原文链接: https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/cut-off-trees-for-golf-event
英文原文
You are asked to cut off all the trees in a forest for a golf event. The forest is represented as an m x n matrix. In this matrix:
0means the cell cannot be walked through.1represents an empty cell that can be walked through.- A number greater than
1represents a tree in a cell that can be walked through, and this number is the tree's height.
In one step, you can walk in any of the four directions: north, east, south, and west. If you are standing in a cell with a tree, you can choose whether to cut it off.
You must cut off the trees in order from shortest to tallest. When you cut off a tree, the value at its cell becomes 1 (an empty cell).
Starting from the point (0, 0), return the minimum steps you need to walk to cut off all the trees. If you cannot cut off all the trees, return -1.
You are guaranteed that no two trees have the same height, and there is at least one tree needs to be cut off.
Example 1:

Input: forest = [[1,2,3],[0,0,4],[7,6,5]] Output: 6 Explanation: Following the path above allows you to cut off the trees from shortest to tallest in 6 steps.
Example 2:
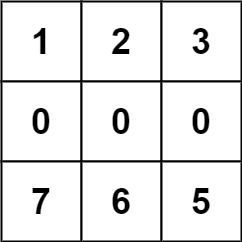
Input: forest = [[1,2,3],[0,0,0],[7,6,5]] Output: -1 Explanation: The trees in the bottom row cannot be accessed as the middle row is blocked.
Example 3:
Input: forest = [[2,3,4],[0,0,5],[8,7,6]] Output: 6 Explanation: You can follow the same path as Example 1 to cut off all the trees. Note that you can cut off the first tree at (0, 0) before making any steps.
Constraints:
m == forest.lengthn == forest[i].length1 <= m, n <= 500 <= forest[i][j] <= 109
中文题目
你被请来给一个要举办高尔夫比赛的树林砍树。树林由一个 m x n 的矩阵表示, 在这个矩阵中:
0表示障碍,无法触碰1表示地面,可以行走比 1 大的数表示有树的单元格,可以行走,数值表示树的高度
每一步,你都可以向上、下、左、右四个方向之一移动一个单位,如果你站的地方有一棵树,那么你可以决定是否要砍倒它。
你需要按照树的高度从低向高砍掉所有的树,每砍过一颗树,该单元格的值变为 1(即变为地面)。
你将从 (0, 0) 点开始工作,返回你砍完所有树需要走的最小步数。 如果你无法砍完所有的树,返回 -1 。
可以保证的是,没有两棵树的高度是相同的,并且你至少需要砍倒一棵树。
示例 1:

输入:forest = [[1,2,3],[0,0,4],[7,6,5]] 输出:6 解释:沿着上面的路径,你可以用 6 步,按从最矮到最高的顺序砍掉这些树。
示例 2:

输入:forest = [[1,2,3],[0,0,0],[7,6,5]] 输出:-1 解释:由于中间一行被障碍阻塞,无法访问最下面一行中的树。
示例 3:
输入:forest = [[2,3,4],[0,0,5],[8,7,6]] 输出:6 解释:可以按与示例 1 相同的路径来砍掉所有的树。 (0,0) 位置的树,可以直接砍去,不用算步数。
提示:
m == forest.lengthn == forest[i].length1 <= m, n <= 500 <= forest[i][j] <= 109
通过代码
官方题解
解决方法:
框架:
- 从
(0, 0)开始,对于每棵树,按照高度顺序,我们将计算我们到下一棵树(并移动到那里)的距离,并将该距离添加到答案中。 - 我们定义距离函数
dist(forest, sr, sc, tr, tc),该函数计算从源(sr, sc)到目标(tr, tc)通过障碍物dist[i][j]==0的路径距离。(如果路径不可能,此距离函数将返回-1)。 - 接下来是代码和复杂性分析,这三种方法都很常见。之后,我们的方法中给出的算法将只关注提供
dist函数。
[ ]class Solution(object): def cutOffTree(self, forest): trees = sorted((v, r, c) for r, row in enumerate(forest) for c, v in enumerate(row) if v > 1) sr = sc = ans = 0 for _, tr, tc in trees: d = dist(forest, sr, sc, tr, tc) if d < 0: return -1 ans += d sr, sc = tr, tc return ans
[ ]class Solution { int[] dr = {-1, 1, 0, 0}; int[] dc = {0, 0, -1, 1}; public int cutOffTree(List<List<Integer>> forest) { List<int[]> trees = new ArrayList(); for (int r = 0; r < forest.size(); ++r) { for (int c = 0; c < forest.get(0).size(); ++c) { int v = forest.get(r).get(c); if (v > 1) trees.add(new int[]{v, r, c}); } } Collections.sort(trees, (a, b) -> Integer.compare(a[0], b[0])); int ans = 0, sr = 0, sc = 0; for (int[] tree: trees) { int d = dist(forest, sr, sc, tree[1], tree[2]); if (d < 0) return -1; ans += d; sr = tree[1]; sc = tree[2]; } return ans; } }
复杂度分析
这三种算法都具有相似的最坏情况复杂度.
