原文链接: https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/transform-to-chessboard
英文原文
You are given an n x n binary grid board. In each move, you can swap any two rows with each other, or any two columns with each other.
Return the minimum number of moves to transform the board into a chessboard board. If the task is impossible, return -1.
A chessboard board is a board where no 0's and no 1's are 4-directionally adjacent.
Example 1:
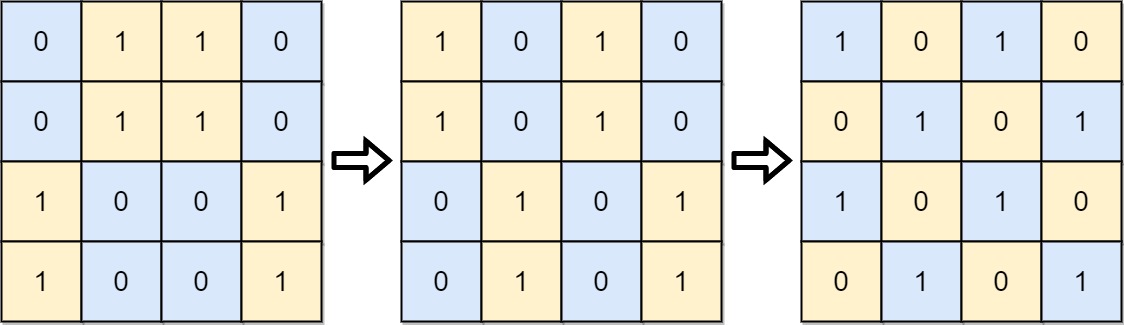
Input: board = [[0,1,1,0],[0,1,1,0],[1,0,0,1],[1,0,0,1]] Output: 2 Explanation: One potential sequence of moves is shown. The first move swaps the first and second column. The second move swaps the second and third row.
Example 2:
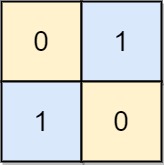
Input: board = [[0,1],[1,0]] Output: 0 Explanation: Also note that the board with 0 in the top left corner, is also a valid chessboard.
Example 3:
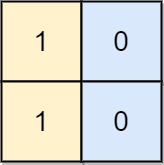
Input: board = [[1,0],[1,0]] Output: -1 Explanation: No matter what sequence of moves you make, you cannot end with a valid chessboard.
Constraints:
n == board.lengthn == board[i].length2 <= n <= 30board[i][j]is either0or1.
中文题目
一个 N x N的 board 仅由 0 和 1 组成 。每次移动,你能任意交换两列或是两行的位置。
输出将这个矩阵变为 “棋盘” 所需的最小移动次数。“棋盘” 是指任意一格的上下左右四个方向的值均与本身不同的矩阵。如果不存在可行的变换,输出 -1。
示例: 输入: board = [[0,1,1,0],[0,1,1,0],[1,0,0,1],[1,0,0,1]] 输出: 2 解释: 一种可行的变换方式如下,从左到右: 0110 1010 1010 0110 --> 1010 --> 0101 1001 0101 1010 1001 0101 0101 第一次移动交换了第一列和第二列。 第二次移动交换了第二行和第三行。 输入: board = [[0, 1], [1, 0]] 输出: 0 解释: 注意左上角的格值为0时也是合法的棋盘,如: 01 10 也是合法的棋盘. 输入: board = [[1, 0], [1, 0]] 输出: -1 解释: 任意的变换都不能使这个输入变为合法的棋盘。
提示:
board是方阵,且行列数的范围是[2, 30]。board[i][j]将只包含0或1。
通过代码
官方题解
方法一:分维度计算【通过】
思路
首先需要思考的是一次交换之后,棋盘会发生什么变化。为了简单起见,这里用交换列来做例子。在对任意两列进行交换之后,可以看到列交换是不会改变任意两行之间的状态的,简单的来说如果这两行原本就相同,列交换之后这两行依旧相同,如果这两行本来就不同,列交换之后也还是不同。由于最终的棋盘只有两种不同的行,最初的棋盘也一定只有两种不同的行,否则不管怎么做列交换都不会得到最终的棋盘。
之后再来看棋盘行的规律,棋盘有两种行,这两种行每一位都互相不同。同时对于每一行来说,一定有一半为 1,一半为 0(如果长度为奇数,会多一个 1 或多一个 0)。对于棋盘的列也是同样的规律。
可以观察到,先换行再换列跟先换列再换行结果是一样的。在这里先将所有的行调到正确的位置,再将所有的列调到正确的位置。
考虑到只有两种不同的行,可以分别用 0,1 对其表示。要达成最终的棋盘实际上等价于将棋盘的行表示成 0,1相隔的状态。假设在将棋盘的行用 0,1 表示之后得到数组为 [0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0],那么只需求这个数组变成 [0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1] 和 [1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0] 的代价,之后取其中最小的代价就好了。同理,对列也是如此,这就将二维问题变成了两个一维问题。
算法
首先需要确认是否有且只有两种行(列)存在,且这两种行(列)的 0,1 排布合法,如果不符合条件直接返回 -1。之后需要生成理想的行(列)的状态(即0,1相隔的数组排列),对于每种理想状态,计算其与初始状态之间变换的代价。举个例子,对于 [0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0] 初始状态来说,有两种理想状态,分别是 [0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1] 和 [1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0],对于 [0, 1, 1, 1, 0] 初始状态只有一种理想状态 [1, 0, 1, 0, 1]。
在 Java 实现中,用整型来表示每行。之后将其与 0b010101010101.....01 进行异或来计算初始状态转换到理想状态的代价。为了代码简洁,这里统一使用 0xAAAAAAAA 和 0x55555555,为了不引入额外的转换代价,还需要根据行的长度 N 生成 0b00...0011...11 掩码与结果做与运算。
