英文原文
Design a Skiplist without using any built-in libraries.
A skiplist is a data structure that takes O(log(n)) time to add, erase and search. Comparing with treap and red-black tree which has the same function and performance, the code length of Skiplist can be comparatively short and the idea behind Skiplists is just simple linked lists.
For example, we have a Skiplist containing [30,40,50,60,70,90] and we want to add 80 and 45 into it. The Skiplist works this way:
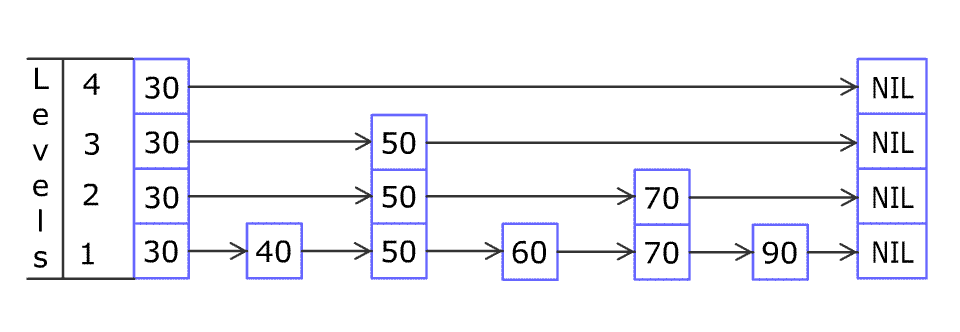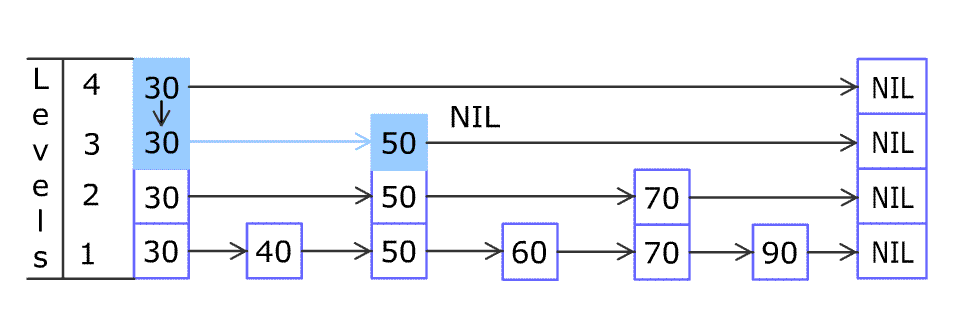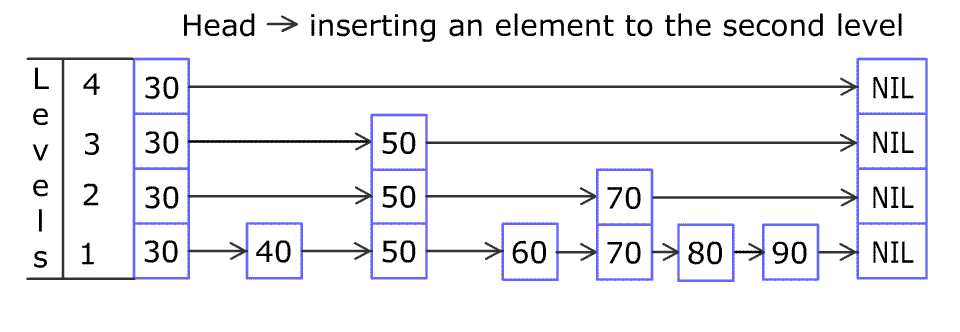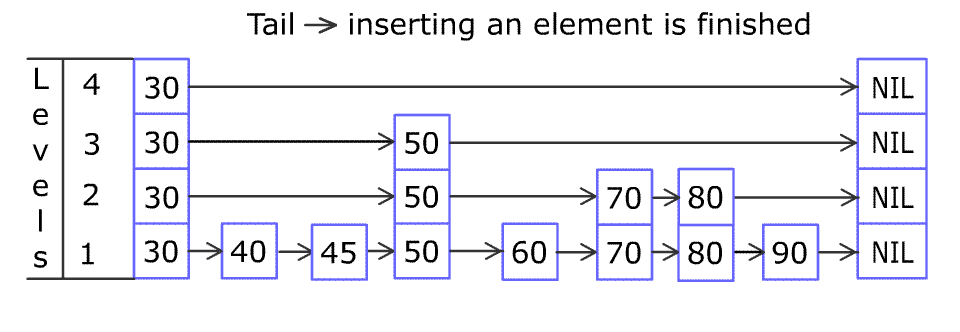
Artyom Kalinin [CC BY-SA 3.0], via Wikimedia Commons
You can see there are many layers in the Skiplist. Each layer is a sorted linked list. With the help of the top layers, add, erase and search can be faster than O(n). It can be proven that the average time complexity for each operation is O(log(n)) and space complexity is O(n).
