原文链接: https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/graph-connectivity-with-threshold
英文原文
We have n cities labeled from 1 to n. Two different cities with labels x and y are directly connected by a bidirectional road if and only if x and y share a common divisor strictly greater than some threshold. More formally, cities with labels x and y have a road between them if there exists an integer z such that all of the following are true:
x % z == 0,y % z == 0, andz > threshold.
Given the two integers, n and threshold, and an array of queries, you must determine for each queries[i] = [ai, bi] if cities ai and bi are connected directly or indirectly. (i.e. there is some path between them).
Return an array answer, where answer.length == queries.length and answer[i] is true if for the ith query, there is a path between ai and bi, or answer[i] is false if there is no path.
Example 1:
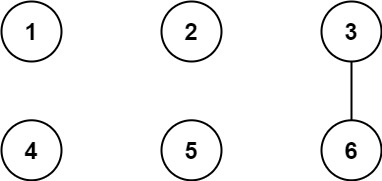
Input: n = 6, threshold = 2, queries = [[1,4],[2,5],[3,6]] Output: [false,false,true] Explanation: The divisors for each number: 1: 1 2: 1, 2 3: 1, 3 4: 1, 2, 4 5: 1, 5 6: 1, 2, 3, 6 Using the underlined divisors above the threshold, only cities 3 and 6 share a common divisor, so they are the only ones directly connected. The result of each query: [1,4] 1 is not connected to 4 [2,5] 2 is not connected to 5 [3,6] 3 is connected to 6 through path 3--6
Example 2:
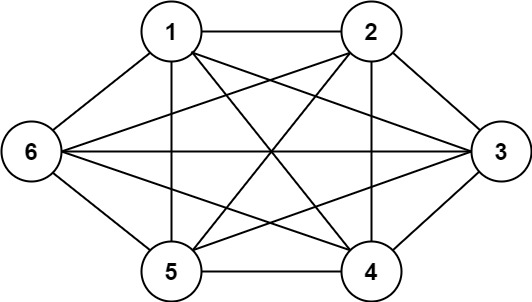
Input: n = 6, threshold = 0, queries = [[4,5],[3,4],[3,2],[2,6],[1,3]] Output: [true,true,true,true,true] Explanation: The divisors for each number are the same as the previous example. However, since the threshold is 0, all divisors can be used. Since all numbers share 1 as a divisor, all cities are connected.
Example 3:
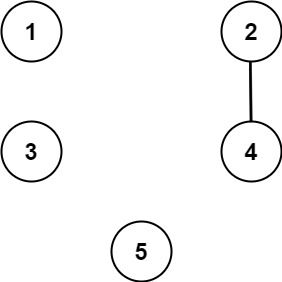
Input: n = 5, threshold = 1, queries = [[4,5],[4,5],[3,2],[2,3],[3,4]] Output: [false,false,false,false,false] Explanation: Only cities 2 and 4 share a common divisor 2 which is strictly greater than the threshold 1, so they are the only ones directly connected. Please notice that there can be multiple queries for the same pair of nodes [x, y], and that the query [x, y] is equivalent to the query [y, x].
Constraints:
2 <= n <= 1040 <= threshold <= n1 <= queries.length <= 105queries[i].length == 21 <= ai, bi <= citiesai != bi
中文题目
有 n 座城市,编号从 1 到 n 。编号为 x 和 y 的两座城市直接连通的前提是: x 和 y 的公因数中,至少有一个 严格大于 某个阈值 threshold 。更正式地说,如果存在整数 z ,且满足以下所有条件,则编号 x 和 y 的城市之间有一条道路:
x % z == 0y % z == 0z > threshold
给你两个整数 n 和 threshold ,以及一个待查询数组,请你判断每个查询 queries[i] = [ai, bi] 指向的城市 ai 和 bi 是否连通(即,它们之间是否存在一条路径)。
返回数组 answer ,其中answer.length == queries.length 。如果第 i 个查询中指向的城市 ai 和 bi 连通,则 answer[i] 为 true ;如果不连通,则 answer[i] 为 false 。
示例 1:
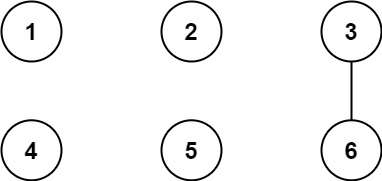
输入:n = 6, threshold = 2, queries = [[1,4],[2,5],[3,6]] 输出:[false,false,true] 解释:每个数的因数如下: 1: 1 2: 1, 2 3: 1, 3 4: 1, 2, 4 5: 1, 5 6: 1, 2, 3, 6 所有大于阈值的的因数已经加粗标识,只有城市 3 和 6 共享公约数 3 ,因此结果是: [1,4] 1 与 4 不连通 [2,5] 2 与 5 不连通 [3,6] 3 与 6 连通,存在路径 3--6
示例 2:
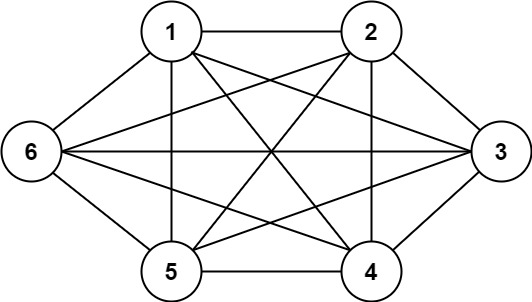
