英文原文
You are given an n x n integer matrix grid where each value grid[i][j] represents the elevation at that point (i, j).
The rain starts to fall. At time t, the depth of the water everywhere is t. You can swim from a square to another 4-directionally adjacent square if and only if the elevation of both squares individually are at most t. You can swim infinite distances in zero time. Of course, you must stay within the boundaries of the grid during your swim.
Return the least time until you can reach the bottom right square (n - 1, n - 1) if you start at the top left square (0, 0).
Example 1:
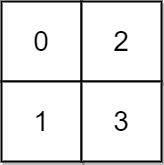
Input: grid = [[0,2],[1,3]] Output: 3 Explanation: At time 0, you are in grid location (0, 0). You cannot go anywhere else because 4-directionally adjacent neighbors have a higher elevation than t = 0. You cannot reach point (1, 1) until time 3. When the depth of water is 3, we can swim anywhere inside the grid.
Example 2:
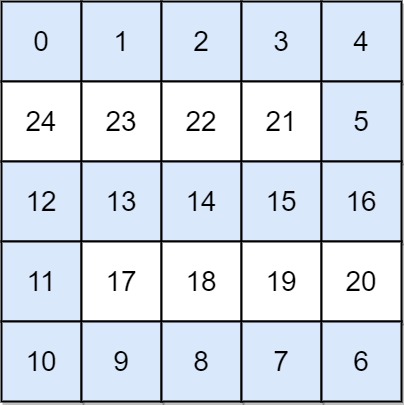
Input: grid = [[0,1,2,3,4],[24,23,22,21,5],[12,13,14,15,16],[11,17,18,19,20],[10,9,8,7,6]] Output: 16 Explanation: The final route is shown. We need to wait until time 16 so that (0, 0) and (4, 4) are connected.
Constraints:
n == grid.lengthn == grid[i].length1 <= n <= 500 <= grid[i][j] < n2- Each value
grid[i][j]is unique.
中文题目
在一个 N x N 的坐标方格 grid 中,每一个方格的值 grid[i][j] 表示在位置 (i,j) 的平台高度。
现在开始下雨了。当时间为 t 时,此时雨水导致水池中任意位置的水位为 t 。你可以从一个平台游向四周相邻的任意一个平台,但是前提是此时水位必须同时淹没这两个平台。假定你可以瞬间移动无限距离,也就是默认在方格内部游动是不耗时的。当然,在你游泳的时候你必须待在坐标方格里面。
你从坐标方格的左上平台 (0,0) 出发。最少耗时多久你才能到达坐标方格的右下平台 (N-1, N-1)?
示例 1:
输入: [[0,2],[1,3]]
输出: 3
解释:
时间为0时,你位于坐标方格的位置为 (0, 0)。
此时你不能游向任意方向,因为四个相邻方向平台的高度都大于当前时间为 0 时的水位。
等时间到达 3 时,你才可以游向平台 (1, 1). 因为此时的水位是 3,坐标方格中的平台没有比水位 3 更高的,所以你可以游向坐标方格中的任意位置
示例2:
输入: [[0,1,2,3,4],[24,23,22,21,5],[12,13,14,15,16],[11,17,18,19,20],[10,9,8,7,6]] 输出: 16 解释: 0 1 2 3 4 24 23 22 21 5 12 13 14 15 16 11 17 18 19 20 10 9 8 7 6 最终的路线用加粗进行了标记。 我们必须等到时间为 16,此时才能保证平台 (0, 0) 和 (4, 4) 是连通的
提示:
2 <= N <= 50.grid[i][j]是[0, ..., N*N - 1]的排列。
通过代码
官方题解
📺 视频讲解
力扣君温馨小贴士:觉得视频时间长的扣友,可以在视频右下角的「设置」按钮处选择 1.5 倍速或者 2 倍速观看。
📖 文字解析
注意题目中的重要信息:假定你可以 瞬间移动 无限距离,游动不耗时。当前这个问题就转换成为:找一个时刻 t,使得这个二维网格上数值 小于等于 t 的部分,存在一条从左上角到右下角的路径。即:经过了时间 t 以后,可以瞬间从左上角(坐标 [0, 0])游到右下角(坐标 [N - 1, N - 1])。
方法一:二分查找 + 遍历
根据题目中的描述:
- 如果等待的时间
t越少,网格上可以游泳的部分就越少,存在从左上角到右下角的一条路径的可能性越小; - 如果等待的时间
t越多,网格上可以游泳的部分就越多,存在从左上角到右下角的一条路径的可能性越大。

这是本问题具有的 单调性。因此可以使用二分查找定位到最短等待时间。具体来说:在区间 [0, N * N - 1] 里猜一个整数,针对这个整数从起点(左上角)开始做一次深度优先遍历或者广度优先遍历。
- 当小于等于该数值时,如果存在一条从左上角到右下角的路径,说明答案可能是这个数值,也可能更小;
- 当小于等于该数值时,如果不存在一条从左上角到右下角的路径,说明答案一定比这个数值更大。
按照这种方式不断缩小搜索的区间,最终找到最少等待时间。
参考代码 1:
说明:选项卡一使用深度优先遍历,选项卡二使用广度优先遍历。
