原文链接: https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/kth-smallest-instructions
英文原文
Bob is standing at cell (0, 0), and he wants to reach destination: (row, column). He can only travel right and down. You are going to help Bob by providing instructions for him to reach destination.
The instructions are represented as a string, where each character is either:
'H', meaning move horizontally (go right), or'V', meaning move vertically (go down).
Multiple instructions will lead Bob to destination. For example, if destination is (2, 3), both "HHHVV" and "HVHVH" are valid instructions.
However, Bob is very picky. Bob has a lucky number k, and he wants the kth lexicographically smallest instructions that will lead him to destination. k is 1-indexed.
Given an integer array destination and an integer k, return the kth lexicographically smallest instructions that will take Bob to destination.
Example 1:
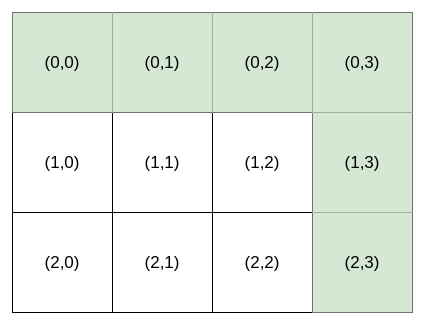
Input: destination = [2,3], k = 1 Output: "HHHVV" Explanation: All the instructions that reach (2, 3) in lexicographic order are as follows: ["HHHVV", "HHVHV", "HHVVH", "HVHHV", "HVHVH", "HVVHH", "VHHHV", "VHHVH", "VHVHH", "VVHHH"].
Example 2:
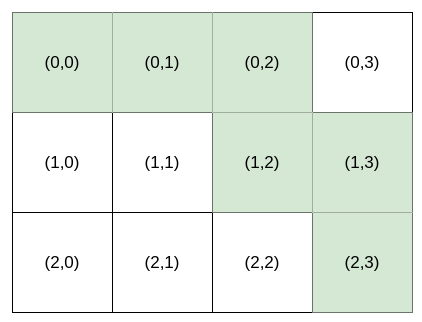
Input: destination = [2,3], k = 2 Output: "HHVHV"
Example 3:
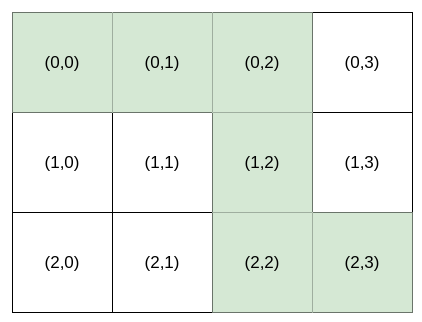
Input: destination = [2,3], k = 3 Output: "HHVVH"
Constraints:
destination.length == 21 <= row, column <= 151 <= k <= nCr(row + column, row), wherenCr(a, b)denotesachooseb.
中文题目
Bob 站在单元格 (0, 0) ,想要前往目的地 destination :(row, column) 。他只能向 右 或向 下 走。你可以为 Bob 提供导航 指令 来帮助他到达目的地 destination 。
指令 用字符串表示,其中每个字符:
'H',意味着水平向右移动'V',意味着竖直向下移动
能够为 Bob 导航到目的地 destination 的指令可以有多种,例如,如果目的地 destination 是 (2, 3),"HHHVV" 和 "HVHVH" 都是有效 指令 。
然而,Bob 很挑剔。因为他的幸运数字是 k,他想要遵循 按字典序排列后的第 k 条最小指令 的导航前往目的地 destination 。k 的编号 从 1 开始 。
给你一个整数数组 destination 和一个整数 k ,请你返回可以为 Bob 提供前往目的地 destination 导航的 按字典序排列后的第 k 条最小指令 。
示例 1:
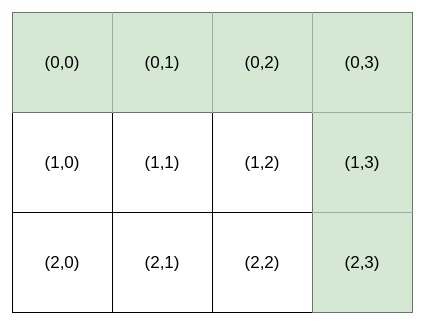
输入:destination = [2,3], k = 1 输出:"HHHVV" 解释:能前往 (2, 3) 的所有导航指令 按字典序排列后 如下所示: ["HHHVV", "HHVHV", "HHVVH", "HVHHV", "HVHVH", "HVVHH", "VHHHV", "VHHVH", "VHVHH", "VVHHH"].
