英文原文
You are given an n x n grid representing a field of cherries, each cell is one of three possible integers.
0means the cell is empty, so you can pass through,1means the cell contains a cherry that you can pick up and pass through, or-1means the cell contains a thorn that blocks your way.
Return the maximum number of cherries you can collect by following the rules below:
- Starting at the position
(0, 0)and reaching(n - 1, n - 1)by moving right or down through valid path cells (cells with value0or1). - After reaching
(n - 1, n - 1), returning to(0, 0)by moving left or up through valid path cells. - When passing through a path cell containing a cherry, you pick it up, and the cell becomes an empty cell
0. - If there is no valid path between
(0, 0)and(n - 1, n - 1), then no cherries can be collected.
Example 1:
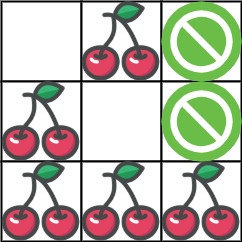
Input: grid = [[0,1,-1],[1,0,-1],[1,1,1]] Output: 5 Explanation: The player started at (0, 0) and went down, down, right right to reach (2, 2). 4 cherries were picked up during this single trip, and the matrix becomes [[0,1,-1],[0,0,-1],[0,0,0]]. Then, the player went left, up, up, left to return home, picking up one more cherry. The total number of cherries picked up is 5, and this is the maximum possible.
Example 2:
Input: grid = [[1,1,-1],[1,-1,1],[-1,1,1]] Output: 0
Constraints:
n == grid.lengthn == grid[i].length1 <= n <= 50grid[i][j]is-1,0, or1.grid[0][0] != -1grid[n - 1][n - 1] != -1
中文题目
一个N x N的网格(grid) 代表了一块樱桃地,每个格子由以下三种数字的一种来表示:
- 0 表示这个格子是空的,所以你可以穿过它。
- 1 表示这个格子里装着一个樱桃,你可以摘到樱桃然后穿过它。
- -1 表示这个格子里有荆棘,挡着你的路。
你的任务是在遵守下列规则的情况下,尽可能的摘到最多樱桃:
- 从位置 (0, 0) 出发,最后到达 (N-1, N-1) ,只能向下或向右走,并且只能穿越有效的格子(即只可以穿过值为0或者1的格子);
- 当到达 (N-1, N-1) 后,你要继续走,直到返回到 (0, 0) ,只能向上或向左走,并且只能穿越有效的格子;
- 当你经过一个格子且这个格子包含一个樱桃时,你将摘到樱桃并且这个格子会变成空的(值变为0);
- 如果在 (0, 0) 和 (N-1, N-1) 之间不存在一条可经过的路径,则没有任何一个樱桃能被摘到。
示例 1:
输入: grid = [[0, 1, -1], [1, 0, -1], [1, 1, 1]] 输出: 5 解释: 玩家从(0,0)点出发,经过了向下走,向下走,向右走,向右走,到达了点(2, 2)。 在这趟单程中,总共摘到了4颗樱桃,矩阵变成了[[0,1,-1],[0,0,-1],[0,0,0]]。 接着,这名玩家向左走,向上走,向上走,向左走,返回了起始点,又摘到了1颗樱桃。 在旅程中,总共摘到了5颗樱桃,这是可以摘到的最大值了。
说明:
grid是一个N*N的二维数组,N的取值范围是1 <= N <= 50。- 每一个
grid[i][j]都是集合{-1, 0, 1}其中的一个数。 - 可以保证起点
grid[0][0]和终点grid[N-1][N-1]的值都不会是 -1。
通过代码
官方题解
本题不可以使用如下的贪心算法:先找到一条樱桃最多的路径走到右下角,然后摘下樱桃,再从摘完后的樱桃地找到最多的樱桃路径返回,摘下樱桃。
在下面的情况,就会找不到最佳的答案:
11100
00101
10100
00100
00111方法一:记忆化递归(自顶向下)
- 与其从左上角走到右下角,再从右下角走到左上角,不如直接考虑从左上角选两条路走到右下角;
- 在走了
t步之后,我们可能处于的位置(x, y)满足x + y = t。因此如果我们在位置(x1, x1)和(x2, x2)有两个人,那么x2 = x1 + y1 - y2。这意味着x1,y1,y2唯一地决定了两个走了t步数的人。
算法:
定义
dp[x1][y1][x2]是两个人从(x1, y1)和(x2, y2)开始,朝着(N - 1, N - 1)所能摘到最多的樱桃数量,其中y2 = x1 + y1 - x2。如果
grid[x1][y1]和grid[r2][x2]不是荆棘,那么dp[x1][y1][x2]的值是(grid[x1][y1] + grid[r2][x2]),加上dp[x1+1][y1][x2],dp[x1][y1+1][x2],dp[x1+1][y1][x2+1],dp[x1][y1+1][x2+1]的最大值。在(x1, y1) == (r2, x2)的情况下,我们要避免重复计数。为什么要加上