- 时间复杂度:$O((RC)^2)$,在给定的
forest中有 $R$ 行和 $C$ 列。我们步行到 $RC$ 树,每一次步行都可以花费 $O(RC)$ 时间搜索树。 - 空间复杂度:$O(R*C)$,所用数据结构的最大大小。
方法一:宽度优先搜索(BFS)
算法:
- 我们执行宽度优先搜索,处理队列中的节点(网格位置)。
seen跟踪在某个时间点已经添加到队列中的节点,这些节点已被处理或在等待处理的队列中。 - 对于下一个要处理的每个节点,我们查看它的周围。如果他们在森林(网格)中,他们没有排队,而且他们不是障碍,我们将把那个相邻节点排队。
- 我们还对每个节点的行驶距离进行计数。如果我们正在处理的节点是我们的 “目标”
(tr, tc),我们将返回答案。
[ ]def bfs(forest, sr, sc, tr, tc): R, C = len(forest), len(forest[0]) queue = collections.deque([(sr, sc, 0)]) seen = {(sr, sc)} while queue: r, c, d = queue.popleft() if r == tr and c == tc: return d for nr, nc in ((r-1, c), (r+1, c), (r, c-1), (r, c+1)): if (0 <= nr < R and 0 <= nc < C and (nr, nc) not in seen and forest[nr][nc]): seen.add((nr, nc)) queue.append((nr, nc, d+1)) return -1
[ ]public int bfs(List<List<Integer>> forest, int sr, int sc, int tr, int tc) { int R = forest.size(), C = forest.get(0).size(); Queue<int[]> queue = new LinkedList(); queue.add(new int[]{sr, sc, 0}); boolean[][] seen = new boolean[R][C]; seen[sr][sc] = true; while (!queue.isEmpty()) { int[] cur = queue.poll(); if (cur[0] == tr && cur[1] == tc) return cur[2]; for (int di = 0; di < 4; ++di) { int r = cur[0] + dr[di]; int c = cur[1] + dc[di]; if (0 <= r && r < R && 0 <= c && c < C && !seen[r][c] && forest.get(r).get(c) > 0) { seen[r][c] = true; queue.add(new int[]{r, c, cur[2]+1}); } } } return -1; }
方法二:A*搜索
算法:
- A*算法是另一种路径查找算法。对于位置
(r, c)的每个节点,我们使node.f = node.g + node.h,其中node.g是从(sr, sc)到(r, c)的实际距离,node.h是从(r, c)到(tr, tc)的距离的启发式(猜测)。在这种情况下,我们的猜测将是node.h = abs(r-tr) + abs(c-tc)。 - 我们保留一个优先队列来决定下一个搜索(扩展)的节点。我们可以证明,如果我们找到目标节点,我们一定走了尽可能短的距离
node.g。例如,通过考虑最后一次两条反向路径是相同的,在不失去一般性的情况下,我们可以假设两条路径的倒数第二个方格是不同的,然后在这种情况下,没有node.f = node.g + 1,根据需要首先扩展显示实际行驶距离较小的路径。 - 对于熟悉
Dijkstra算法的人来说,知道一个 A*搜索是Dijkstra的一个特例,且node.h总是 0。
[ ]def astar(forest, sr, sc, tr, tc): R, C = len(forest), len(forest[0]) heap = [(0, 0, sr, sc)] cost = {(sr, sc): 0} while heap: f, g, r, c = heapq.heappop(heap) if r == tr and c == tc: return g for nr, nc in ((r-1,c), (r+1,c), (r,c-1), (r,c+1)): if 0 <= nr < R and 0 <= nc < C and forest[nr][nc]: ncost = g + 1 + abs(nr - tr) + abs(nc - tc) if ncost < cost.get((nr, nc), 9999): cost[nr, nc] = ncost heapq.heappush(heap, (ncost, g+1, nr, nc)) return -1
