原文链接: https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/kth-ancestor-of-a-tree-node
英文原文
You are given a tree with n nodes numbered from 0 to n - 1 in the form of a parent array parent where parent[i] is the parent of ith node. The root of the tree is node 0. Find the kth ancestor of a given node.
The kth ancestor of a tree node is the kth node in the path from that node to the root node.
Implement the TreeAncestor class:
TreeAncestor(int n, int[] parent)Initializes the object with the number of nodes in the tree and the parent array.int getKthAncestor(int node, int k)return thekthancestor of the given nodenode. If there is no such ancestor, return-1.
Example 1:
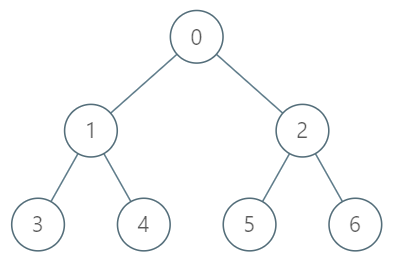
Input ["TreeAncestor", "getKthAncestor", "getKthAncestor", "getKthAncestor"] [[7, [-1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 2, 2]], [3, 1], [5, 2], [6, 3]] Output [null, 1, 0, -1]Explanation
TreeAncestor treeAncestor = new TreeAncestor(7, [-1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 2, 2]);
treeAncestor.getKthAncestor(3, 1); // returns 1 which is the parent of 3
treeAncestor.getKthAncestor(5, 2); // returns 0 which is the grandparent of 5
treeAncestor.getKthAncestor(6, 3); // returns -1 because there is no such ancestor
Constraints:
1 <= k <= n <= 5 * 104parent.length == nparent[0] == -10 <= parent[i] < nfor all0 < i < n0 <= node < n- There will be at most
5 * 104queries.
中文题目
给你一棵树,树上有 n 个节点,按从 0 到 n-1 编号。树以父节点数组的形式给出,其中 parent[i] 是节点 i 的父节点。树的根节点是编号为 0 的节点。
请你设计并实现 getKthAncestor(int node, int k) 函数,函数返回节点 node 的第 k 个祖先节点。如果不存在这样的祖先节点,返回 -1 。
树节点的第 k 个祖先节点是从该节点到根节点路径上的第 k 个节点。
示例:
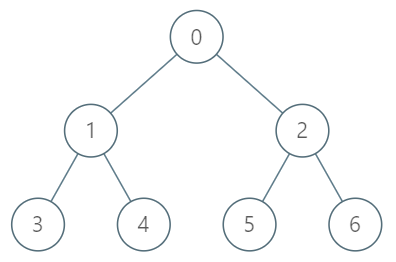
输入: ["TreeAncestor","getKthAncestor","getKthAncestor","getKthAncestor"] [[7,[-1,0,0,1,1,2,2]],[3,1],[5,2],[6,3]] 输出: [null,1,0,-1] 解释: TreeAncestor treeAncestor = new TreeAncestor(7, [-1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 2, 2]); treeAncestor.getKthAncestor(3, 1); // 返回 1 ,它是 3 的父节点 treeAncestor.getKthAncestor(5, 2); // 返回 0 ,它是 5 的祖父节点 treeAncestor.getKthAncestor(6, 3); // 返回 -1 因为不存在满足要求的祖先节点
提示:
1 <= k <= n <= 5*10^4parent[0] == -1表示编号为0的节点是根节点。- 对于所有的
0 < i < n,0 <= parent[i] < n总成立 0 <= node < n- 至多查询
5*10^4次
通过代码
高赞题解
因为力扣的数据还是有些弱的,所以这个问题我看到一些相对“暴力”的解也能过。但是这个问题的“正规解”应该是 Binary Lifting。
Binary Lifting 的本质其实是 dp。dp[node][j] 存储的是 node 节点距离为 2^j 的祖先是谁。
根据定义,dp[node][0] 就是 parent[node],即 node 的距离为 1 的祖先是 parent[node]。
状态转移是: dp[node][j] = dp[dp[node][j - 1]][j - 1]。
意思是:要想找到 node 的距离 2^j 的祖先,先找到 node 的距离 2^(j - 1) 的祖先,然后,再找这个祖先的距离 2^(j - 1) 的祖先。两步得到 node 的距离为 2^j 的祖先。
所以,我们要找到每一个 node 的距离为 1, 2, 4, 8, 16, 32, … 的祖先,直到达到树的最大的高度。树的最大的高度是 logn 级别的。
这样做,状态总数是 O(nlogn),可以使用 O(nlogn) 的时间做预处理。
之后,根据预处理的结果,可以在 O(logn) 的时间里完成每次查询:对于每一个查询 k,把 k 拆解成二进制表示,然后根据二进制表示中 1 的位置,累计向上查询。
我的参考代码(C++):
class TreeAncestor {
private:
vector<vector<int>> dp;
public:
TreeAncestor(int n, vector<int>& parent) : dp(n) {
for(int i = 0; i < n; i ++)
dp[i].push_back(parent[i]);
for(int j = 1; ; j ++){
bool allneg = true;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i ++){
int t = dp[i][j - 1] != -1 ? dp[dp[i][j - 1]][j - 1] : -1;
dp[i].push_back(t);
if(t != -1) allneg = false;
}
if(allneg) break; // 所有的节点的 2^j 的祖先都是 -1 了,就不用再计算了
}
}
int getKthAncestor(int node, int k) {
if(k == 0 || node== -1) return node;
int pos = ffs(k) - 1; // C++ 语言中 ffs(k) 求解出 k 的最右侧第一个 1 的位置(1-based)
return pos < dp[node].size() ? getKthAncestor(dp[node][pos], k - (1 << pos)) : -1;
}
};上面的 query 使用递归写法,再提供一个非递归写法,可能对有些同学来说更清晰:
int getKthAncestor(int node, int k) {
int res = node, pos = 0;
while(k && res != -1){
if(pos >= dp[res].size()) return -1;
if(k & 1) res = dp[res][pos];
k >>= 1, pos ++;
}
return res;
}觉得有帮助请点赞哇!
统计信息
| 通过次数 | 提交次数 | AC比率 |
|---|---|---|
| 3458 | 11487 | 30.1% |
提交历史
| 提交时间 | 提交结果 | 执行时间 | 内存消耗 | 语言 |
|---|




