原文链接: https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/minimum-absolute-difference-in-bst
英文原文
Given the root of a Binary Search Tree (BST), return the minimum absolute difference between the values of any two different nodes in the tree.
Example 1:
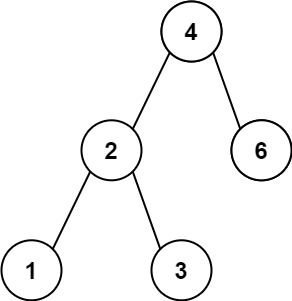
Input: root = [4,2,6,1,3] Output: 1
Example 2:
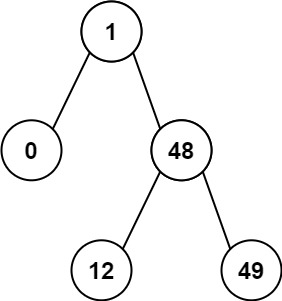
Input: root = [1,0,48,null,null,12,49] Output: 1
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[2, 104]. 0 <= Node.val <= 105
Note: This question is the same as 783: https://leetcode.com/problems/minimum-distance-between-bst-nodes/
中文题目
给你一个二叉搜索树的根节点 root ,返回 树中任意两不同节点值之间的最小差值 。
差值是一个正数,其数值等于两值之差的绝对值。
示例 1:

输入:root = [4,2,6,1,3] 输出:1
示例 2:

输入:root = [1,0,48,null,null,12,49] 输出:1
提示:
- 树中节点的数目范围是
[2, 104] 0 <= Node.val <= 105
注意:本题与 783 https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/minimum-distance-between-bst-nodes/ 相同
通过代码
高赞题解
通过中序遍历二叉搜索树得到的关键码序列是一个递增序列。
这是二叉搜索树的一个重要性质,巧妙利用这一性质可以解决一系列二叉搜索树问题。
本系列以以下非递归中序遍历代码为核心,解决一系列相关问题。
p = root
st = [] # 用列表模拟实现栈的功能
while p is not None or st:
while p is not None:
st.append(p)
p = p.left
p = st.pop()
proc(p.val)
p = p.right
一 二叉搜索树迭代器
(一)算法思路
中序遍历二叉树
(二)算法实现
class BSTIterator:
def __init__(self, root: TreeNode):
self.root = root
self.st = []
self.current = self.root
def next(self) -> int:
"""
@return the next smallest number
"""
while self.current is not None or self.st:
while self.current is not None:
self.st.append(self.current)
self.current = self.current.left
self.current = self.st.pop()
node = self.current
self.current = self.current.right
return node.val
def hasNext(self) -> bool:
"""
@return whether we have a next smallest number
"""
return self.current or self.st
二 二叉搜索树的最小绝对差
(一)算法思路
中序遍历二叉搜索树,第一个结点外的每个节点与其前一节点的差值,如果该值小于最小绝对差,就用它更新最小绝对差(初始可设为无穷)。
(二)算法实现
class Solution:
def getMinimumDifference(self, root: TreeNode) -> int:
st = []
p = root
pre = -float('inf')
min_val = float('inf')
while p is not None or st:
while p is not None:
st.append(p)
p = p.left
p = st.pop()
cur = p.val
if cur - pre < min_val:
min_val = cur - pre
pre = cur
p = p.right
return min_val
(三)复杂度分析
时间复杂度:O(N),N为树中节点个数。
空间复杂度:O(log(N))。
三 二叉搜索树中第k小的元素
(一)算法思路
二叉搜索树的中序遍历序列为递增序列,因此可中序遍历二叉搜索树,返回第K个元素。
(二)算法实现
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.left = None
# self.right = None
class Solution:
def kthSmallest(self, root: TreeNode, k: int) -> int:
st = []
p = root
s = 0
while p is not None or st:
while p is not None:
st.append(p)
p = p.left
p = st.pop()
