class Solution { public boolean isBalanced(TreeNode root) { return recur(root) != -1; } private int recur(TreeNode root) { if (root == null) return 0; int left = recur(root.left); if(left == -1) return -1; int right = recur(root.right); if(right == -1) return -1; return Math.abs(left - right) < 2 ? Math.max(left, right) + 1 : -1; } }
从顶至底(暴力法)
此方法容易想到,但会产生大量重复计算,时间复杂度较高。
思路是构造一个获取当前节点最大深度的方法 depth(root) ,通过比较此子树的左右子树的最大高度差abs(depth(root.left) - depth(root.right)),来判断此子树是否是二叉平衡树。若树的所有子树都平衡时,此树才平衡。
算法流程:
isBalanced(root) :判断树 root 是否平衡
- 特例处理: 若树根节点
root为空,则直接返回 $true$ ; - 返回值: 所有子树都需要满足平衡树性质,因此以下三者使用与逻辑 $&&$ 连接;
abs(self.depth(root.left) - self.depth(root.right)) <= 1:判断 当前子树 是否是平衡树;self.isBalanced(root.left): 先序遍历递归,判断 当前子树的左子树 是否是平衡树;self.isBalanced(root.right): 先序遍历递归,判断 当前子树的右子树 是否是平衡树;
depth(root) : 计算树 root 的最大高度
- 终止条件: 当
root为空,即越过叶子节点,则返回高度 $0$ ; - 返回值: 返回左 / 右子树的最大高度加 $1$ 。
复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度 $O(Nlog_2 N)$: 最差情况下,
isBalanced(root)遍历树所有节点,占用 $O(N)$ ;判断每个节点的最大高度depth(root)需要遍历 各子树的所有节点 ,子树的节点数的复杂度为 $O(log_2 N)$ 。 - 空间复杂度 $O(N)$: 最差情况下(树退化为链表时),系统递归需要使用 $O(N)$ 的栈空间。
[]class Solution: def isBalanced(self, root: TreeNode) -> bool: if not root: return True return abs(self.depth(root.left) - self.depth(root.right)) <= 1 and \ self.isBalanced(root.left) and self.isBalanced(root.right) def depth(self, root): if not root: return 0 return max(self.depth(root.left), self.depth(root.right)) + 1
[]class Solution { public boolean isBalanced(TreeNode root) { if (root == null) return true; return Math.abs(depth(root.left) - depth(root.right)) <= 1 && isBalanced(root.left) && isBalanced(root.right); } private int depth(TreeNode root) { if (root == null) return 0; return Math.max(depth(root.left), depth(root.right)) + 1; } }
统计信息
| 通过次数 | 提交次数 | AC比率 |
|---|---|---|
| 277495 | 491843 | 56.4% |
提交历史
| 提交时间 | 提交结果 | 执行时间 | 内存消耗 | 语言 |
|---|
相似题目
| 题目 | 难度 |
|---|---|
| 二叉树的最大深度 | 简单 |




