原文链接: https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/minimum-cost-to-cut-a-stick
英文原文
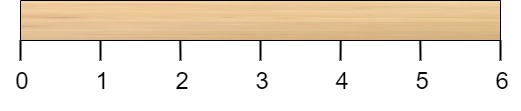
Given a wooden stick of length n units. The stick is labelled from 0 to n. For example, a stick of length 6 is labelled as follows:
Given an integer array cuts where cuts[i] denotes a position you should perform a cut at.
You should perform the cuts in order, you can change the order of the cuts as you wish.
The cost of one cut is the length of the stick to be cut, the total cost is the sum of costs of all cuts. When you cut a stick, it will be split into two smaller sticks (i.e. the sum of their lengths is the length of the stick before the cut). Please refer to the first example for a better explanation.
Return the minimum total cost of the cuts.
Example 1:
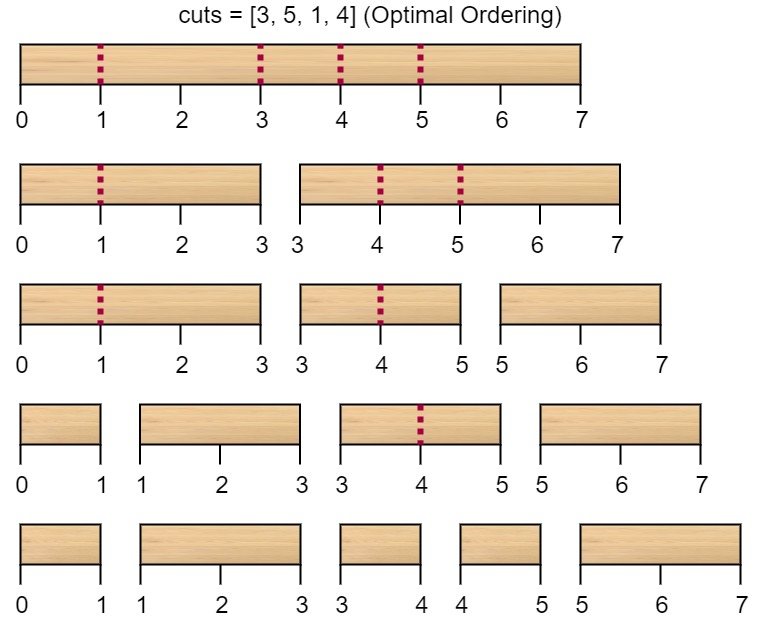
Input: n = 7, cuts = [1,3,4,5] Output: 16 Explanation: Using cuts order = [1, 3, 4, 5] as in the input leads to the following scenario:The first cut is done to a rod of length 7 so the cost is 7. The second cut is done to a rod of length 6 (i.e. the second part of the first cut), the third is done to a rod of length 4 and the last cut is to a rod of length 3. The total cost is 7 + 6 + 4 + 3 = 20. Rearranging the cuts to be [3, 5, 1, 4] for example will lead to a scenario with total cost = 16 (as shown in the example photo 7 + 4 + 3 + 2 = 16).
Example 2:
Input: n = 9, cuts = [5,6,1,4,2] Output: 22 Explanation: If you try the given cuts ordering the cost will be 25. There are much ordering with total cost <= 25, for example, the order [4, 6, 5, 2, 1] has total cost = 22 which is the minimum possible.
Constraints:
2 <= n <= 1061 <= cuts.length <= min(n - 1, 100)1 <= cuts[i] <= n - 1- All the integers in
cutsarray are distinct.
