原文链接: https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/cells-with-odd-values-in-a-matrix
英文原文
There is an m x n matrix that is initialized to all 0's. There is also a 2D array indices where each indices[i] = [ri, ci] represents a 0-indexed location to perform some increment operations on the matrix.
For each location indices[i], do both of the following:
- Increment all the cells on row
ri. - Increment all the cells on column
ci.
Given m, n, and indices, return the number of odd-valued cells in the matrix after applying the increment to all locations in indices.
Example 1:
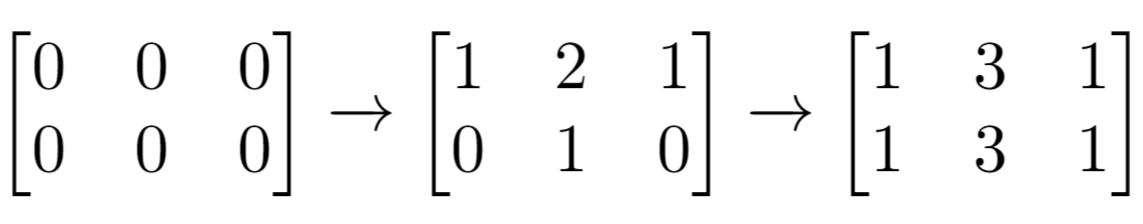
Input: m = 2, n = 3, indices = [[0,1],[1,1]] Output: 6 Explanation: Initial matrix = [[0,0,0],[0,0,0]]. After applying first increment it becomes [[1,2,1],[0,1,0]]. The final matrix is [[1,3,1],[1,3,1]], which contains 6 odd numbers.
Example 2:
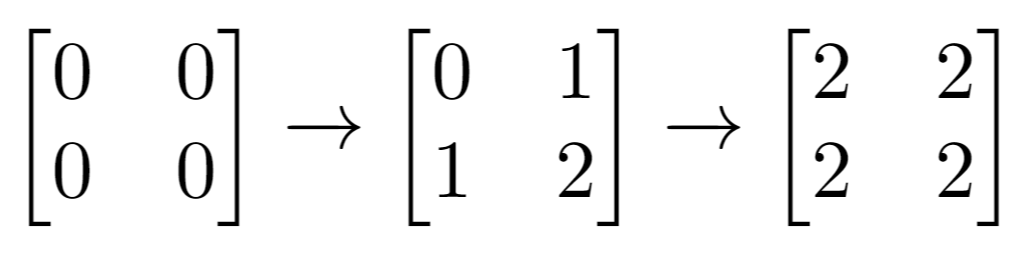
Input: m = 2, n = 2, indices = [[1,1],[0,0]] Output: 0 Explanation: Final matrix = [[2,2],[2,2]]. There are no odd numbers in the final matrix.
Constraints:
1 <= m, n <= 501 <= indices.length <= 1000 <= ri < m0 <= ci < n
Follow up: Could you solve this in O(n + m + indices.length) time with only O(n + m) extra space?
中文题目
给你一个 m x n 的矩阵,最开始的时候,每个单元格中的值都是 0。
另有一个二维索引数组 indices,indices[i] = [ri, ci] 指向矩阵中的某个位置,其中 ri 和 ci 分别表示指定的行和列(从 0 开始编号)。
对 indices[i] 所指向的每个位置,应同时执行下述增量操作:
ri行上的所有单元格,加1。ci列上的所有单元格,加1。
给你 m、n 和 indices 。请你在执行完所有 indices 指定的增量操作后,返回矩阵中 奇数值单元格 的数目。
示例 1:
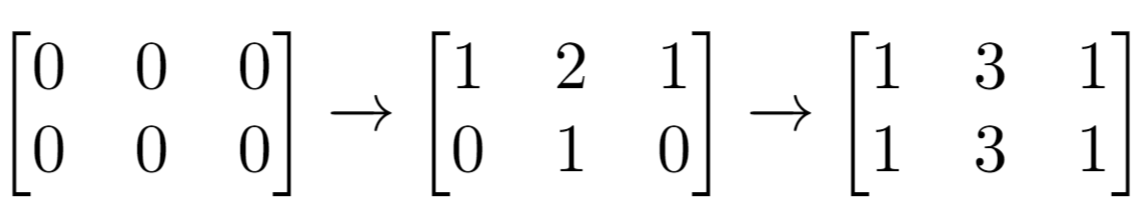
输入:m = 2, n = 3, indices = [[0,1],[1,1]] 输出:6 解释:最开始的矩阵是 [[0,0,0],[0,0,0]]。 第一次增量操作后得到 [[1,2,1],[0,1,0]]。 最后的矩阵是 [[1,3,1],[1,3,1]],里面有 6 个奇数。
示例 2:
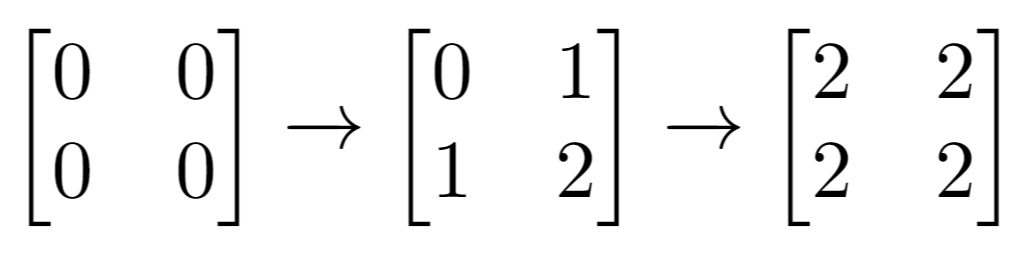
输入:m = 2, n = 2, indices = [[1,1],[0,0]] 输出:0 解释:最后的矩阵是 [[2,2],[2,2]],里面没有奇数。
提示:
1 <= m, n <= 501 <= indices.length <= 1000 <= ri < m0 <= ci < n
