原文链接: https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/minimum-possible-integer-after-at-most-k-adjacent-swaps-on-digits
英文原文
Given a string num representing the digits of a very large integer and an integer k.
You are allowed to swap any two adjacent digits of the integer at most k times.
Return the minimum integer you can obtain also as a string.
Example 1:
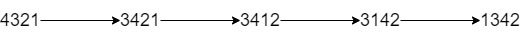
Input: num = "4321", k = 4 Output: "1342" Explanation: The steps to obtain the minimum integer from 4321 with 4 adjacent swaps are shown.
Example 2:
Input: num = "100", k = 1 Output: "010" Explanation: It's ok for the output to have leading zeros, but the input is guaranteed not to have any leading zeros.
Example 3:
Input: num = "36789", k = 1000 Output: "36789" Explanation: We can keep the number without any swaps.
Example 4:
Input: num = "22", k = 22 Output: "22"
Example 5:
Input: num = "9438957234785635408", k = 23 Output: "0345989723478563548"
Constraints:
1 <= num.length <= 30000numcontains digits only and doesn't have leading zeros.1 <= k <= 10^9
中文题目
给你一个字符串 num 和一个整数 k 。其中,num 表示一个很大的整数,字符串中的每个字符依次对应整数上的各个 数位 。
你可以交换这个整数相邻数位的数字 最多 k 次。
请你返回你能得到的最小整数,并以字符串形式返回。
示例 1:
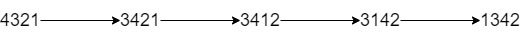
输入:num = "4321", k = 4 输出:"1342" 解释:4321 通过 4 次交换相邻数位得到最小整数的步骤如上图所示。
示例 2:
输入:num = "100", k = 1 输出:"010" 解释:输出可以包含前导 0 ,但输入保证不会有前导 0 。
示例 3:
输入:num = "36789", k = 1000 输出:"36789" 解释:不需要做任何交换。
示例 4:
输入:num = "22", k = 22 输出:"22"
示例 5:
输入:num = "9438957234785635408", k = 23 输出:"0345989723478563548"
提示:
1 <= num.length <= 30000num只包含 数字 且不含有 前导 0 。1 <= k <= 10^9
通过代码
高赞题解
思路
这个题直接暴力按照数据规模来说是不行的,当然也看到了有人说暴力就能过,那是数据集太简单的问题,思路如下:
首先暴力之所以会不高效是因为每次查找满足条件(间距小于k且比当前值小的最小值,贪心体现在这里)时都要进行遍历(O(n)),那一种高效的代替方法是做预处理:记录下所有的0-9的位置然后用这些预处理的位置来进行查找,好处是每次查找时不需要重头开始遍历。比如上一次0的所有下标我已经判断到了第四个,那下一次再对0进行判断时直接从第五个开始就行,因为前面已经被用了或者不满足条件,这样就提高了效率,所有查找过程的总时间复杂度为O(n),均摊为O(1)。
那这种方案带来的问题是不好计算置换次数(暴力法好计算是因为切实地挨个做了置换!),比如我们处理的数组中间有4个数:..., 7,1,2,4, ....,而且假设此时我们已经获悉7要和4置换,其中1和2都已经被置换过了,此时的置换次数是1,因此计算置换次数需要我们记录所有已经被用过的元素并对范围进行求和。
说到这里大家应该就懂得差不多了,范围求和,我们可以认为元素使用过就为1。那高效的RMQ可以用FenwichTree或者SegmentTree,都可以来解这个题。
总的来说,思路不难想,但是如果很久没有手撸RMQ想快速写出来有些难度(你记录下了模板直接copy过来的话当我没说),挺有价值的一道题,代码已加注释,不难理解。
时间复杂度 O(nlgn)
代码(Fenwich Tree)
class Solution {
public String minInteger(String num, int k) {
// 统计0-9的所有位置
List<Integer>[] idLists = new List[10];
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
idLists[i] = new ArrayList<>();
}
int n = num.length();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
idLists[num.charAt(i) - '0'].add(i);
}
// 指向idLists的0-9的当前位置
int[] ids = new int[10];
boolean[] seen = new boolean[n];
StringBuilder res = new StringBuilder();
// 统计范围内已被使用的下标,计算需要转换的次数时需要去掉已被转换到前面的那些下标
FenwichTree fwt = new FenwichTree(new int[n]);
outer:
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (seen[i]) { // 如果已经被置换过了,跳过
continue;
}
int cur = num.charAt(i) - '0';
// 查找比当前元素小且满足条件的最小值的下标
for (int j = 0; j < cur; j++) {
while (ids[j] < idLists[j].size() && idLists[j].get(ids[j]) < i) {
ids[j]++;
}
if (ids[j] == idLists[j].size()) {
continue;
}
int index = idLists[j].get(ids[j]);
int seenNum = fwt.sumRange(0, index - 1);
if (index - seenNum <= k) {
// 找到了满足条件的值,更新状态
k -= index - seenNum;
ids[j]++;
seen[index] = true;
fwt.update(index, 1);
i--;
res.append(j);
continue outer;
}
}
// 找不到满足条件且小于当前值的值,更新状态
seen[i] = true;
fwt.update(i, 1);
res.append(cur);
}
return res.toString();
}
}
class FenwichTree {
private int[] sums;
private int[] nums;
public FenwichTree(int[] nums) {
this.sums = new int[nums.length + 1];
this.nums = nums;
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
updateBit(i + 1, nums[i]);
}
}
public void update(int i, int val) {
updateBit(i + 1, val - nums[i]);
nums[i] = val;
}
private void updateBit(int i, int diff) {
while (i < sums.length) {
sums[i] += diff;
i += lowBit(i);
}
}
public int sumRange(int i, int j) {
return preSum(j + 1) - preSum(i);
}
private int preSum(int i) {
int sum = 0;
while (i > 0) {
sum += sums[i];
i -= lowBit(i);
}
return sum;
}
private int lowBit(int i) {
return i & (-i);
}
}耗时

统计信息
| 通过次数 | 提交次数 | AC比率 |
|---|---|---|
| 3383 | 9342 | 36.2% |
提交历史
| 提交时间 | 提交结果 | 执行时间 | 内存消耗 | 语言 |
|---|




