原文链接: https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/frog-position-after-t-seconds
英文原文
Given an undirected tree consisting of n vertices numbered from 1 to n. A frog starts jumping from vertex 1. In one second, the frog jumps from its current vertex to another unvisited vertex if they are directly connected. The frog can not jump back to a visited vertex. In case the frog can jump to several vertices, it jumps randomly to one of them with the same probability. Otherwise, when the frog can not jump to any unvisited vertex, it jumps forever on the same vertex.
The edges of the undirected tree are given in the array edges, where edges[i] = [ai, bi] means that exists an edge connecting the vertices ai and bi.
Return the probability that after t seconds the frog is on the vertex target.
Example 1:
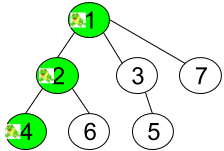
Input: n = 7, edges = [[1,2],[1,3],[1,7],[2,4],[2,6],[3,5]], t = 2, target = 4 Output: 0.16666666666666666 Explanation: The figure above shows the given graph. The frog starts at vertex 1, jumping with 1/3 probability to the vertex 2 after second 1 and then jumping with 1/2 probability to vertex 4 after second 2. Thus the probability for the frog is on the vertex 4 after 2 seconds is 1/3 * 1/2 = 1/6 = 0.16666666666666666.
Example 2:

Input: n = 7, edges = [[1,2],[1,3],[1,7],[2,4],[2,6],[3,5]], t = 1, target = 7 Output: 0.3333333333333333 Explanation: The figure above shows the given graph. The frog starts at vertex 1, jumping with 1/3 = 0.3333333333333333 probability to the vertex 7 after second 1.
Example 3:
Input: n = 7, edges = [[1,2],[1,3],[1,7],[2,4],[2,6],[3,5]], t = 20, target = 6 Output: 0.16666666666666666
Constraints:
1 <= n <= 100edges.length == n - 1edges[i].length == 21 <= ai, bi <= n1 <= t <= 501 <= target <= n- Answers within
10-5of the actual value will be accepted as correct.
中文题目
给你一棵由 n 个顶点组成的无向树,顶点编号从 1 到 n。青蛙从 顶点 1 开始起跳。规则如下:
- 在一秒内,青蛙从它所在的当前顶点跳到另一个 未访问 过的顶点(如果它们直接相连)。
- 青蛙无法跳回已经访问过的顶点。
- 如果青蛙可以跳到多个不同顶点,那么它跳到其中任意一个顶点上的机率都相同。
- 如果青蛙不能跳到任何未访问过的顶点上,那么它每次跳跃都会停留在原地。
无向树的边用数组 edges 描述,其中 edges[i] = [fromi, toi] 意味着存在一条直接连通 fromi 和 toi 两个顶点的边。
返回青蛙在 t 秒后位于目标顶点 target 上的概率。
示例 1:
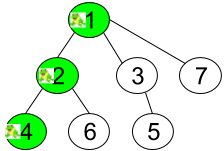
输入:n = 7, edges = [[1,2],[1,3],[1,7],[2,4],[2,6],[3,5]], t = 2, target = 4 输出:0.16666666666666666 解释:上图显示了青蛙的跳跃路径。青蛙从顶点 1 起跳,第 1 秒 有 1/3 的概率跳到顶点 2 ,然后第 2 秒 有 1/2 的概率跳到顶点 4,因此青蛙在 2 秒后位于顶点 4 的概率是 1/3 * 1/2 = 1/6 = 0.16666666666666666 。
示例 2:

输入:n = 7, edges = [[1,2],[1,3],[1,7],[2,4],[2,6],[3,5]], t = 1, target = 7 输出:0.3333333333333333 解释:上图显示了青蛙的跳跃路径。青蛙从顶点 1 起跳,有 1/3 = 0.3333333333333333 的概率能够 1 秒 后跳到顶点 7 。
示例 3:
输入:n = 7, edges = [[1,2],[1,3],[1,7],[2,4],[2,6],[3,5]], t = 20, target = 6 输出:0.16666666666666666
提示:
1 <= n <= 100edges.length == n-1edges[i].length == 21 <= edges[i][0], edges[i][1] <= n1 <= t <= 501 <= target <= n- 与准确值误差在
10^-5之内的结果将被判定为正确。
通过代码
高赞题解
关注公众号【算法码上来】,每日算法干货马上就来!

