原文链接: https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/last-day-where-you-can-still-cross
英文原文
There is a 1-based binary matrix where 0 represents land and 1 represents water. You are given integers row and col representing the number of rows and columns in the matrix, respectively.
Initially on day 0, the entire matrix is land. However, each day a new cell becomes flooded with water. You are given a 1-based 2D array cells, where cells[i] = [ri, ci] represents that on the ith day, the cell on the rith row and cith column (1-based coordinates) will be covered with water (i.e., changed to 1).
You want to find the last day that it is possible to walk from the top to the bottom by only walking on land cells. You can start from any cell in the top row and end at any cell in the bottom row. You can only travel in the four cardinal directions (left, right, up, and down).
Return the last day where it is possible to walk from the top to the bottom by only walking on land cells.
Example 1:
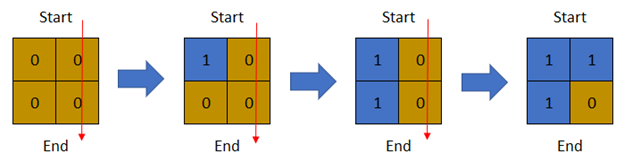
Input: row = 2, col = 2, cells = [[1,1],[2,1],[1,2],[2,2]] Output: 2 Explanation: The above image depicts how the matrix changes each day starting from day 0. The last day where it is possible to cross from top to bottom is on day 2.
Example 2:
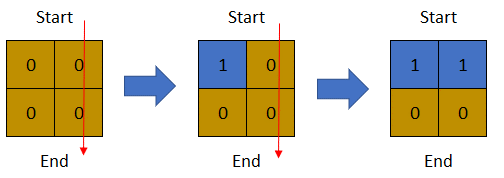
Input: row = 2, col = 2, cells = [[1,1],[1,2],[2,1],[2,2]] Output: 1 Explanation: The above image depicts how the matrix changes each day starting from day 0. The last day where it is possible to cross from top to bottom is on day 1.
Example 3:
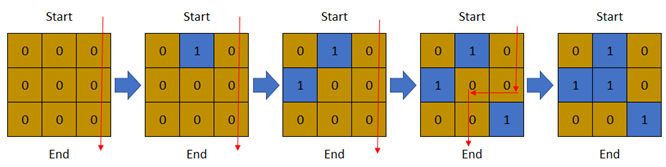
Input: row = 3, col = 3, cells = [[1,2],[2,1],[3,3],[2,2],[1,1],[1,3],[2,3],[3,2],[3,1]] Output: 3 Explanation: The above image depicts how the matrix changes each day starting from day 0. The last day where it is possible to cross from top to bottom is on day 3.
Constraints:
2 <= row, col <= 2 * 1044 <= row * col <= 2 * 104cells.length == row * col1 <= ri <= row1 <= ci <= col- All the values of
cellsare unique.
中文题目
给你一个下标从 1 开始的二进制矩阵,其中 0 表示陆地,1 表示水域。同时给你 row 和 col 分别表示矩阵中行和列的数目。
一开始在第 0 天,整个 矩阵都是 陆地 。但每一天都会有一块新陆地被 水 淹没变成水域。给你一个下标从 1 开始的二维数组 cells ,其中 cells[i] = [ri, ci] 表示在第 i 天,第 ri 行 ci 列(下标都是从 1 开始)的陆地会变成 水域 (也就是 0 变成 1 )。
你想知道从矩阵最 上面 一行走到最 下面 一行,且只经过陆地格子的 最后一天 是哪一天。你可以从最上面一行的 任意 格子出发,到达最下面一行的 任意 格子。你只能沿着 四个 基本方向移动(也就是上下左右)。
请返回只经过陆地格子能从最 上面 一行走到最 下面 一行的 最后一天 。
示例 1:

输入:row = 2, col = 2, cells = [[1,1],[2,1],[1,2],[2,2]] 输出:2 解释:上图描述了矩阵从第 0 天开始是如何变化的。 可以从最上面一行到最下面一行的最后一天是第 2 天。
示例 2:

输入:row = 2, col = 2, cells = [[1,1],[1,2],[2,1],[2,2]] 输出:1 解释:上图描述了矩阵从第 0 天开始是如何变化的。 可以从最上面一行到最下面一行的最后一天是第 1 天。
示例 3:

输入:row = 3, col = 3, cells = [[1,2],[2,1],[3,3],[2,2],[1,1],[1,3],[2,3],[3,2],[3,1]] 输出:3 解释:上图描述了矩阵从第 0 天开始是如何变化的。 可以从最上面一行到最下面一行的最后一天是第 3 天。
提示:
2 <= row, col <= 2 * 1044 <= row * col <= 2 * 104cells.length == row * col1 <= ri <= row1 <= ci <= colcells中的所有格子坐标都是 唯一 的。
通过代码
高赞题解
前言
本题和 1631. 最小体力消耗路径 是几乎一样的题目。
