英文原文
Write a program to solve a Sudoku puzzle by filling the empty cells.
A sudoku solution must satisfy all of the following rules:
- Each of the digits
1-9must occur exactly once in each row. - Each of the digits
1-9must occur exactly once in each column. - Each of the digits
1-9must occur exactly once in each of the 93x3sub-boxes of the grid.
The '.' character indicates empty cells.
Example 1:

Input: board = [["5","3",".",".","7",".",".",".","."],["6",".",".","1","9","5",".",".","."],[".","9","8",".",".",".",".","6","."],["8",".",".",".","6",".",".",".","3"],["4",".",".","8",".","3",".",".","1"],["7",".",".",".","2",".",".",".","6"],[".","6",".",".",".",".","2","8","."],[".",".",".","4","1","9",".",".","5"],[".",".",".",".","8",".",".","7","9"]] Output: [["5","3","4","6","7","8","9","1","2"],["6","7","2","1","9","5","3","4","8"],["1","9","8","3","4","2","5","6","7"],["8","5","9","7","6","1","4","2","3"],["4","2","6","8","5","3","7","9","1"],["7","1","3","9","2","4","8","5","6"],["9","6","1","5","3","7","2","8","4"],["2","8","7","4","1","9","6","3","5"],["3","4","5","2","8","6","1","7","9"]] Explanation: The input board is shown above and the only valid solution is shown below:
Constraints:
board.length == 9board[i].length == 9board[i][j]is a digit or'.'.- It is guaranteed that the input board has only one solution.
中文题目
编写一个程序,通过填充空格来解决数独问题。
数独的解法需 遵循如下规则:
- 数字
1-9在每一行只能出现一次。 - 数字
1-9在每一列只能出现一次。 - 数字
1-9在每一个以粗实线分隔的3x3宫内只能出现一次。(请参考示例图)
数独部分空格内已填入了数字,空白格用 '.' 表示。
示例:
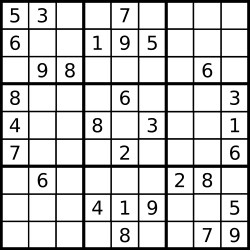
输入:board = [["5","3",".",".","7",".",".",".","."],["6",".",".","1","9","5",".",".","."],[".","9","8",".",".",".",".","6","."],["8",".",".",".","6",".",".",".","3"],["4",".",".","8",".","3",".",".","1"],["7",".",".",".","2",".",".",".","6"],[".","6",".",".",".",".","2","8","."],[".",".",".","4","1","9",".",".","5"],[".",".",".",".","8",".",".","7","9"]] 输出:[["5","3","4","6","7","8","9","1","2"],["6","7","2","1","9","5","3","4","8"],["1","9","8","3","4","2","5","6","7"],["8","5","9","7","6","1","4","2","3"],["4","2","6","8","5","3","7","9","1"],["7","1","3","9","2","4","8","5","6"],["9","6","1","5","3","7","2","8","4"],["2","8","7","4","1","9","6","3","5"],["3","4","5","2","8","6","1","7","9"]] 解释:输入的数独如上图所示,唯一有效的解决方案如下所示: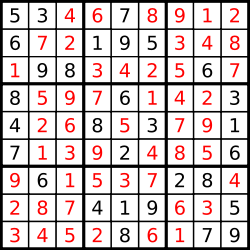
提示:
board.length == 9board[i].length == 9board[i][j]是一位数字或者'.'- 题目数据 保证 输入数独仅有一个解
通过代码
高赞题解
思路
状态压缩
使用
bitset<9>来压缩存储每一行、每一列、每一个3x3宫格中1-9是否出现这样每一个格子就可以计算出所有不能填的数字,然后得到所有能填的数字
getPossibleStatus()填入数字和回溯时,只需要更新存储信息
每个格子在使用时,会根据存储信息重新计算能填的数字
回溯
每次都使用
getNext()选择能填的数字最少的格子开始填,这样填错的概率最小,回溯次数也会变少使用
fillNum()在填入和回溯时负责更新存储信息一旦全部填写成功,一路返回 true ,结束递归
图解

答题
[]class Solution { public: bitset<9> getPossibleStatus(int x, int y) { return ~(rows[x] | cols[y] | cells[x / 3][y / 3]); } vector<int> getNext(vector<vector<char>>& board) { vector<int> ret; int minCnt = 10; for (int i = 0; i < board.size(); i++) { for (int j = 0; j < board[i].size(); j++) { if (board[i][j] != '.') continue; auto cur = getPossibleStatus(i, j); if (cur.count() >= minCnt) continue; ret = { i, j }; minCnt = cur.count(); } } return ret; } void fillNum(int x, int y, int n, bool fillFlag) { rows[x][n] = (fillFlag) ? 1 : 0; cols[y][n] = (fillFlag) ? 1 : 0; cells[x/3][y/3][n] = (fillFlag) ? 1: 0; } bool dfs(vector<vector<char>>& board, int cnt) { if (cnt == 0) return true; auto next = getNext(board); auto bits = getPossibleStatus(next[0], next[1]); for (int n = 0; n < bits.size(); n++) { if (!bits.test(n)) continue; fillNum(next[0], next[1], n, true); board[next[0]][next[1]] = n + '1'; if (dfs(board, cnt - 1)) return true; board[next[0]][next[1]] = '.'; fillNum(next[0], next[1], n, false); } return false; } void solveSudoku(vector<vector<char>>& board) { rows = vector<bitset<9>>(9, bitset<9>()); cols = vector<bitset<9>>(9, bitset<9>()); cells = vector<vector<bitset<9>>>(3, vector<bitset<9>>(3, bitset<9>())); int cnt = 0; for (int i = 0; i < board.size(); i++) { for (int j = 0; j < board[i].size(); j++) { cnt += (board[i][j] == '.'); if (board[i][j] == '.') continue; int n = board[i][j] - '1'; rows[i] |= (1 << n); cols[j] |= (1 << n); cells[i / 3][j / 3] |= (1 << n); } } dfs(board, cnt); } private: vector<bitset<9>> rows; vector<bitset<9>> cols; vector<vector<bitset<9>>> cells; };
感谢 @cocowy 提供的 bitset 风格的 fillNum() ,可读性得到质的提升,已更新到上面
下面是我原来位运算风格的 fillNum()
[]void fillNum(int x, int y, int n, bool fillFlag) { bitset<9> pick(1 << n); rows[x] = (fillFlag) ? (rows[x] | pick) : (rows[x] ^ pick); cols[y] = (fillFlag) ? (cols[y] | pick) : (cols[y] ^ pick); cells[x / 3][y / 3] = (fillFlag) ? (cells[x / 3][y / 3] | pick) : (cells[x / 3][y / 3] ^ pick); }
执行时间

对格子填入顺序的选择,使得搜索效率大大提升(加上运气好),击败 100%
得益于状态压缩,内存的使用也击败 100%
(别太较真儿,看个乐就好)
致谢
感谢您的观看,希望对您有帮助,欢迎热烈的交流!
如果感觉还不错就点个赞吧~
统计信息
| 通过次数 | 提交次数 | AC比率 |
|---|---|---|
| 109590 | 163431 | 67.1% |
提交历史
| 提交时间 | 提交结果 | 执行时间 | 内存消耗 | 语言 |
|---|
相似题目
| 题目 | 难度 |
|---|---|
| 有效的数独 | 中等 |
| 不同路径 III | 困难 |




