英文原文
There are several squares being dropped onto the X-axis of a 2D plane.
You are given a 2D integer array positions where positions[i] = [lefti, sideLengthi] represents the ith square with a side length of sideLengthi that is dropped with its left edge aligned with X-coordinate lefti.
Each square is dropped one at a time from a height above any landed squares. It then falls downward (negative Y direction) until it either lands on the top side of another square or on the X-axis. A square brushing the left/right side of another square does not count as landing on it. Once it lands, it freezes in place and cannot be moved.
After each square is dropped, you must record the height of the current tallest stack of squares.
Return an integer array ans where ans[i] represents the height described above after dropping the ith square.
Example 1:
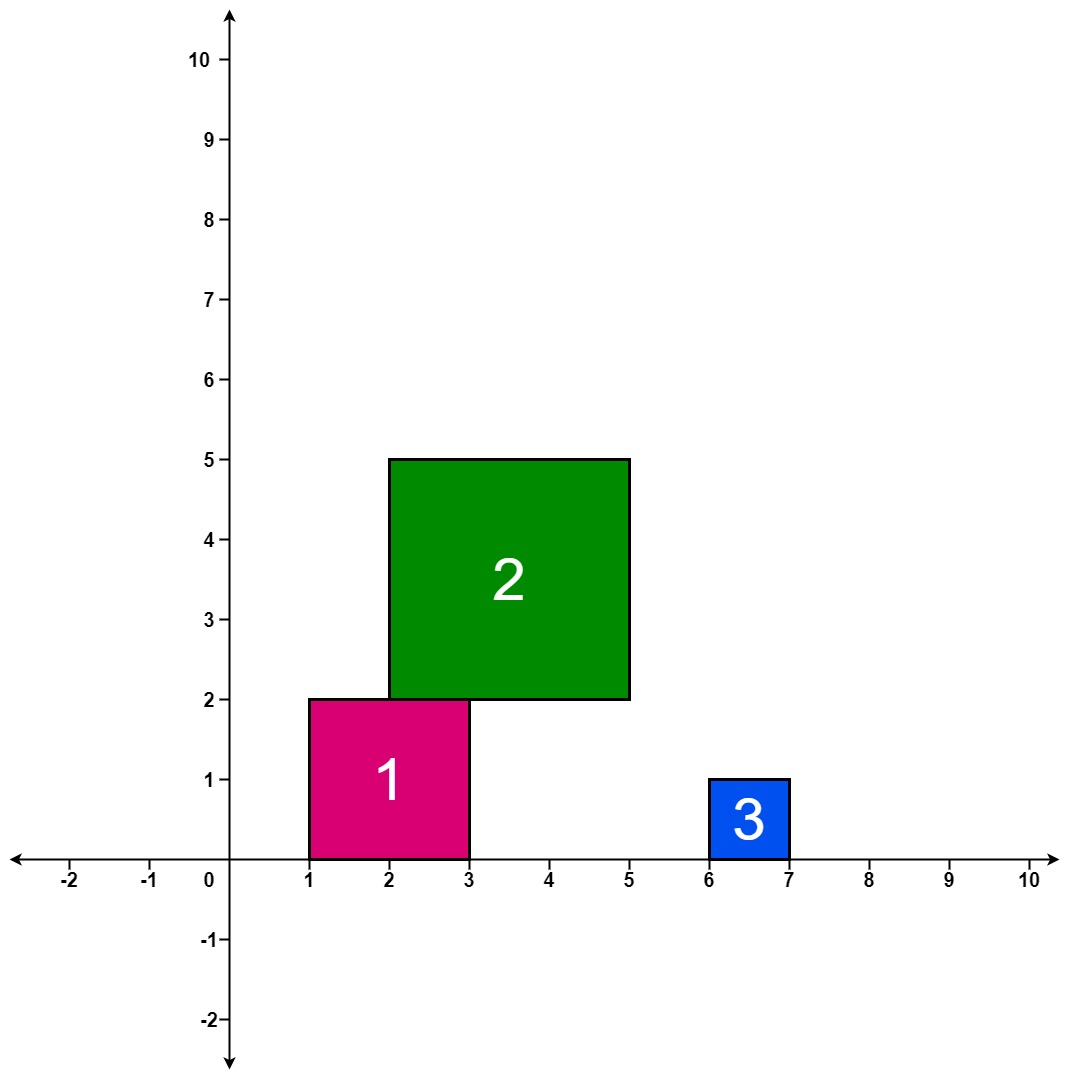
Input: positions = [[1,2],[2,3],[6,1]] Output: [2,5,5] Explanation: After the first drop, the tallest stack is square 1 with a height of 2. After the second drop, the tallest stack is squares 1 and 2 with a height of 5. After the third drop, the tallest stack is still squares 1 and 2 with a height of 5. Thus, we return an answer of [2, 5, 5].