方法一:二分查找 + 广度优先搜索
思路与算法
如果第 $k$ 天我们能够从最上面一行走到最下面一行,那么第 $0, 1, \cdots, k-1$ 天我们也可以。
因此,一定存在一个最大值 $k’$ 使得:
当 $k \leq k’$ 时,我们可以在第 $k$ 天从最上面一行走到最下面一行;
当 $k > k’$ 时,我们不可以在第 $k$ 天从最上面一行走到最下面一行。
我们可以使用二分查找的方法找出 $k’$。二分查找的下界为 $0$,上界为 $\textit{row} \times \textit{col}$。
在二分查找的每一步中,我们需要对于二分到的 $k$ 值,判断是否可以最上面一行走到最下面一行。一种可行的方法是,我们构造一个 $\textit{row} \times \textit{col}$ 的全 $1$ 矩阵,并把 $\textit{cells}$ 中前 $k$ 个坐标在矩阵中对应的格子置为 $0$。随后,我们将第一行的所有格子(如果格子上的值为 $1$)放入队列中,进行广度优先搜索,搜索的过程中只能走向上下左右相邻并且值为 $1$ 的格子。如果能够搜索到最后一行的某个格子,那么说明存在一条从最上面一行走到最下面一行的路径,我们修改二分的下界,否则修改二分的上界。
代码
[sol1-C++]class Solution { private: static constexpr int dirs[4][2] = {{-1, 0}, {1, 0}, {0, -1}, {0, 1}}; public: int latestDayToCross(int row, int col, vector<vector<int>>& cells) { int left = 0, right = row * col, ans = 0; while (left <= right) { int mid = (left + right) / 2; vector<vector<int>> grid(row, vector<int>(col, 1)); for (int i = 0; i < mid; ++i) { grid[cells[i][0] - 1][cells[i][1] - 1] = 0; } queue<pair<int, int>> q; for (int i = 0; i < col; ++i) { if (grid[0][i]) { q.emplace(0, i); grid[0][i] = 0; } } bool found = false; while (!q.empty()) { auto [x, y] = q.front(); q.pop(); for (int d = 0; d < 4; ++d) { int nx = x + dirs[d][0]; int ny = y + dirs[d][1]; if (nx >= 0 && nx < row && ny >= 0 && ny < col && grid[nx][ny]) { if (nx == row - 1) { found = true; break; } q.emplace(nx, ny); grid[nx][ny] = 0; } } } if (found) { ans = mid; left = mid + 1; } else { right = mid - 1; } } return ans; } };
[sol1-Python3]class Solution: def latestDayToCross(self, row: int, col: int, cells: List[List[int]]) -> int: left, right, ans = 0, row * col, 0 while left <= right: mid = (left + right) // 2 grid = [[1] * col for _ in range(row)] for x, y in cells[:mid]: grid[x - 1][y - 1] = 0 q = deque() for i in range(col): if grid[0][i]: q.append((0, i)) grid[0][i] = 0 found = False while q: x, y = q.popleft() for nx, ny in [(x - 1, y), (x + 1, y), (x, y - 1), (x, y + 1)]: if 0 <= nx < row and 0 <= ny < col and grid[nx][ny]: if nx == row - 1: found = True break q.append((nx, ny)) grid[nx][ny] = 0 if found: ans = mid left = mid + 1 else: right = mid - 1 return ans
复杂度分析
时间复杂度:$O(\textit{row} \times \textit{col} \times \log(\textit{row} \times \textit{col}))$。二分查找的次数为 $O(\log(\textit{row} \times \textit{col}))$,在二分查找的每一步中,我们需要 $O(\textit{row} \times \textit{col})$ 的时间进行广度优先搜索。
空间复杂度:$O(\textit{row} \times \textit{col})$,即为广度优先搜索中的矩阵以及队列需要使用的空间。
方法二:时光倒流 + 并查集
思路与算法
我们也可以倒着考虑这个问题:
在第 $\textit{row} \times \textit{col}$ 天时,矩阵中的每个格子都是水域。随后每往前推一天,就会有一个格子从水域变为陆地,问最少往前推几天可以从最上面一行走到最下面一行。
因此,我们可以将矩阵中的每一个格子看成并查集中的一个节点。当我们将 $(x, y)$ 从水域变为陆地时,我们将 $(x, y)$ 在并查集中的节点与上下左右四个方向的格子(如果对应的格子也是陆地)在并查集中的节点进行合并。
由于我们需要判断的是最上面一行与最下面一行的连通性,所以我们可以在并查集中额外添加两个超级节点 $s$ 和 $t$,分别表示最上面一行(整体)与最下面一行(整体)。如果 $(x, y)$ 中的 $x=0$,我们就将 $s$ 与 $(x, y)$ 在并查集中的节点进行合并;如果 $x=\textit{row}-1$,我们就将 $t$ 与 $(x, y)$ 在并查集中的节点进行合并。这样一来,只要 $(s, t)$ 在并查集中连通,就说明我们可以从最上面一行走到最下面一行。
代码