LeetCode 5352. 生成每种字符都是奇数个的字符串
题目链接
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/generate-a-string-with-characters-that-have-odd-counts/
题解
这题就没什么好说的了,如果 $n$ 是奇数,那就生成 $n$ 个 $a$ 。如果 $n$ 是偶数,那就生成 $n-1$ 个 $a$ ,再加上 $1$ 个 $b$ 。
代码(python)
class Solution:
def generateTheString(self, n: int) -> str:
if n % 2 == 0:
return "a"+"b"*(n-1)
return "a"*nLeetCode 5353. 灯泡开关 III
题目链接
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/bulb-switcher-iii/
题解
如果某一个时刻灯都是蓝色的,等价于所有的亮灯都连续排列在数组最左边,没有间断。所以只需要判断当前时刻亮灯的最大编号是否等于亮灯的数量就行了。
比赛的时候傻 x 了,第一个想到的竟然是树状数组,于是直接把模板套过来过了。
代码(c++)
class Solution {
public:
int numTimesAllBlue(vector<int>& light) {
int res = 0, maxx = 0;
for (int i = 0, sz = light.size(); i < sz; ++i) {
maxx = max(maxx, light[i]);
if (maxx == i + 1) res++;
}
return res;
}
};树状数组:
class Solution {
public:
static const int MAXN = 50010;
int bit[MAXN];
int numTimesAllBlue(vector<int>& light) {
memset(bit, 0, sizeof bit);
int maxx = 0, res = 0;
for (int i = 0, sz = light.size(); i < sz; ++i) {
add(light[i], 1);
maxx = max(maxx, light[i]);
if (sum(maxx) == maxx) res++;
}
return res;
}
int lowbit(int x) {
return x&(-x);
}
void add(int i, int x) {
while (i < MAXN) {
bit[i] += x;
i += lowbit(i);
}
}
void sub(int i, int x) {
while (i < MAXN) {
bit[i] -= x;
i += lowbit(i);
}
}
int sum(int i) {
int s = 0;
while (i > 0) {
s += bit[i];
i -= lowbit(i);
}
return s;
}
};LeetCode 5354. 通知所有员工所需的时间
题目链接
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/time-needed-to-inform-all-employees/
题解
首先根据 $manager$ 数组来建图,边权就是父结点到子结点的通知时间。然后从根结点开始做 dfs ,求出根结点到每个叶子结点的路径长度的最大值。
代码(c++)
class Solution {
public:
static const int N = 100010;
vector<int> G[N];
int numOfMinutes(int n, int headID, vector<int>& manager, vector<int>& informTime) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
if (manager[i] != -1) {
G[manager[i]].push_back(i);
}
}
return f(headID, informTime);
}
int f(int headID, vector<int>& informTime) {
if (!informTime[headID]) return 0;
int maxx = 0;
for (int i = 0, sz = G[headID].size(); i < sz; ++i) {
maxx = max(maxx, f(G[headID][i], informTime));
}
return maxx+informTime[headID];
}
};LeetCode 5355. T 秒后青蛙的位置
题目链接
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/frog-position-after-t-seconds/
题解
首先建图,然后从 $1$ 号结点开始,还是用 dfs 。每往下走一次,时间 $t$ 减 $1$ 。如果 $t = 0$ 或者到了叶子结点了,就判断结点是否为 $target$ ,是就返回 $1$ ,不是就返回 $0$ 。每次概率除以当前结点的子结点个数,然后再乘上所有子结点 dfs 结果的最大值(因为结果不是 $0$ 就是正确概率)。
代码(c++)
class Solution {
public:
double frogPosition(int n, vector<vector<int>>& edges, int t, int target) {
if (n == 1) return 1.0;
vector<vector<int>> G(110);
for (int i = 0; i < n-1; ++i) {
int u = edges[i][0], v = edges[i][1];
G[u].push_back(v);
G[v].push_back(u);
}
return dfs(1, 0, t, target, G);
}
double dfs(int u, int fa, int t, int target, vector<vector<int>>& G) {
int sz = G[u].size();
if (!t || (fa && sz == 1)) {
if (u == target) return 1;
else return 0;
}
double p = 1.0 / (fa ? sz-1 : sz), maxx = 0;
for (int i = 0, sz = G[u].size(); i < sz; ++i) {
int v = G[u][i];
if (v == fa) continue;
maxx = max(maxx, dfs(v, u, t-1, target, G));
}
return p*maxx;
}
};统计信息
| 通过次数 | 提交次数 | AC比率 |
|---|---|---|
| 4378 | 13370 | 32.7% |
提交历史
| 提交时间 | 提交结果 | 执行时间 | 内存消耗 | 语言 |
|---|