Example 2:
Input: positions = [[100,100],[200,100]] Output: [100,100] Explanation: After the first drop, the tallest stack is square 1 with a height of 100. After the second drop, the tallest stack is either square 1 or square 2, both with heights of 100. Thus, we return an answer of [100, 100]. Note that square 2 only brushes the right side of square 1, which does not count as landing on it.
Constraints:
1 <= positions.length <= 10001 <= lefti <= 1081 <= sideLengthi <= 106
中文题目
在无限长的数轴(即 x 轴)上,我们根据给定的顺序放置对应的正方形方块。
第 i 个掉落的方块(positions[i] = (left, side_length))是正方形,其中 left 表示该方块最左边的点位置(positions[i][0]),side_length 表示该方块的边长(positions[i][1])。
每个方块的底部边缘平行于数轴(即 x 轴),并且从一个比目前所有的落地方块更高的高度掉落而下。在上一个方块结束掉落,并保持静止后,才开始掉落新方块。
方块的底边具有非常大的粘性,并将保持固定在它们所接触的任何长度表面上(无论是数轴还是其他方块)。邻接掉落的边不会过早地粘合在一起,因为只有底边才具有粘性。
返回一个堆叠高度列表 ans 。每一个堆叠高度 ans[i] 表示在通过 positions[0], positions[1], ..., positions[i] 表示的方块掉落结束后,目前所有已经落稳的方块堆叠的最高高度。
示例 1:
输入: [[1, 2], [2, 3], [6, 1]] 输出: [2, 5, 5] 解释: 第一个方块positions[0] = [1, 2]掉落:_aa _aa -------方块最大高度为 2 。 第二个方块positions[1] = [2, 3]掉落:__aaa __aaa __aaa _aa__ _aa__ --------------方块最大高度为5。 大的方块保持在较小的方块的顶部,不论它的重心在哪里,因为方块的底部边缘有非常大的粘性。 第三个方块positions[1] = [6, 1]掉落:__aaa __aaa __aaa _aa _aa___a --------------方块最大高度为5。 因此,我们返回结果[2, 5, 5]。
示例 2:
输入: [[100, 100], [200, 100]] 输出: [100, 100] 解释: 相邻的方块不会过早地卡住,只有它们的底部边缘才能粘在表面上。
注意:
1 <= positions.length <= 1000.1 <= positions[i][0] <= 10^8.1 <= positions[i][1] <= 10^6.