See more about Skiplist: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Skip_list
Implement the Skiplist class:
Skiplist()Initializes the object of the skiplist.bool search(int target)Returnstrueif the integertargetexists in the Skiplist orfalseotherwise.void add(int num)Inserts the valuenuminto the SkipList.bool erase(int num)Removes the valuenumfrom the Skiplist and returnstrue. Ifnumdoes not exist in the Skiplist, do nothing and returnfalse. If there exist multiplenumvalues, removing any one of them is fine.
Note that duplicates may exist in the Skiplist, your code needs to handle this situation.
Example 1:
Input ["Skiplist", "add", "add", "add", "search", "add", "search", "erase", "erase", "search"] [[], [1], [2], [3], [0], [4], [1], [0], [1], [1]] Output [null, null, null, null, false, null, true, false, true, false] Explanation Skiplist skiplist = new Skiplist(); skiplist.add(1); skiplist.add(2); skiplist.add(3); skiplist.search(0); // return False skiplist.add(4); skiplist.search(1); // return True skiplist.erase(0); // return False, 0 is not in skiplist. skiplist.erase(1); // return True skiplist.search(1); // return False, 1 has already been erased.
Constraints:
0 <= num, target <= 2 * 104- At most
5 * 104calls will be made tosearch,add, anderase.
中文题目
不使用任何库函数,设计一个跳表。
跳表是在 O(log(n)) 时间内完成增加、删除、搜索操作的数据结构。跳表相比于树堆与红黑树,其功能与性能相当,并且跳表的代码长度相较下更短,其设计思想与链表相似。
例如,一个跳表包含 [30, 40, 50, 60, 70, 90],然后增加 80、45 到跳表中,以下图的方式操作:

Artyom Kalinin [CC BY-SA 3.0], via Wikimedia Commons
跳表中有很多层,每一层是一个短的链表。在第一层的作用下,增加、删除和搜索操作的时间复杂度不超过 O(n)。跳表的每一个操作的平均时间复杂度是 O(log(n)),空间复杂度是 O(n)。
在本题中,你的设计应该要包含这些函数:
bool search(int target): 返回target是否存在于跳表中。void add(int num): 插入一个元素到跳表。bool erase(int num): 在跳表中删除一个值,如果num不存在,直接返回false. 如果存在多个num,删除其中任意一个即可。
了解更多 : https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Skip_list
注意,跳表中可能存在多个相同的值,你的代码需要处理这种情况。
样例:
Skiplist skiplist = new Skiplist(); skiplist.add(1); skiplist.add(2); skiplist.add(3); skiplist.search(0); // 返回 false skiplist.add(4); skiplist.search(1); // 返回 true skiplist.erase(0); // 返回 false,0 不在跳表中 skiplist.erase(1); // 返回 true skiplist.search(1); // 返回 false,1 已被擦除
约束条件:
0 <= num, target <= 20000- 最多调用
50000次search,add, 以及erase操作。
通过代码
高赞题解
解题思路
跳表实现的主要难度在于插入(add)算法。只要把add方法搞明白之后,一切都迎刃而解了。
关于跳表的插入,一张图即可描述出来,
通过这张图,可以先确定跳表中每个节点的数据结构:
class Node{
Integer value; //节点值
Node[] next; // 节点在不同层的下一个节点
public Node(Integer value,int size) { // 用size表示当前节点在跳表中索引几层
this.value = value;
this.next = new Node[size];
}
}然后就需要考虑:我插入一个节点Node,它到底应该是索引到第几层呢?
一开始我还想着如何准确的维护上一层是下一层的1/2,发现越想越复杂;然后通过相关资料,发现人家早就给出一个解决方案:随机出来一个层数。
这里有一个疑惑:就凭随机出来的一个层数,能保证查询与插入性能吗?