[]public class Solution { private int N; public static final int[][] DIRECTIONS = {{0, 1}, {0, -1}, {1, 0}, {-1, 0}}; public int swimInWater(int[][] grid) { this.N = grid.length; int left = 0; int right = N * N - 1; while (left < right) { // left + right 不会溢出 int mid = (left + right) / 2; boolean[][] visited = new boolean[N][N]; if (grid[0][0] <= mid && dfs(grid, 0, 0, visited, mid)) { // mid 可以,尝试 mid 小一点是不是也可以呢?下一轮搜索的区间 [left, mid] right = mid; } else { left = mid + 1; } } return left; } /** * 使用深度优先遍历得到从 (x, y) 开始向四个方向的所有小于等于 threshold 且与 (x, y) 连通的结点 * * @param grid * @param x * @param y * @param visited * @param threshold * @return */ private boolean dfs(int[][] grid, int x, int y, boolean[][] visited, int threshold) { visited[x][y] = true; for (int[] direction : DIRECTIONS) { int newX = x + direction[0]; int newY = y + direction[1]; if (inArea(newX, newY) && !visited[newX][newY] && grid[newX][newY] <= threshold) { if (newX == N - 1 && newY == N - 1) { return true; } if (dfs(grid, newX, newY, visited, threshold)) { return true; } } } return false; } private boolean inArea(int x, int y) { return x >= 0 && x < N && y >= 0 && y < N; } }
[]import java.util.LinkedList; import java.util.Queue; public class Solution { private int N; public static final int[][] DIRECTIONS = {{0, 1}, {0, -1}, {1, 0}, {-1, 0}}; public int swimInWater(int[][] grid) { this.N = grid.length; int left = 0; int right = N * N - 1; while (left < right) { int mid = (left + right) / 2; if (grid[0][0] <= mid && bfs(grid, mid)) { // mid 可以,尝试 mid 小一点是不是也可以呢?// [left, mid] right = mid; } else { left = mid + 1; } } return left; } /** * 使用广度优先遍历得到从 (x, y) 开始向四个方向的所有小于等于 threshold 且与 (x, y) 连通的结点 * * @param grid * @param threshold * @return */ private boolean bfs(int[][] grid, int threshold) { Queue<int[]> queue = new LinkedList<>(); queue.offer(new int[]{0, 0}); boolean[][] visited = new boolean[N][N]; visited[0][0] = true; while (!queue.isEmpty()) { int[] front = queue.poll(); int x = front[0]; int y = front[1]; for (int[] direction : DIRECTIONS) { int newX = x + direction[0]; int newY = y + direction[1]; if (inArea(newX, newY) && !visited[newX][newY] && grid[newX][newY] <= threshold) { if (newX == N - 1 && newY == N - 1) { return true; } queue.offer(new int[]{newX, newY}); visited[newX][newY] = true; } } } return false; } private boolean inArea(int x, int y) { return x >= 0 && x < N && y >= 0 && y < N; } }
复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度:$O(N^2 \log N)$。
其中 $N$ 是方格的边长。最差情况下进行 $\log N^2$ 次二分查找,每一次二分查找最差情况下要遍历所有单元格一次,时间复杂度为 $O(N^2)$。总的时间复杂度为 $O(N^2 \log N^2) = O(2N^2 \log N) = O(N^2 \log N)$; - 空间复杂度:$O(N^2)$。
数组visited的大小为 $N^2$ ,如果使用深度优先遍历,须要使用的栈的大小最多为 $N^2$ ,如果使用广度优先遍历,须要使用的栈的大小最多为 $N^2$。
关于连通性的问题,如果只问结果,不问具体怎么连起来的,还可以考虑使用并查集。
方法二:并查集
由于题目要我们找的是最少等待时间,可以模拟下雨的过程,把网格抽象成一个无权图,每经过一个时刻,就考虑此时和雨水高度相等的单元格,考虑这个单元格的上、下、左、右、四个方向,并且高度更低的单元格,把它们在并查集中进行合并。

参考代码 2:
[]public class Solution { private int N; public static final int[][] DIRECTIONS = {{0, 1}, {0, -1}, {1, 0}, {-1, 0}}; public int swimInWater(int[][] grid) { this.N = grid.length; int len = N * N; // 下标:方格的高度,值:对应在方格中的坐标 int[] index = new int[len]; for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < N; j++) { index[grid[i][j]] = getIndex(i, j); } } UnionFind unionFind = new UnionFind(len); for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) { int x = index[i] / N; int y = index[i] % N; for (int[] direction : DIRECTIONS) { int newX = x + direction[0]; int newY = y + direction[1]; if (inArea(newX, newY) && grid[newX][newY] <= i) { unionFind.union(index[i], getIndex(newX, newY)); } if (unionFind.isConnected(0, len - 1)) { return i; } } } return -1; } private int getIndex(int x, int y) { return x * N + y; } private boolean inArea(int x, int y) { return x >= 0 && x < N && y >= 0 && y < N; } private class UnionFind { private int[] parent; public UnionFind(int n) { this.parent = new int[n]; for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { parent[i] = i; } } public int root(int x) { while (x != parent[x]) { parent[x] = parent[parent[x]]; x = parent[x]; } return x; } public boolean isConnected(int x, int y) { return root(x) == root(y); } public void union(int p, int q) { if (isConnected(p, q)) { return; } parent[root(p)] = root(q); } } }
复杂度分析
- 时间复杂度:$O(N^2 \log N)$,其中 $N$ 是方格的边长,计数排序 $O(N^2)$,合并四周、检查起点和终点是否同属于一个连通分量 $O(\log N^2)$,总的时间复杂度为 $O(N^2 + N^2\log N^2) = O(N^2 + 2N^2 \log N) = O(N^2 \log N)$;
- 空间复杂度:$O(N^2)$,数组
index的长度,并查集底层的长度均为 $N^2$。
方法三:Dijkstra 算法
注意这个问题求的是从一个源点到目标顶点的最短路径,并且这条路径上的边没有负数(**这一点非常重要,单元格的高度大于等于 $0$**),符合 Dijkstra 算法的应用场景。为此我们可以把问题抽象成一个带权有向图,权值是有向边指向的顶点的高度。如下图所示:
 {:width=400}
{:width=400}
Dijkstra 算法是应用很广泛的求解 没有负权边 的单源最短路径算法,《算法(第 4 版)》对这个算法做了详细的介绍,大家还可以阅读这本书的配套英文教程的 4.4 Shortest Paths 进行学习。没有负权边是应用 Dijkstra 算法的前提,也是理解 Dijkstra 算法执行流程的关键。
Dijkstra 算法应用在示例 2 寻找最短路径的过程如下图所示:

参考代码 3:
[]import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.Comparator; import java.util.PriorityQueue; import java.util.Queue; public class Solution { // Dijkstra 算法(应用前提:没有负权边,找单源最短路径) public int swimInWater(int[][] grid) { int n = grid.length; Queue<int[]> minHeap = new PriorityQueue<>(Comparator.comparingInt(o -> grid[o[0]][o[1]])); minHeap.offer(new int[]{0, 0}); boolean[][] visited = new boolean[n][n]; // distTo[i][j] 表示:到顶点 [i, j] 须要等待的最少的时间 int[][] distTo = new int[n][n]; for (int[] row : distTo) { Arrays.fill(row, n * n); } distTo[0][0] = grid[0][0]; int[][] directions = {{0, 1}, {0, -1}, {1, 0}, {-1, 0}}; while (!minHeap.isEmpty()) { // 找最短的边 int[] front = minHeap.poll(); int currentX = front[0]; int currentY = front[1]; if (visited[currentX][currentY]) { continue; } // 确定最短路径顶点 visited[currentX][currentY] = true; if (currentX == n - 1 && currentY == n - 1) { return distTo[n - 1][n - 1]; } // 更新 for (int[] direction : directions) { int newX = currentX + direction[0]; int newY = currentY + direction[1]; if (inArea(newX, newY, n) && !visited[newX][newY] && Math.max(distTo[currentX][currentY], grid[newX][newY]) < distTo[newX][newY]) { distTo[newX][newY] = Math.max(distTo[currentX][currentY], grid[newX][newY]); minHeap.offer(new int[]{newX, newY}); } } } return -1; } private boolean inArea(int x, int y, int n) { return x >= 0 && x < n && y >= 0 && y < n; } }
复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度:$O(N^2 \log N)$。
使用了优先队列的 Dijkstra 算法的时间复杂度是 $O(E \log E)$ ,这里 $E$ 是边数,至多是顶点数的 $4$ 倍,顶点数为 $N^2$,因此 $O(E \log E) = O(4N^2 \log N^2) = O(N^2 \log N)$; - 空间复杂度:$O(N^2)$。
数组visited、distTo的大小为 $O(N^2)$,优先队列中保存的边的总数也是 $N^2$ 级别的。
统计信息
| 通过次数 | 提交次数 | AC比率 |
|---|---|---|
| 24260 | 40905 | 59.3% |
提交历史
| 提交时间 | 提交结果 | 执行时间 | 内存消耗 | 语言 |
|---|