通过代码
官方题解
方法框架
思路
共有两种操作:update:掉落一个方块后,更新对应区间的高度;query:查询当前区间内的最大高度。
坐标压缩
数轴上最多有 2 * len(positions) 个临界点,即每个方块的左右边缘,使用坐标压缩将这些临界点映射到相应的整数位置,具体实现如下图代码所示。
为了简便起见,在具体实现方法中不添加这部分代码。
[snippet1-Java]Set<Integer> coords = new HashSet(); for (int[] pos: positions) { coords.add(pos[0]); coords.add(pos[0] + pos[1] - 1); } List<Integer> sortedCoords = new ArrayList(coords); Collections.sort(sortedCoords); Map<Integer, Integer> index = new HashMap(); int t = 0; for (int coord: sortedCoords) index.put(coord, t++);
[snippet1-Python]coords = set() for left, size in positions: coords.add(left) coords.add(left + size - 1) index = {x: i for i, x in enumerate(sorted(coords))}
方法一:模拟方块掉落
思路
不要思考“哪个方块影响次此位置的高度?”,应该思考“一个方块影响哪些位置的高度?”。
算法
令 qans[i] 表示 positions[i] 的最大高度。最后返回数组 qans 中的最大值即可。
由于每个方块的初始高度 positions[i] 比所有已经落地的方块高度更高,因此只需要更新每个掉落方块所在坐标轴的区间 [left, right], (left = positions[i][0], right = positions[i][0] + positions[i][1]) 的高度即可。
[solution1-Java]class Solution { public List<Integer> fallingSquares(int[][] positions) { int[] qans = new int[positions.length]; for (int i = 0; i < positions.length; i++) { int left = positions[i][0]; int size = positions[i][1]; int right = left + size; qans[i] += size; for (int j = i+1; j < positions.length; j++) { int left2 = positions[j][0]; int size2 = positions[j][1]; int right2 = left2 + size2; if (left2 < right && left < right2) { //intersect qans[j] = Math.max(qans[j], qans[i]); } } } List<Integer> ans = new ArrayList(); int cur = -1; for (int x: qans) { cur = Math.max(cur, x); ans.add(cur); } return ans; } }
[solution1-Python]class Solution(object): def fallingSquares(self, positions): qans = [0] * len(positions) for i, (left, size) in enumerate(positions): right = left + size qans[i] += size for j in xrange(i+1, len(positions)): left2, size2 = positions[j] right2 = left2 + size2 if left2 < right and left < right2: #intersect qans[j] = max(qans[j], qans[i]) ans = [] for x in qans: ans.append(max(ans[-1], x) if ans else x) return ans
复杂度分析
时间复杂度:$O(N^2)$,其中 $N$ 是
positions的长度,两层 for 循环,每层的复杂度都是 $O(N)$。空间复杂度:$O(N)$,
qans和ans的存储空间。
方法二:使用坐标压缩的暴力解法
思路和算法
令 N = len(positions),将原始的坐标轴映射到 $2* N \leq 2000$ 的长度上,然后使用暴力解法模拟方块掉落。
计算结果是在映射后坐标轴上的,最后还需要映射回原坐标上。
[solution1-Java]class Solution { int[] heights; public int query(int L, int R) { int ans = 0; for (int i = L; i <= R; i++) { ans = Math.max(ans, heights[i]); } return ans; } public void update(int L, int R, int h) { for (int i = L; i <= R; i++) { heights[i] = Math.max(heights[i], h); } } public List<Integer> fallingSquares(int[][] positions) { //Coordinate Compression //HashMap<Integer, Integer> index = ...; //int t = ...; heights = new int[t]; int best = 0; List<Integer> ans = new ArrayList(); for (int[] pos: positions) { int L = index.get(pos[0]); int R = index.get(pos[0] + pos[1] - 1); int h = query(L, R) + pos[1]; update(L, R, h); best = Math.max(best, h); ans.add(best); } return ans; } }
[solution1-Python]class Solution(object): def fallingSquares(self, positions): #Coordinate Compression #index = ... heights = [0] * len(index) def query(L, R): return max(heights[i] for i in xrange(L, R+1)) def update(L, R, h): for i in xrange(L, R+1): heights[i] = max(heights[i], h) best = 0 ans = [] for left, size in positions: L = index[left] R = index[left + size - 1] h = query(L, R) + size update(L, R, h) best = max(best, h) ans.append(best) return ans
复杂度分析
