原文链接: https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/projection-area-of-3d-shapes
英文原文
You are given an n x n grid where we place some 1 x 1 x 1 cubes that are axis-aligned with the x, y, and z axes.
Each value v = grid[i][j] represents a tower of v cubes placed on top of the cell (i, j).
We view the projection of these cubes onto the xy, yz, and zx planes.
A projection is like a shadow, that maps our 3-dimensional figure to a 2-dimensional plane. We are viewing the "shadow" when looking at the cubes from the top, the front, and the side.
Return the total area of all three projections.
Example 1:
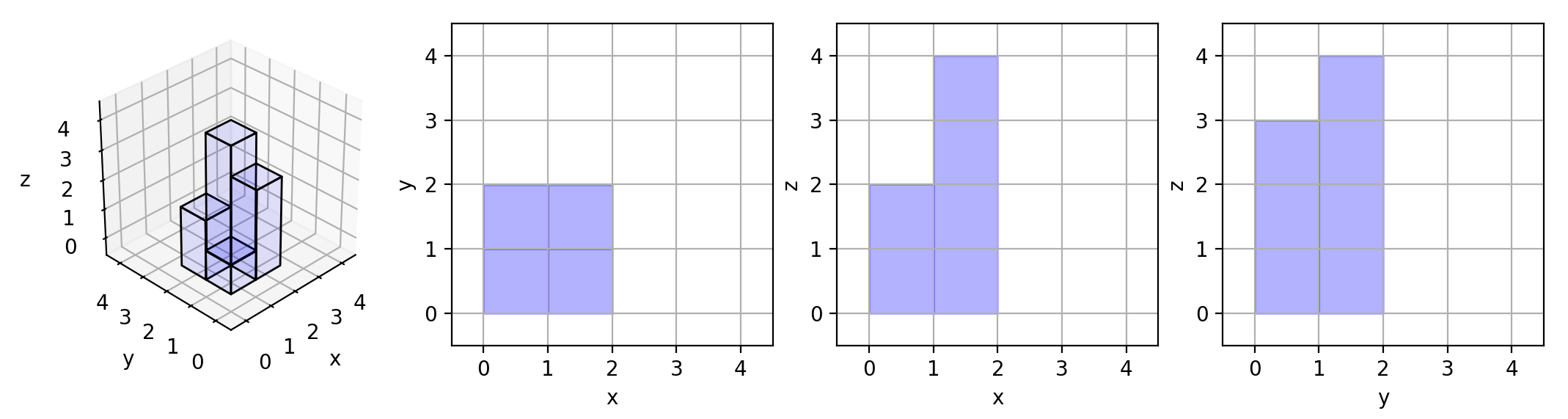
Input: grid = [[1,2],[3,4]]
Output: 17
Explanation: Here are the three projections ("shadows") of the shape made with each axis-aligned plane.
Example 2:
Input: grid = [[2]] Output: 5
Example 3:
Input: grid = [[1,0],[0,2]] Output: 8
Example 4:
Input: grid = [[1,1,1],[1,0,1],[1,1,1]] Output: 14
Example 5:
Input: grid = [[2,2,2],[2,1,2],[2,2,2]] Output: 21
Constraints:
n == grid.lengthn == grid[i].length1 <= n <= 500 <= grid[i][j] <= 50
中文题目
在 N * N 的网格中,我们放置了一些与 x,y,z 三轴对齐的 1 * 1 * 1 立方体。
每个值 v = grid[i][j] 表示 v 个正方体叠放在单元格 (i, j) 上。
现在,我们查看这些立方体在 xy、yz 和 zx 平面上的投影。
投影就像影子,将三维形体映射到一个二维平面上。
在这里,从顶部、前面和侧面看立方体时,我们会看到“影子”。
返回所有三个投影的总面积。
示例 1:
输入:[[2]] 输出:5
示例 2:
输入:[[1,2],[3,4]] 输出:17 解释: 这里有该形体在三个轴对齐平面上的三个投影(“阴影部分”)。
示例 3:
输入:[[1,0],[0,2]] 输出:8
示例 4:
输入:[[1,1,1],[1,0,1],[1,1,1]] 输出:14
示例 5:
输入:[[2,2,2],[2,1,2],[2,2,2]] 输出:21
提示:
1 <= grid.length = grid[0].length <= 500 <= grid[i][j] <= 50
通过代码
官方题解
方法:数学
思路和算法
从顶部看,由该形状生成的阴影将是网格中非零值的数目。
从侧面看,由该形状生成的阴影将是网格中每一行的最大值。
从前面看,由该形状生成的阴影将是网格中每一列的最大值。
示例
例如 [[1,2],[3,4]]:
顶部的阴影将为 4,因为网格中有四个非零值;
侧面的阴影为
2 + 4,因为第一行的最大值为2,第二行的最大值为4;前面的阴影是
3 + 4,因为第一列的最大值是3,第二列的最大值是4。
[DoBY8EpQ-C++]class Solution { public: int projectionArea(vector<vector<int>>& grid) { int N = grid.size(); int ans = 0; for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i) { int bestRow = 0; // largest of grid[i][j] int bestCol = 0; // largest of grid[j][i] for (int j = 0; j < N; ++j) { if (grid[i][j] > 0) ans++; // top shadow bestRow = max(bestRow, grid[i][j]); bestCol = max(bestCol, grid[j][i]); } ans += bestRow + bestCol; } return ans; } };
[DoBY8EpQ-Java]class Solution { public int projectionArea(int[][] grid) { int N = grid.length; int ans = 0; for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i) { int bestRow = 0; // largest of grid[i][j] int bestCol = 0; // largest of grid[j][i] for (int j = 0; j < N; ++j) { if (grid[i][j] > 0) ans++; // top shadow bestRow = Math.max(bestRow, grid[i][j]); bestCol = Math.max(bestCol, grid[j][i]); } ans += bestRow + bestCol; } return ans; } }
[DoBY8EpQ-Python]class Solution: def projectionArea(self, grid): N = len(grid) ans = 0 for i in xrange(N): best_row = 0 # max of grid[i][j] best_col = 0 # max of grid[j][i] for j in xrange(N): if grid[i][j]: ans += 1 # top shadow best_row = max(best_row, grid[i][j]) best_col = max(best_col, grid[j][i]) ans += best_row + best_col return ans """ Alternative solution: ans = sum(map(max, grid)) ans += sum(map(max, zip(*grid))) ans += sum(v > 0 for row in grid for v in row) """
复杂度分析
时间复杂度:$O(N^2)$,其中 $N$ 是
grid的长度。空间复杂度:$O(1)$.
统计信息
| 通过次数 | 提交次数 | AC比率 |
|---|---|---|
| 11285 | 16316 | 69.2% |
提交历史
| 提交时间 | 提交结果 | 执行时间 | 内存消耗 | 语言 |
|---|