中文题目
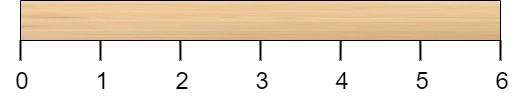
有一根长度为 n 个单位的木棍,棍上从 0 到 n 标记了若干位置。例如,长度为 6 的棍子可以标记如下:
给你一个整数数组 cuts ,其中 cuts[i] 表示你需要将棍子切开的位置。
你可以按顺序完成切割,也可以根据需要更改切割的顺序。
每次切割的成本都是当前要切割的棍子的长度,切棍子的总成本是历次切割成本的总和。对棍子进行切割将会把一根木棍分成两根较小的木棍(这两根木棍的长度和就是切割前木棍的长度)。请参阅第一个示例以获得更直观的解释。
返回切棍子的 最小总成本 。
示例 1:
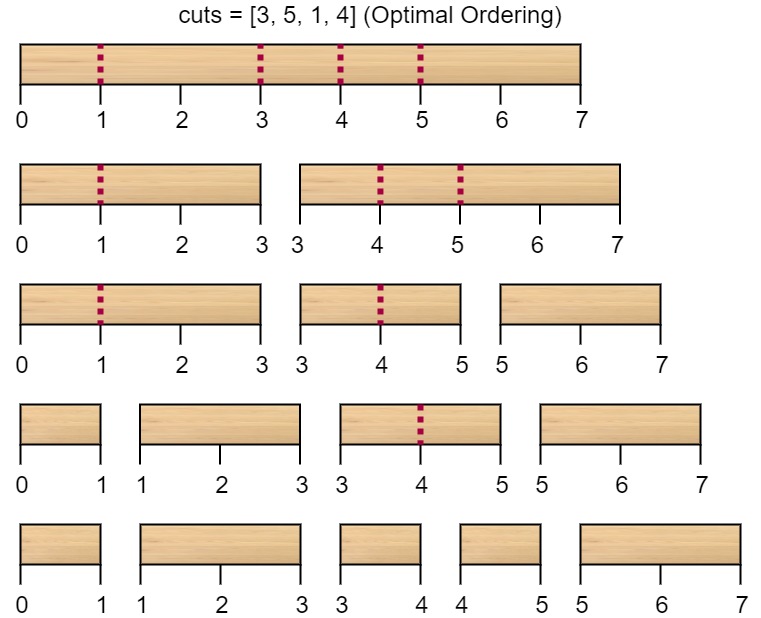
输入:n = 7, cuts = [1,3,4,5] 输出:16 解释:按 [1, 3, 4, 5] 的顺序切割的情况如下所示:第一次切割长度为 7 的棍子,成本为 7 。第二次切割长度为 6 的棍子(即第一次切割得到的第二根棍子),第三次切割为长度 4 的棍子,最后切割长度为 3 的棍子。总成本为 7 + 6 + 4 + 3 = 20 。 而将切割顺序重新排列为 [3, 5, 1, 4] 后,总成本 = 16(如示例图中 7 + 4 + 3 + 2 = 16)。
示例 2:
输入:n = 9, cuts = [5,6,1,4,2] 输出:22 解释:如果按给定的顺序切割,则总成本为 25 。总成本 <= 25 的切割顺序很多,例如,[4, 6, 5, 2, 1] 的总成本 = 22,是所有可能方案中成本最小的。
提示:
2 <= n <= 10^61 <= cuts.length <= min(n - 1, 100)1 <= cuts[i] <= n - 1cuts数组中的所有整数都 互不相同
通过代码
高赞题解
5486. 切棍子的最小成本
知识点:动态规划
设 dp[L][R] 为切割以L,R为左右端点的木棍的最小成本。显然 L,R 的取值只能是 0,n,或者 cuts中的某个数。
如果不存在 i 满足 L < cuts[i] < R,那么dp[L][R] = 0,因为根本不用切了。
如果存在 i 满足上述条件,则 dp[L][R] = min(dp[L][cuts[i]] + dp[cuts[i]][R]) + R-L。
class Solution {
public:
// 为了方便实现,
// dp[l][r] 代表 切割以 cuts[l], cuts[r] 为左右端点的木棍的最小花费
int dp[103][103];
int dfs(int l, int r, const vector<int>& cuts) {
// 保存已经计算过的答案,避免子问题的重复计算
if(dp[l][r] != -1) {
return dp[l][r];
}
// l+1 == r 时,说明不用再切了。
if(l+1 == r) {
dp[l][r] = 0;
return 0;
}
// 枚举切割的地方,记录最优解。
for(int i = l+1; i < r; i++) {
int cost = dfs(l, i, cuts) + dfs(i, r, cuts) + cuts[r] - cuts[l];;
if(dp[l][r] == -1 || dp[l][r] > cost) {
dp[l][r] = cost;
}
}
return dp[l][r];
}
int minCost(int n, vector<int>& cuts) {
memset(dp, -1, sizeof(dp));
cuts.push_back(0);
cuts.push_back(n);
sort(cuts.begin(), cuts.end());
// 向 cuts 中加入 0 和 n。
// 这不会影响答案,因为我们不会从这两处切割。
return dfs(0, cuts.size()-1, cuts);
}
};统计信息
| 通过次数 | 提交次数 | AC比率 |
|---|---|---|
| 4157 | 7729 | 53.8% |
提交历史
| 提交时间 | 提交结果 | 执行时间 | 内存消耗 | 语言 |
|---|