时间复杂度:$O(N^2)$,其中 $N$ 是
positions的长度,共两层 for 循环,每层的复杂度都是 $O(N)$(使用了坐标压缩)。空间复杂度:$O(N)$,
heights的存储空间。
方法三:方块(平方根)分解
思路
在坐标轴是上执行 update 和 query 操作之前,先将长度为 $W$ 的坐标轴分为 $\sqrt{W}$ 个块。
每次方块掉落时,不仅更新方块所在坐标区间每个位置的高度,还更新方块数组 blocks,其中 blocks[i] 表示第 $i$ 个块,共 $B = \lfloor \sqrt{W} \rfloor$ 个位置的高度,即 heights[B*i], heights[B*i + 1], ..., heights[B*i + B-1]。
算法
实际上还需要一个数组 blocks_read。更新块 b = i / B 中 i 个位置的高度时,同时更新 blocks_read[b] 和 blocks[b] 的值。如果查询整个块的值,则可以直接从 blocks_read 中读取。
如果查询块 b = i / B 中的第 i 个位置的高度,可以通过 heights[i] 和 blocks[b] 中读取。
query 和 update 操作类似。当 left 或者 right 不是 B 的倍数时,使用暴力解法。最后 [left, right+1) 表示的连续块的长度和 left 都是 B 的倍数,
query 和 update 操作类似。虽然 left 和 right 不是 B 的倍数,但可以通过方块位置暴力计算得到区间 [left, right+1) 对应的块序列。
[solution3-Java]class Solution { int[] heights; int[] blocks; int[] blocks_read; int B; public int query(int left, int right) { int ans = 0; while (left % B > 0 && left <= right) { ans = Math.max(ans, heights[left]); ans = Math.max(ans, blocks[left / B]); left++; } while (right % B != B - 1 && left <= right) { ans = Math.max(ans, heights[right]); ans = Math.max(ans, blocks[right / B]); right--; } while (left <= right) { ans = Math.max(ans, blocks[left / B]); ans = Math.max(ans, blocks_read[left / B]); left += B; } return ans; } public void update(int left, int right, int h) { while (left % B > 0 && left <= right) { heights[left] = Math.max(heights[left], h); blocks_read[left / B] = Math.max(blocks_read[left / B], h); left++; } while (right % B != B - 1 && left <= right) { heights[right] = Math.max(heights[right], h); blocks_read[right / B] = Math.max(blocks_read[right / B], h); right--; } while (left <= right) { blocks[left / B] = Math.max(blocks[left / B], h); left += B; } } public List<Integer> fallingSquares(int[][] positions) { //Coordinate Compression //HashMap<Integer, Integer> index = ...; //int t = ...; heights = new int[t]; B = (int) Math.sqrt(t); blocks = new int[B+2]; blocks_read = new int[B+2]; int best = 0; List<Integer> ans = new ArrayList(); for (int[] pos: positions) { int L = index.get(pos[0]); int R = index.get(pos[0] + pos[1] - 1); int h = query(L, R) + pos[1]; update(L, R, h); best = Math.max(best, h); ans.add(best); } return ans; } }
[solution3-Python]class Solution(object): def fallingSquares(self, positions): #Coordinate compression #index = ... W = len(index) B = int(W**.5) heights = [0] * W blocks = [0] * (B+2) blocks_read = [0] * (B+2) def query(left, right): ans = 0 while left % B and left <= right: ans = max(ans, heights[left], blocks[left / B]) left += 1 while right % B != B-1 and left <= right: ans = max(ans, heights[right], blocks[right / B]) right -= 1 while left <= right: ans = max(ans, blocks[left / B], blocks_read[left / B]) left += B return ans def update(left, right, h): while left % B and left <= right: heights[left] = max(heights[left], h) blocks_read[left / B] = max(blocks_read[left / B], h) left += 1 while right % B != B-1 and left <= right: heights[right] = max(heights[right], h) blocks_read[right / B] = max(blocks_read[right / B], h) right -= 1 while left <= right: blocks[left / B] = max(blocks[left / B], h) left += B best = 0 ans = [] for left, size in positions: L = index[left] R = index[left + size - 1] h = query(L, R) + size update(L, R, h) best = max(best, h) ans.append(best) return ans
复杂度分析
时间复杂度:$O(N\sqrt{N})$,其中 $N$ 是
positions的长度,query和update的复杂度都是 $O(\sqrt{N})$。空间复杂度:$O(N)$,
heights的存储空间。