在分析之前,我们还需要着重指出的是,执行插入操作时计算随机数的过程,是一个很关键的过程,它对skiplist的统计特性有着很重要的影响。这并不是一个普通的服从均匀分布的随机数,它的计算过程如下:
首先,每个节点肯定都有第1层指针(每个节点都在第1层链表里)。
如果一个节点有第i层(i>=1)指针(即节点已经在第1层到第i层链表中),那么它有第(i+1)层指针的概率为p。
节点最大的层数不允许超过一个最大值,记为MaxLevel。
这个计算随机层数的伪码如下所示:
int randomLevel()
int level = 1;
while (Math.random()<p && level<MaxLevel){
level ++ ;
}
return level;randomLevel()的伪码中包含两个参数,一个是p,一个是MaxLevel。在Redis的skiplist实现中,这两个参数的取值为:
p = 1/4
MaxLevel = 32from : http://zhangtielei.com/posts/blog-redis-skiplist.html
知道了层数,这下就好办了。思路如下:
先随机出来一个层数,new要插入的节点,先叫做插入节点newNode;
根据跳表实际的总层数从上往下分析,要插入一个节点newNode时,先找到节点在该层的位置:因为是链表,所以需要一个节点node,满足插入插入节点newNode的值刚好不大于node的下一个节点值,当然,如果node的下个节点为空,那么也是满足的。
我们先把找节点在某一层位置的方法封装起来:
/**
* 找到level层 value 刚好不小于node 的节点
* @param node 从哪个节点开始找
* @param levelIndex 所在层
* @param value 要插入的节点值
* @return
*/
private Node findClosest(Node node,int levelIndex,int value){
while ((node.next[levelIndex])!=null && value >node.next[levelIndex].value){
node = node.next[levelIndex];
}
return node;
}确定插入节点newNode在该层的位置后,先判断下newNode的随机层数是否小于当前跳表的总层数,如果是,则用链表的插入方法将newNode插入即可。
如此循环,直到最底层插入newNode完毕。
循环完毕后,还需要判断下newNode随机出来的层数是否比跳表的实际层数还要大,如果是,直接将超过实际层数的跳表的头节点指向newNode即可,该跳表的实际层数也就变为newNode的随机层数了。
以上就是插入的算法。
理解了插入算法后,查找跟删除就简单多了。
不管是插入、查找还是删除,均是从跳表上层往下层分析,复用上面的findClosest方法,找到要查询的值 在该层closest的节点。比如查询,只需要判断findClosest出来的节点值是否等于该查询值即可,是就返回,不是则继续往下层判断。删除方法思想也是一致的。
代码
class Skiplist {
/**
* 最大层数
*/
private static int DEFAULT_MAX_LEVEL = 32;
/**
* 随机层数概率,也就是随机出的层数,在 第1层以上(不包括第一层)的概率,层数不超过maxLevel,层数的起始号为1
*/
private static double DEFAULT_P_FACTOR = 0.25;
Node head = new Node(null,DEFAULT_MAX_LEVEL); //头节点
int currentLevel = 1; //表示当前nodes的实际层数,它从1开始
public Skiplist() {
}
public boolean search(int target) {
Node searchNode = head;
for (int i = currentLevel-1; i >=0; i--) {
searchNode = findClosest(searchNode, i, target);
if (searchNode.next[i]!=null && searchNode.next[i].value == target){
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
/**
*
* @param num
*/
public void add(int num) {
int level = randomLevel();
Node updateNode = head;
Node newNode = new Node(num,level);
// 计算出当前num 索引的实际层数,从该层开始添加索引
for (int i = currentLevel-1; i>=0; i--) {
//找到本层最近离num最近的list
updateNode = findClosest(updateNode,i,num);
if (i<level){
if (updateNode.next[i]==null){
updateNode.next[i] = newNode;
}else{
Node temp = updateNode.next[i];
updateNode.next[i] = newNode;
newNode.next[i] = temp;
}
}
}
if (level > currentLevel){ //如果随机出来的层数比当前的层数还大,那么超过currentLevel的head 直接指向newNode
for (int i = currentLevel; i < level; i++) {
head.next[i] = newNode;
}
currentLevel = level;
}
}
public boolean erase(int num) {
boolean flag = false;
Node searchNode = head;
for (int i = currentLevel-1; i >=0; i--) {
searchNode = findClosest(searchNode, i, num);
if (searchNode.next[i]!=null && searchNode.next[i].value == num){
//找到该层中该节点
searchNode.next[i] = searchNode.next[i].next[i];
flag = true;
continue;
}
}
return flag;
}
/**
* 找到level层 value 大于node 的节点
* @param node
* @param levelIndex
* @param value
* @return
*/
private Node findClosest(Node node,int levelIndex,int value){
while ((node.next[levelIndex])!=null && value >node.next[levelIndex].value){
node = node.next[levelIndex];
}
return node;
}
/**
* 随机一个层数
*/
private static int randomLevel(){
int level = 1;
while (Math.random()<DEFAULT_P_FACTOR && level<DEFAULT_MAX_LEVEL){
level ++ ;
}
return level;
}
class Node{
Integer value;
Node[] next;
public Node(Integer value,int size) {
this.value = value;
this.next = new Node[size];
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return String.valueOf(value);
}
}
}统计信息
| 通过次数 | 提交次数 | AC比率 |
|---|---|---|
| 7573 | 12358 | 61.3% |
提交历史
| 提交时间 | 提交结果 | 执行时间 | 内存消耗 | 语言 |
|---|