进阶:你可以设计一个时间复杂度为 O(n + m + indices.length) 且仅用 O(n + m) 额外空间的算法来解决此问题吗?
通过代码
高赞题解
方法一:模拟
我们可以使用一个 n * m 的矩阵来存放操作的结果,对于 indices 中的每一对 [ri, ci],将矩阵第 ri 行的所有数增加 1,第 ci 列的所有数增加 1。
在所有操作模拟完毕后,我们遍历矩阵,得到奇数的数目。
[sol1]class Solution: def oddCells(self, n: int, m: int, indices: List[List[int]]) -> int: matrix = [[0] * m for _ in range(n)] for x, y in indices: for i in range(n): matrix[i][y] += 1 for j in range(m): matrix[x][j] += 1 return sum(elem % 2 == 1 for line in matrix for elem in line)
复杂度分析
时间复杂度:$O(L(M + N) + MN)$,其中 $L$ 是
indices数组的长度。空间复杂度:$O(MN)$。
方法二:模拟 + 空间优化
由于每次操作只会将一行和一列的数增加 1,因此我们可以使用一个行数组 rows 和列数组 cols 分别记录每一行和每一列被增加的次数。对于 indices 中的每一对 [ri, ci],我们将 rows[ri] 和 cols[ci] 的值分别增加 1。
在所有操作模拟完毕后,矩阵中位于 (x, y) 位置的数即为 rows[x] + cols[y]。我们遍历矩阵,得到奇数的数目。
[sol2]class Solution: def oddCells(self, n: int, m: int, indices: List[List[int]]) -> int: rows = [0] * n cols = [0] * m for x, y in indices: rows[x] += 1 cols[y] += 1 return sum((rows[x] + cols[y]) % 2 == 1 for x in range(n) for y in range(m))
复杂度分析
时间复杂度:$O(L + MN)$,其中 $L$ 是
indices数组的长度。空间复杂度:$O(M + N)$。
方法三:计数
我们可以继续对方法二进行优化。可以发现,矩阵中位于 (x, y) 位置的数为奇数,当且仅当 rows[x] 和 cols[y] 中恰好有一个为奇数。因此对于 rows[x] 为偶数,那么在第 x 行有 count_odd(cols) 个位置的数为奇数;对于 rows[x] 为奇数,那么在第 x 行有 m - count_odd(cols) 个位置的数为偶数,其中 count_odd(cols) 表示数组 cols 中奇数的个数。将所有的行 x 进行求和,可以得到奇数的数目为 count_odd(rows) * (m - count_odd(cols)) + (n - count_odd(rows)) * count_odd(cols)。
[sol3]class Solution: def oddCells(self, n: int, m: int, indices: List[List[int]]) -> int: rows = [0] * n cols = [0] * m for x, y in indices: rows[x] += 1 cols[y] += 1 odd_rows = sum(x % 2 == 1 for x in rows) odd_cols = sum(y % 2 == 1 for y in cols) return odd_rows * (m - odd_cols) + (n - odd_rows) * odd_cols
复杂度分析
时间复杂度:$O(L + M + N)$,其中 $L$ 是
indices数组的长度。空间复杂度:$O(M + N)$。
统计信息
| 通过次数 | 提交次数 | AC比率 |
|---|---|---|
| 18405 | 24557 | 74.9% |
提交历史
| 提交时间 | 提交结果 | 执行时间 | 内存消耗 | 语言 |
|---|