方法四:懒惰传播的线段树
思路
线段树支持查询和更新操作,使用线段树可以很容易的解决此问题。
算法
线段树将整个区间分割为多个不连续的子区间,子区间的数量不超过 log(width)。更新某个元素的值,只需要更新 log(width) 个区间,并且这些区间都包含在一个包含该元素的大区间内。
一次性更新一个区间时,需要使用懒惰传播保证效率。
[solution4-Java]class Solution { public List<Integer> fallingSquares(int[][] positions) { //Coordinate Compression //HashMap<Integer, Integer> index = ...; SegmentTree tree = new SegmentTree(sortedCoords.size()); int best = 0; List<Integer> ans = new ArrayList(); for (int[] pos: positions) { int L = index.get(pos[0]); int R = index.get(pos[0] + pos[1] - 1); int h = tree.query(L, R) + pos[1]; tree.update(L, R, h); best = Math.max(best, h); ans.add(best); } return ans; } } class SegmentTree { int N, H; int[] tree, lazy; SegmentTree(int N) { this.N = N; H = 1; while ((1 << H) < N) H++; tree = new int[2 * N]; lazy = new int[N]; } private void apply(int x, int val) { tree[x] = Math.max(tree[x], val); if (x < N) lazy[x] = Math.max(lazy[x], val); } private void pull(int x) { while (x > 1) { x >>= 1; tree[x] = Math.max(tree[x * 2], tree[x * 2 + 1]); tree[x] = Math.max(tree[x], lazy[x]); } } private void push(int x) { for (int h = H; h > 0; h--) { int y = x >> h; if (lazy[y] > 0) { apply(y * 2, lazy[y]); apply(y * 2 + 1, lazy[y]); lazy[y] = 0; } } } public void update(int L, int R, int h) { L += N; R += N; int L0 = L, R0 = R, ans = 0; while (L <= R) { if ((L & 1) == 1) apply(L++, h); if ((R & 1) == 0) apply(R--, h); L >>= 1; R >>= 1; } pull(L0); pull(R0); } public int query(int L, int R) { L += N; R += N; int ans = 0; push(L); push(R); while (L <= R) { if ((L & 1) == 1) ans = Math.max(ans, tree[L++]); if ((R & 1) == 0) ans = Math.max(ans, tree[R--]); L >>= 1; R >>= 1; } return ans; } }
[solution4-Python]class SegmentTree(object): def __init__(self, N, update_fn, query_fn): self.N = N self.H = 1 while 1 << self.H < N: self.H += 1 self.update_fn = update_fn self.query_fn = query_fn self.tree = [0] * (2 * N) self.lazy = [0] * N def _apply(self, x, val): self.tree[x] = self.update_fn(self.tree[x], val) if x < self.N: self.lazy[x] = self.update_fn(self.lazy[x], val) def _pull(self, x): while x > 1: x /= 2 self.tree[x] = self.query_fn(self.tree[x*2], self.tree[x*2 + 1]) self.tree[x] = self.update_fn(self.tree[x], self.lazy[x]) def _push(self, x): for h in xrange(self.H, 0, -1): y = x >> h if self.lazy[y]: self._apply(y * 2, self.lazy[y]) self._apply(y * 2+ 1, self.lazy[y]) self.lazy[y] = 0 def update(self, L, R, h): L += self.N R += self.N L0, R0 = L, R while L <= R: if L & 1: self._apply(L, h) L += 1 if R & 1 == 0: self._apply(R, h) R -= 1 L /= 2; R /= 2 self._pull(L0) self._pull(R0) def query(self, L, R): L += self.N R += self.N self._push(L); self._push(R) ans = 0 while L <= R: if L & 1: ans = self.query_fn(ans, self.tree[L]) L += 1 if R & 1 == 0: ans = self.query_fn(ans, self.tree[R]) R -= 1 L /= 2; R /= 2 return ans class Solution(object): def fallingSquares(self, positions): #Coordinate compression #index = ... tree = SegmentTree(len(index), max, max) best = 0 ans = [] for left, size in positions: L, R = index[left], index[left + size - 1] h = tree.query(L, R) + size tree.update(L, R, h) best = max(best, h) ans.append(best) return ans
复杂度分析
时间复杂度:$O(N \log N)$,其中 $N$ 是
positions的长度,这也是线段树的时间复杂度。空间复杂度:$O(N)$,线段树的存储空间。
统计信息
| 通过次数 | 提交次数 | AC比率 |
|---|---|---|
| 2898 | 6032 | 48.0% |
提交历史
| 提交时间 | 提交结果 | 执行时间 | 内存消耗 | 语言 |
|---|
相似题目
| 题目 | 难度 |
|---|---|
| 天际线问题 | 困难 |