s += 1
if s == k:
return p.val
p = p.right
(三) 复杂度分析
时间复杂度:O(N),N为树中节点个数。
空间复杂度:O(log(N))。
四 二叉搜索树中的众数
(一) 算法思想
二叉搜索树的中序遍历序列单调不减(或曰非严格单调递增),因此可考虑中序遍历二叉搜索树。
用max_times记录已访问节点的最大重复元素个数,time表示当前访问节点的元素值的出现次数,用res=[]记录结果。
若time == max_times,则将当前节点值添加到结果集。
若time > max_times,则以当前节点值构造新的列表作为结果,并用time更新max_times。
中序遍历结束后,返回结果res。
(二) 算法实现
class Solution:
def findMode(self, root: TreeNode) -> List[int]:
if root is None:
return []
p = root
st = []
res = []
max_times = 1
time = 1
pre = float("inf")
while p is not None or st:
while p is not None:
st.append(p)
p = p.left
p = st.pop()
cur = p.val
if cur == pre:
time += 1
else:
time = 1
pre = cur
if time == max_times:
res.append(cur)
if time > max_times:
res = [cur]
max_times = time
p = p.right
return res
(三) 复杂度分析
时间复杂度:O(N),N为树中节点个数。
空间复杂度:最坏情况下为O(N), 例如树畸形(树的高度为线性)或每个元素出现一次的情形。
五 二叉搜索树的范围和
(一)算法思路
中序遍历二叉搜索树
当节点的值等于L时开始累加,当节点的值等于R时停止累加并返回累加的结果。
(二)算法实现
class Solution:
def rangeSumBST(self, root: TreeNode, L: int, R: int) -> int:
st = []
p = root
s = 0
while p is not None or st:
while p is not None:
st.append(p)
p = p.left
p = st.pop()
if p.val == L:
s = L
p = p.right
break
p = p.right
while p is not None or st:
while p is not None:
st.append(p)
p = p.left
p = st.pop()
s += p.val
if p.val == R:
return s
p = p.right
(三)复杂度分析
时间复杂度:O(N), N为树中节点数。
空间复杂度:O(log(N))。
六 两数之和IV-输入BST
(一)算法思路
中序遍历+双指针
(二)算法实现
class Solution(object):
def findTarget(self, root, k):
"""
:type root: TreeNode
:type k: int
:rtype: bool
"""
nums = []
st = []
p = root
while p is not None or st:
while p is not None:
st.append(p)
p = p.left
p = st.pop()
nums.append(p.val)
p = p.right
n = len(nums)
i, j = 0, n-1
while i < j:
if nums[i] + nums[j] == k:
return True
elif nums[i] + nums[j] > k:
j -= 1
else:
i += 1
return False
(三)复杂度分析
时间复杂度:O(N)
空间复杂度:O(N)
七 验证二叉搜索树
(一)算法思路
一棵二叉树是二叉搜索树的充要条件是它的中序遍历序列单调递增,因此可以通过判断一个树的中序遍历序列是否单调递增来验证该树是否为二叉搜索树。
(二)算法实现
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode(object):
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.left = None
# self.right = None
class Solution(object):
def isValidBST(self, root):
"""
:type root: TreeNode
:rtype: bool
"""
pre = -float('inf')
p = root
st = []
while p is not None or st:
while p is not None:
st.append(p)
p = p.left
p = st.pop()
if p.val > pre:
pre = p.val
else:
return False
p = p.right
return True
(三)复杂度分析
时间复杂度:O(N)。
空间复杂度:O(log(N))。
统计信息
| 通过次数 | 提交次数 | AC比率 |
|---|---|---|
| 84665 | 136234 | 62.1% |
提交历史
| 提交时间 | 提交结果 | 执行时间 | 内存消耗 | 语言 |
|---|
相似题目
| 题目 | 难度 |
|---|---|
| 数组中的 k-diff 数对 | 中等 |