dp[r+1][y1][x2],dp[x1][y1+1][x2],dp[x1+1][y1][x2+1],dp[x1][y1+1][x2+1]的最大值?它对应 1 号和人 2 号向下或向右移动的 4 种可能性:- 1 号向下和 2 号向下:
dp[x1 + 1][y1][x2]; - 1 号向右和 2 号向下:
dp[x1][y1 + 1][x2]; - 1 号向下和 2 号向右:
dp[x1 + 1][y1][x2 + 1]; - 1 号向右和 2 号向右:
dp[x1][y1 + 1][x2 + 1]。
- 1 号向下和 2 号向下:
[]class Solution { private int[][][] memo; private int[][] grid; private int N; public int cherryPickup(int[][] grid) { this.grid = grid; N = grid.length; memo = new int[N][N][N]; for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < N; j++) { Arrays.fill(memo[i][j], Integer.MIN_VALUE); } } return Math.max(0, dfs(0, 0, 0)); } public int dfs(int x1, int y1, int x2) { int y2 = x1 + y1 - x2; // 越界或者遇到障碍的时候 if (x1 == N || y2 == N || y1 == N || x2 == N || grid[x1][y1] == -1 || grid[x2][y2] == -1) { return -1; } // 走到了边,注意是并且并且 if (x1 == N - 1 && y1 == N - 1) { return grid[x1][y1]; } // 记忆化 if (memo[x1][y1][x2] != Integer.MIN_VALUE) { return memo[x1][y1][x2]; } int res = Math.max(Math.max(dfs(x1, y1 + 1, x2 + 1), dfs(x1 + 1, y1, x2 + 1)), Math.max(dfs(x1, y1 + 1, x2), dfs(x1 + 1, y1, x2))); if (res < 0) { return memo[x1][y1][x2] = -1; } res += grid[x1][y1]; if (x1 != x2) { res += grid[x2][y2]; } return memo[x1][y1][x2] = res; } }
复杂度分析
- 时间复杂度:$O(N^3)$。其中 $N$ 是
grid的长度,动态规划有 $O(N^3)$ 的状态。 - 空间复杂度:$O(N^3)$,
memo所使用的空间。
方法二:动态规划(自底向上)
假设 r1+c1=t 是第 t 层。因为递归只能引用下一层,所以我们一次需要在内存中保留两层。
算法:
在第 t 步,dp[c1][c2] 为两个人从 (0, 0) 到 (r1, c1) 和 (0, 0) 到 (r2, c2) 能摘到最多樱桃的数量,其中 r1 = t-c1, r2 = t-c2。我们的动态规划类似于方法一。
[]class Solution { public int cherryPickup(int[][] grid) { int N = grid.length; int[][] dp = new int[N][N]; for (int[] row : dp) { Arrays.fill(row, Integer.MIN_VALUE); } dp[0][0] = grid[0][0]; // 一共要走 2 * N - 2 步,满足横纵坐标之和为 t for (int t = 1; t <= 2 * N - 2; t++) { int[][] dp2 = new int[N][N]; for (int[] row : dp2) { Arrays.fill(row, Integer.MIN_VALUE); } // 枚举横坐标 for (int i = Math.max(0, t - (N - 1)); i <= Math.min(N - 1, t); i++) { // 枚举纵坐标 for (int j = Math.max(0, t - (N - 1)); j <= Math.min(N - 1, t); j++) { // 遇到墙 if (grid[i][t - i] == -1 || grid[j][t - j] == -1) { continue; } // 否则加上 0 或者加上 1 int res = grid[i][t - i]; if (i != j) { // 不重合的时候加上另一个坐标 res += grid[j][t - j]; } // 枚举上一步的坐标 for (int pi = i - 1; pi <= i; pi++) { for (int pj = j - 1; pj <= j; pj++) { if (pi >= 0 && pj >= 0) { dp2[i][j] = Math.max(dp2[i][j], dp[pi][pj] + res); } } } } } dp = dp2; } return Math.max(0, dp[N - 1][N - 1]); } }
复杂度分析
- 时间复杂度:$O(N^3)$。其中 $N$ 是
grid的长度。 - 空间复杂度:$O(N^2)$,
dp和dp2所使用的空间。
统计信息
| 通过次数 | 提交次数 | AC比率 |
|---|---|---|
| 4153 | 11257 | 36.9% |
提交历史
| 提交时间 | 提交结果 | 执行时间 | 内存消耗 | 语言 |
|---|
相似题目
| 题目 | 难度 |
|---|---|
| 最小路径和 | 中等 |
| 地下城游戏 | 困难 |