示例 2:
输入:destination = [2,3], k = 2 输出:"HHVHV"
示例 3:
输入:destination = [2,3], k = 3 输出:"HHVVH"
提示:
destination.length == 21 <= row, column <= 151 <= k <= nCr(row + column, row),其中nCr(a, b)表示组合数,即从a个物品中选b个物品的不同方案数。
通过代码
高赞题解
方法一:优先确定高位 + 组合计数
思路与算法
当字符串中每一种字符的数量固定时(例如对于本题,我们需要在字符串中放入 $h$ 个 $\texttt{H}$ 和 $v$ 个 $\texttt{V}$),如果需要求出字典序第 $k$ 小的字符串,可以考虑从高位高位向低位依次确定每一个位置的字符。
如果我们在最高位放置了 $\texttt{H}$,那么剩余的 $(h-1,v)$ 就是一个规模减少的相同问题;同理如果我们在最高位放置了 $\texttt{V}$,那么剩余的 $(h,v-1)$ 也是一个规模减少的相同问题。
我们考虑最高位是放 $\texttt{H}$ 还是 $\texttt{V}$。由于后者的字典序较大,因此如果最高位放 $\texttt{V}$,那么所有最高位为 $\texttt{H}$ 的字符串的字典序都比它小,这样的字符串共有
$$
o = \binom{h+v-1}{h-1}
$$
个。也就是确定了最高位为 $\texttt{H}$,剩余 $h+v-1$ 个位置中选择 $h-1$ 个放入 $\texttt{H}$,其余位置自动放入 $\texttt{V}$ 的方案数。因此:
如果 $k$ 大于这个组合数 $o$,那么最高位一定是 $\texttt{V}$。我们将 $v$ 减少 $1$,**并且需要将 $k$ 减少 $o$**,这是因为剩余部分应当是包含 $(h,v-1)$ 的字典序第 $k-o$ 小的字符串;
如果 $k$ 小于 $o$,那么最高位是 $\texttt{H}$。我们将 $h$ 减少 $1$,但我们不需要改变 $k$ 的值,这是因为剩余部分就是包含 $(h-1,v)$ 的字典序第 $k$ 小的字符串。
这样一来,我们就可以从高位开始,依次确定每一个位置的字符了。需要注意的是,当 $h=0$ 时,我们只能放 $\texttt{V}$,无需进行判断。
代码
对于 Python 语言,可以使用 math.comb() 方便地求出组合数。但对于 C++ 而言,由于本题会导致乘法溢出,因此可以考虑使用组合数的递推式
$$
c[n][k] = c[n-1][k-1] + c[n-1][k]
$$
预处理处所有可能需要用到的组合数。
本题中,可能需要计算的最大组合数为 $\dbinom{29}{14}$,在 C++ 语言中,直接通过先乘法后除法的方法计算该组合数,在乘法过程中就会超出 $64$ 位无符号整数的上限。
[sol1-C++]class Solution { public: string kthSmallestPath(vector<int>& destination, int k) { int h = destination[1]; int v = destination[0]; // 预处理组合数 vector<vector<int>> comb(h + v, vector<int>(h)); comb[0][0] = 1; for (int i = 1; i < h + v; ++i) { comb[i][0] = 1; for (int j = 1; j <= i && j < h; ++j) { comb[i][j] = comb[i - 1][j - 1] + comb[i - 1][j]; } } string ans; for (int i = 0, imax = h + v; i < imax; ++i) { if (h > 0) { int o = comb[h + v - 1][h - 1]; if (k > o) { ans += 'V'; --v; k -= o; } else { ans += 'H'; --h; } } else { ans += 'V'; --v; } } return ans; } };
[sol1-Python3]class Solution: def kthSmallestPath(self, destination: List[int], k: int) -> str: v, h = destination ans = list() for i in range(h + v): if h > 0: o = math.comb(h + v - 1, h - 1) if k > o: ans.append("V") v -= 1 k -= o else: ans.append("H") h -= 1 else: ans.append("V") v -= 1 return "".join(ans)
复杂度分析
时间复杂度:
Python$O\big((h+v)h)$。字符串的位数为 $h+v$,对于每一位我们需要计算组合数,时间复杂度为 $O(h)$,相乘即得到时间复杂度;C++同样是 $O\big((h+v)h)$,但它是预处理组合数的时间复杂度,在枚举字符串的每一位时,我们就可以 $O(1)$ 得到组合数的值。
空间复杂度:
Python$O(1)$,C++需要存储预处理的组合数,因此为 $O\big((h+v)^2\big)$。
统计信息
| 通过次数 | 提交次数 | AC比率 |
|---|---|---|
| 2358 | 5181 | 45.5% |
提交历史
| 提交时间 | 提交结果 | 执行时间 | 内存消耗 | 语言 |
|---|