输入:n = 6, threshold = 0, queries = [[4,5],[3,4],[3,2],[2,6],[1,3]] 输出:[true,true,true,true,true] 解释:每个数的因数与上一个例子相同。但是,由于阈值为 0 ,所有的因数都大于阈值。因为所有的数字共享公因数 1 ,所以所有的城市都互相连通。
示例 3:
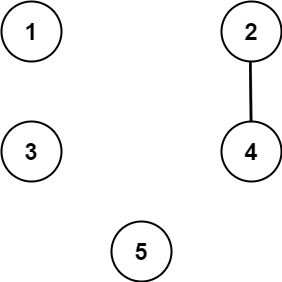
输入:n = 5, threshold = 1, queries = [[4,5],[4,5],[3,2],[2,3],[3,4]] 输出:[false,false,false,false,false] 解释:只有城市 2 和 4 共享的公约数 2 严格大于阈值 1 ,所以只有这两座城市是连通的。 注意,同一对节点 [x, y] 可以有多个查询,并且查询 [x,y] 等同于查询 [y,x] 。
提示:
2 <= n <= 1040 <= threshold <= n1 <= queries.length <= 105queries[i].length == 21 <= ai, bi <= citiesai != bi
通过代码
高赞题解
前言
看到「连通性」,我们很容易想到「并查集」这一数据结构。然而本题的图中如果有 $n$ 个点,那么边的数量在最坏情况下(即当 $\textit{threshold} = 0$ 时)是 $O(n^2)$ 的,形成一个完全图,导致超出时间限制。
然而我们可以这样想。
假设我们考虑公因数 $z$,那么 $[1, n]$ 中有 $\lfloor \dfrac{n}{z} \rfloor$ 个 $z$ 的倍数。这 $\lfloor \dfrac{n}{z} \rfloor$ 个点两两之间存在一条边,那么我们需要添加的边数为 $O\big((\dfrac{n}{z})^2\big)$。
然而,我们添加边的作用实际上只是为了维护整个图的连通性,使得这 $\lfloor \dfrac{n}{z} \rfloor$ 个点直接或者间接相连。因此,我们实际上只需要:
- 连接第 $0$ 个点和第 $1$ 个点;
- 连接第 $1$ 个点和第 $2$ 个点;
- $\cdots$
- 连接第 $\lfloor \dfrac{n}{z} \rfloor - 2$ 个点和第 $\lfloor \dfrac{n}{z} \rfloor - 1$ 个点。
也就是添加 $\lfloor \dfrac{n}{z} \rfloor - 1 = O(\dfrac{n}{z})$ 条边就行了!剩余我们没有添加的边都是「冗余」的。
那么这样做在最坏情况下会添加多少条边呢?我们粗略地计算一下,即为下面这个求和公式:
$$
\sum_{z=1}^n \frac{n}{z} = n \cdot \sum_{z=1}^n \frac{1}{z}
$$
右侧就是著名的调和级数,可以证明调和级数的增长趋势是对数的,因此添加的边的数量为 $O(n \log n)$。使用优化的并查集,单次操作的均摊时间复杂度是 $O(\alpha(n))$ 的,因此整个算法:
- 需要 $O(n \log n \cdot \alpha(n))$ 的时间预处理出整个图的连通性;
- 需要 $O(\alpha(n))$ 的时间判断每一组询问是否是连通的。
方法一:并查集
贴一下我常用的并查集模板:
[uf-C++]class UF { public: vector<int> fa; vector<int> sz; int n; int comp_cnt; public: UF(int _n): n(_n), comp_cnt(_n), fa(_n), sz(_n, 1) { iota(fa.begin(), fa.end(), 0); } int findset(int x) { return fa[x] == x ? x : fa[x] = findset(fa[x]); } void unite(int x, int y) { x = findset(x); y = findset(y); if (x != y) { if (sz[x] < sz[y]) { swap(x, y); } fa[y] = x; sz[x] += sz[y]; --comp_cnt; } } bool connected(int x, int y) { x = findset(x); y = findset(y); return x == y; } };
直接使用模板即可。
[sol1-C++]class Solution { public: vector<bool> areConnected(int n, int threshold, vector<vector<int>>& queries) { UF uf(n + 1); // 枚举公因数 for (int z = threshold + 1; z <= n; ++z) { // 枚举两个 z 的倍数的点并连接 for (int p = z, q = z * 2; q <= n; p += z, q += z) { uf.unite(p, q); } } vector<bool> ans; for (const auto& q: queries) { int x = q[0]; int y = q[1]; ans.push_back(uf.connected(x, y)); } return ans; } };
方法二:一些奇怪操作
上面这个过程有点像质数筛法,我们可以将其替换成埃氏筛法,时间复杂度降低至 $O(n \log\log n \cdot \alpha(n))$。
[sol2-C++]class Solution { public: vector<bool> areConnected(int n, int threshold, vector<vector<int>>& queries) { UF uf(n + 1); vector<int> isPrime(n + 1, 1); for (int z = threshold + 1; z <= n; ++z) { if (isPrime[z]) { for (int p = z, q = z * 2; q <= n; p += z, q += z) { isPrime[q] = false; uf.unite(p, q); } } } vector<bool> ans; for (const auto& q: queries) { int x = q[0]; int y = q[1]; ans.push_back(uf.connected(x, y)); } return ans; } };
如果可以套用欧拉筛法(线性筛)的话,时间复杂度降低至 $O(n \alpha(n))$,但是我没有想出来怎么做。暂时留个坑在这吧。
统计信息
| 通过次数 | 提交次数 | AC比率 |
|---|---|---|
| 2542 | 6610 | 38.5% |
提交历史
| 提交时间 | 提交结果 | 执行时间 | 内存消耗 | 语言 |
|---|