[ ]public int cutOffTree(List<List<Integer>> forest, int sr, int sc, int tr, int tc) { int R = forest.size(), C = forest.get(0).size(); PriorityQueue<int[]> heap = new PriorityQueue<int[]>( (a, b) -> Integer.compare(a[0], b[0])); heap.offer(new int[]{0, 0, sr, sc}); HashMap<Integer, Integer> cost = new HashMap(); cost.put(sr * C + sc, 0); while (!heap.isEmpty()) { int[] cur = heap.poll(); int g = cur[1], r = cur[2], c = cur[3]; if (r == tr && c == tc) return g; for (int di = 0; di < 4; ++di) { int nr = r + dr[di], nc = c + dc[di]; if (0 <= nr && nr < R && 0 <= nc && nc < C && forest.get(nr).get(nc) > 0) { int ncost = g + 1 + Math.abs(nr-tr) + Math.abs(nc-tr); if (ncost < cost.getOrDefault(nr * C + nc, 9999)) { cost.put(nr * C + nc, ncost); heap.offer(new int[]{ncost, g+1, nr, nc}); } } } } return -1; }
方法三:Hadlock 算法
没有任何障碍物,从 source = (sr, sc) 到 target = (tr, tc) 的距离就是 taxi(source, target) = abs(sr-tr) + abs(sc-tc)。这表示必须行驶的最小距离。每当我们离开目标时,我们都会将这个最小值增加2,因为我们一步一个移动,再加上 taxicab 离我们新位置的距离增加了 1。
我们称 detour 为一次绕开目标的移动,可以证明,从源到目标的距离仅为 taxi(source, target) + 2 * detours,其中,从 source 到 target 的任何路径中,detours 的数量最小。
算法:
- 对于一个
source和target,称一个方格的迂回数为从source到该方格的任何路径中可能出现的最小迂回数。(这里,迂回道是针对target定义的——距离目标的步数。) - 我们将按照
detour编号的顺序执行优先级优先搜索。如果找到目标,则找到最低的detour,因此相应距离最低。同时使用processed跟踪节点,防止节点被访问两次。 - 由于每个相邻节点只能有相同的
detour编号或更高的detour编号,因此一次最多只能考虑两个优先级。因此,我们可以使用deque(双端队列)来执行此实现。我们将首先放置具有相同要展开的detour编号的节点,在完成所有具有当前编号的节点之后,将展开具有更高迂回道编号的节点。
[ ]def hadlocks(forest, sr, sc, tr, tc): R, C = len(forest), len(forest[0]) processed = set() deque = collections.deque([(0, sr, sc)]) while deque: detours, r, c = deque.popleft() if (r, c) not in processed: processed.add((r, c)) if r == tr and c == tc: return abs(sr-tr) + abs(sc-tc) + 2*detours for nr, nc, closer in ((r-1, c, r > tr), (r+1, c, r < tr), (r, c-1, c > tc), (r, c+1, c < tc)): if 0 <= nr < R and 0 <= nc < C and forest[nr][nc]: if closer: deque.appendleft((detours, nr, nc)) else: deque.append((detours+1, nr, nc)) return -1
[ ]public int hadlocks(List<List<Integer>> forest, int sr, int sc, int tr, int tc) { int R = forest.size(), C = forest.get(0).size(); Set<Integer> processed = new HashSet(); Deque<int[]> deque = new ArrayDeque(); deque.offerFirst(new int[]{0, sr, sc}); while (!deque.isEmpty()) { int[] cur = deque.pollFirst(); int detours = cur[0], r = cur[1], c = cur[2]; if (!processed.contains(r*C + c)) { processed.add(r*C + c); if (r == tr && c == tc) { return Math.abs(sr-tr) + Math.abs(sc-tc) + 2 * detours; } for (int di = 0; di < 4; ++di) { int nr = r + dr[di]; int nc = c + dc[di]; boolean closer; if (di <= 1) closer = di == 0 ? r > tr : r < tr; else closer = di == 2 ? c > tc : c < tc; if (0 <= nr && nr < R && 0 <= nc && nc < C && forest.get(nr).get(nc) > 0) { if (closer) deque.offerFirst(new int[]{detours, nr, nc}); else deque.offerLast(new int[]{detours+1, nr, nc}); } } } } return -1; }
统计信息
| 通过次数 | 提交次数 | AC比率 |
|---|---|---|
| 3055 | 7619 | 40.1% |
提交历史
| 提交时间 | 提交结果 | 执行时间 | 内存消耗 | 语言 |
|---|