[solution1-Java]class Solution { public int movesToChessboard(int[][] board) { int N = board.length; // count[code] = v, where code is an integer // that represents the row in binary, and v // is the number of occurrences of that row Map<Integer, Integer> count = new HashMap(); for (int[] row: board) { int code = 0; for (int x: row) code = 2 * code + x; count.put(code, count.getOrDefault(code, 0) + 1); } int k1 = analyzeCount(count, N); if (k1 == -1) return -1; // count[code], as before except with columns count = new HashMap(); for (int c = 0; c < N; ++c) { int code = 0; for (int r = 0; r < N; ++r) code = 2 * code + board[r][c]; count.put(code, count.getOrDefault(code, 0) + 1); } int k2 = analyzeCount(count, N); return k2 >= 0 ? k1 + k2 : -1; } public int analyzeCount(Map<Integer, Integer> count, int N) { // Return -1 if count is invalid // Otherwise, return number of swaps required if (count.size() != 2) return -1; List<Integer> keys = new ArrayList(count.keySet()); int k1 = keys.get(0), k2 = keys.get(1); // If lines aren't in the right quantity if (!(count.get(k1) == N/2 && count.get(k2) == (N+1)/2) && !(count.get(k2) == N/2 && count.get(k1) == (N+1)/2)) return -1; // If lines aren't opposite if ((k1 ^ k2) != (1<<N) - 1) return -1; int Nones = (1 << N) - 1; int ones = Integer.bitCount(k1 & Nones); // bitCount统计二进制中1的个数 int cand = Integer.MAX_VALUE; if (N%2 == 0 || ones * 2 < N) // zero start cand = Math.min(cand, Integer.bitCount(k1 ^ 0xAAAAAAAA & Nones) / 2); if (N%2 == 0 || ones * 2 > N) // ones start cand = Math.min(cand, Integer.bitCount(k1 ^ 0x55555555 & Nones) / 2); return cand; } }
[solution1-Python]class Solution(object): def movesToChessboard(self, board): N = len(board) ans = 0 # For each count of lines from {rows, columns}... for count in (collections.Counter(map(tuple, board)), collections.Counter(zip(*board))): # If there are more than 2 kinds of lines, # or if the number of kinds is not appropriate ... if len(count) != 2 or sorted(count.values()) != [N/2, (N+1)/2]: return -1 # If the lines are not opposite each other, impossible line1, line2 = count if not all(x ^ y for x, y in zip(line1, line2)): return -1 # starts = what could be the starting value of line1 # If N is odd, then we have to start with the more # frequent element starts = [+(line1.count(1) * 2 > N)] if N%2 else [0, 1] # To transform line1 into the ideal line [i%2 for i ...], # we take the number of differences and divide by two ans += min(sum((i-x) % 2 for i, x in enumerate(line1, start)) for start in starts) / 2 return ans
复杂度分析
时间复杂度:$O(N^2)$,其中 $N$ 是
board的行(或列)的长度。空间复杂度:$O(N)$,
count的空间。
统计信息
| 通过次数 | 提交次数 | AC比率 |
|---|---|---|
| 1562 | 3784 | 41.3% |
提交历史
| 提交时间 | 提交结果 | 执行时间 | 内存消耗 | 语言 |
|---|




