原文链接: https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/maximum-profit-in-job-scheduling
英文原文
We have n jobs, where every job is scheduled to be done from startTime[i] to endTime[i], obtaining a profit of profit[i].
You're given the startTime, endTime and profit arrays, return the maximum profit you can take such that there are no two jobs in the subset with overlapping time range.
If you choose a job that ends at time X you will be able to start another job that starts at time X.
Example 1:
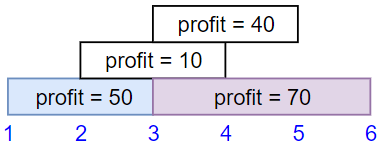
Input: startTime = [1,2,3,3], endTime = [3,4,5,6], profit = [50,10,40,70] Output: 120 Explanation: The subset chosen is the first and fourth job. Time range [1-3]+[3-6] , we get profit of 120 = 50 + 70.
Example 2:
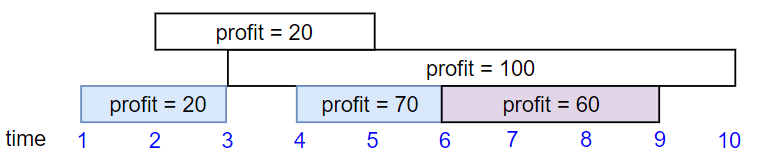
Input: startTime = [1,2,3,4,6], endTime = [3,5,10,6,9], profit = [20,20,100,70,60] Output: 150 Explanation: The subset chosen is the first, fourth and fifth job. Profit obtained 150 = 20 + 70 + 60.
Example 3:
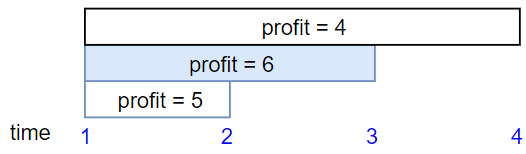
Input: startTime = [1,1,1], endTime = [2,3,4], profit = [5,6,4] Output: 6
Constraints:
1 <= startTime.length == endTime.length == profit.length <= 5 * 1041 <= startTime[i] < endTime[i] <= 1091 <= profit[i] <= 104
中文题目
你打算利用空闲时间来做兼职工作赚些零花钱。
这里有 n 份兼职工作,每份工作预计从 startTime[i] 开始到 endTime[i] 结束,报酬为 profit[i]。
给你一份兼职工作表,包含开始时间 startTime,结束时间 endTime 和预计报酬 profit 三个数组,请你计算并返回可以获得的最大报酬。
注意,时间上出现重叠的 2 份工作不能同时进行。
如果你选择的工作在时间 X 结束,那么你可以立刻进行在时间 X 开始的下一份工作。
示例 1:
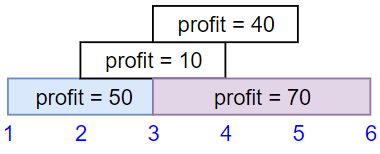
输入:startTime = [1,2,3,3], endTime = [3,4,5,6], profit = [50,10,40,70] 输出:120 解释: 我们选出第 1 份和第 4 份工作, 时间范围是 [1-3]+[3-6],共获得报酬 120 = 50 + 70。
示例 2:
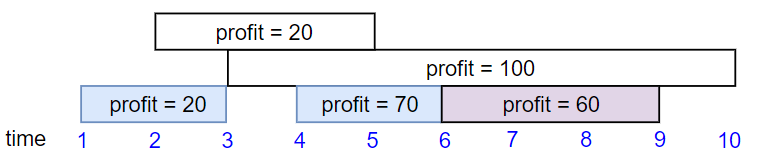
输入:startTime = [1,2,3,4,6], endTime = [3,5,10,6,9], profit = [20,20,100,70,60] 输出:150 解释: 我们选择第 1,4,5 份工作。 共获得报酬 150 = 20 + 70 + 60。
示例 3:
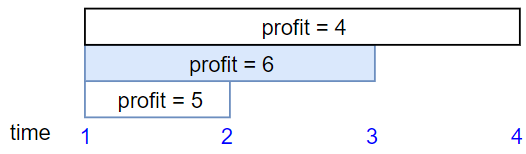
输入:startTime = [1,1,1], endTime = [2,3,4], profit = [5,6,4] 输出:6
提示:
1 <= startTime.length == endTime.length == profit.length <= 5 * 10^41 <= startTime[i] < endTime[i] <= 10^91 <= profit[i] <= 10^4
通过代码
高赞题解
我们把示例2拿出来重新按工作的结束时间排序,如图所示:
具体来说:
我们使用一个dp数组,dp[i]表示做包括i号工作之前的所有工作能取得的最大收益
再使用一个prev数组,prev[i]表示i号工作之前最近能做的工作
0号工作之前没有能做的工作了,所以prev[0]=0;
1号工作之前没有能做的工作了,所以prev[1]=0;
2号工作之前没有能做的工作了,所以prev[2]=0;
3号工作之前最近能做的工作是1,所以prev[3]=1;
4号工作之前最近能做的工作是3,所以prev[4]=3;
5号工作之前最近能做的工作是1,所以prev[5]=1;
对于每个兼职工作,都有做与不做两种状态:
一.假如我们做1号工作,能够获得20元,加上在1号工作之前最近能做的0号工作(虚拟的工作,收益也是0)的最大收益0元;如果不做1号工作,能够获得收益是0,于是做包括1号工作之前的所有工作能取的最大收益就是两中情况的最大值20。
二.假如我们做5号工作,能够获得收益是100,加上在5号工作之前最近能做的prev[5]=1号工作的最大收益dp[1];如果不做5号工作,能够获得收益就是做剩余4个工作最大收益dp[4],于是做包括5号工作之前的所有工作能取的最大收益就是两中情况的最大值=max(dp[1]+profit[5],dp[4])。
所以状态转移方程就是
dp[i]=max(dp[i-1],dp[prev[i]]+profit[i])具体到题目中来说,由于题目的输入导致一些不同,我们可以开一个二维数组vector<vector<int>>job;把开始时间、结束时间和收益拷贝过来,再把这个二维数组排成如图所示的顺序,但是这样效率不高,因为拷贝也是要花时间的,一个比较好的办法直接对下标排序获得如图所示的顺序。
prev数组的获得是直接向前遍历,找第一个结束时间小于等于当前工作开始时间的工作,感觉这里应该还是有优化的空间的。
由于加入了一个虚拟的0号工作,所以下标还有些变化,具体看代码。这个工作到底有没么必要加呢,如果你有解决方案请告诉我。
class Solution {
public:
int jobScheduling(vector<int>& startTime, vector<int>& endTime, vector<int>& profit) {
int n = startTime.size();
vector<int>job(n+1);
iota(job.begin(), job.end(), 0);
sort(job.begin()+1, job.end(), [&](int& a, int& b) {return endTime[a-1]< endTime[b-1]; });
vector<int>prev(n + 1);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
for (int j = i - 1; j >= 1; j--)
if (endTime[job[j]-1] <=startTime[ job[i]-1])
{
prev[i] = j;
break;
}
vector<int>dp(n + 1);
dp[1] = profit[job[1]-1];
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
dp[i] = max(dp[i - 1], profit[job[i]-1] + dp[prev[i]]);
return dp[n];
}
};统计信息
| 通过次数 | 提交次数 | AC比率 |
|---|---|---|
| 6933 | 14816 | 46.8% |
提交历史
| 提交时间 | 提交结果 | 执行时间 | 内存消耗 | 语言 |
|---|