[sol2-C++]// 并查集模板 class UnionFind { public: vector<int> parent; vector<int> size; int n; // 当前连通分量数目 int setCount; public: UnionFind(int _n): n(_n), setCount(_n), parent(_n), size(_n, 1) { iota(parent.begin(), parent.end(), 0); } int findset(int x) { return parent[x] == x ? x : parent[x] = findset(parent[x]); } bool unite(int x, int y) { x = findset(x); y = findset(y); if (x == y) { return false; } if (size[x] < size[y]) { swap(x, y); } parent[y] = x; size[x] += size[y]; --setCount; return true; } bool connected(int x, int y) { x = findset(x); y = findset(y); return x == y; } }; class Solution { public: int latestDayToCross(int row, int col, vector<vector<int>>& cells) { // 编号为 n 的节点是超级节点 s // 编号为 n+1 的节点是超级节点 t int n = row * col; auto uf = UnionFind(n + 2); vector<vector<int>> valid(row, vector<int>(col)); int ans = 0; for (int i = n - 1; i >= 0; --i) { int x = cells[i][0] - 1, y = cells[i][1] - 1; valid[x][y] = true; // 并查集是一维的,(x, y) 坐标是二维的,需要进行转换 int id = x * col + y; if (x - 1 >= 0 && valid[x - 1][y]) { uf.unite(id, id - col); } if (x + 1 < row && valid[x + 1][y]) { uf.unite(id, id + col); } if (y - 1 >= 0 && valid[x][y - 1]) { uf.unite(id, id - 1); } if (y + 1 < col && valid[x][y + 1]) { uf.unite(id, id + 1); } if (x == 0) { uf.unite(id, n); } if (x == row - 1) { uf.unite(id, n + 1); } if (uf.connected(n, n + 1)) { ans = i; break; } } return ans; } };
[sol2-Python3]# 并查集模板 class UnionFind: def __init__(self, n: int): self.parent = list(range(n)) self.size = [1] * n self.n = n # 当前连通分量数目 self.setCount = n def findset(self, x: int) -> int: if self.parent[x] == x: return x self.parent[x] = self.findset(self.parent[x]) return self.parent[x] def unite(self, x: int, y: int) -> bool: x, y = self.findset(x), self.findset(y) if x == y: return False if self.size[x] < self.size[y]: x, y = y, x self.parent[y] = x self.size[x] += self.size[y] self.setCount -= 1 return True def connected(self, x: int, y: int) -> bool: x, y = self.findset(x), self.findset(y) return x == y class Solution: def latestDayToCross(self, row: int, col: int, cells: List[List[int]]) -> int: # 编号为 n 的节点是超级节点 s # 编号为 n+1 的节点是超级节点 t n = row * col uf = UnionFind(n + 2) valid = [[0] * col for _ in range(row)] ans = 0 for i in range(n - 1, -1, -1): x, y = cells[i][0] - 1, cells[i][1] - 1 valid[x][y] = 1 # 并查集是一维的,(x, y) 坐标是二维的,需要进行转换 idx = x * col + y if x - 1 >= 0 and valid[x - 1][y]: uf.unite(idx, idx - col) if x + 1 < row and valid[x + 1][y]: uf.unite(idx, idx + col) if y - 1 >= 0 and valid[x][y - 1]: uf.unite(idx, idx - 1) if y + 1 < col and valid[x][y + 1]: uf.unite(idx, idx + 1) if x == 0: uf.unite(idx, n) if x == row - 1: uf.unite(idx, n + 1) if uf.connected(n, n + 1): ans = i break return ans
复杂度分析
时间复杂度:$O(\textit{row} \times \textit{col} \times \alpha(\textit{row} \times \textit{col}))$。其中 $\alpha$ 是阿克曼函数的反函数,表示并查集在均摊意义下单次操作需要的时间。
空间复杂度:$O(\textit{row} \times \textit{col})$,即为并查集需要的空间。
统计信息
| 通过次数 | 提交次数 | AC比率 |
|---|---|---|
| 2325 | 4850 | 47.9% |
提交历史
| 提交时间 | 提交结果 | 执行时间 | 内存消耗 | 语言 |
|---|




