原文链接: https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/vertical-order-traversal-of-a-binary-tree
英文原文
Given the root of a binary tree, calculate the vertical order traversal of the binary tree.
For each node at position (row, col), its left and right children will be at positions (row + 1, col - 1) and (row + 1, col + 1) respectively. The root of the tree is at (0, 0).
The vertical order traversal of a binary tree is a list of top-to-bottom orderings for each column index starting from the leftmost column and ending on the rightmost column. There may be multiple nodes in the same row and same column. In such a case, sort these nodes by their values.
Return the vertical order traversal of the binary tree.
Example 1:
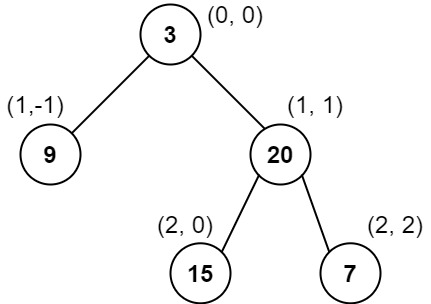
Input: root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7] Output: [[9],[3,15],[20],[7]] Explanation: Column -1: Only node 9 is in this column. Column 0: Nodes 3 and 15 are in this column in that order from top to bottom. Column 1: Only node 20 is in this column. Column 2: Only node 7 is in this column.
Example 2:
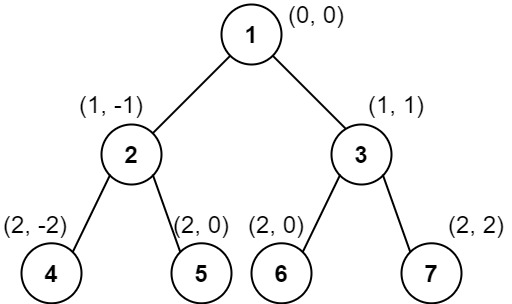
Input: root = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7]
Output: [[4],[2],[1,5,6],[3],[7]]
Explanation:
Column -2: Only node 4 is in this column.
Column -1: Only node 2 is in this column.
Column 0: Nodes 1, 5, and 6 are in this column.
1 is at the top, so it comes first.
5 and 6 are at the same position (2, 0), so we order them by their value, 5 before 6.
Column 1: Only node 3 is in this column.
Column 2: Only node 7 is in this column.
Example 3:
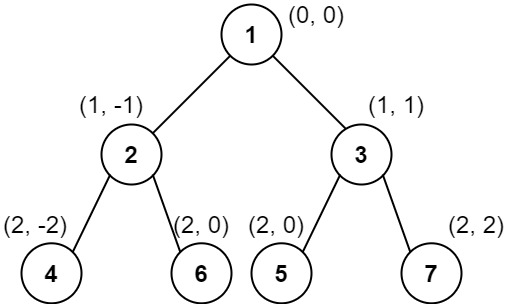
Input: root = [1,2,3,4,6,5,7] Output: [[4],[2],[1,5,6],[3],[7]] Explanation: This case is the exact same as example 2, but with nodes 5 and 6 swapped. Note that the solution remains the same since 5 and 6 are in the same location and should be ordered by their values.
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[1, 1000]. 0 <= Node.val <= 1000
中文题目
给你二叉树的根结点 root ,请你设计算法计算二叉树的 垂序遍历 序列。
对位于 (row, col) 的每个结点而言,其左右子结点分别位于 (row + 1, col - 1) 和 (row + 1, col + 1) 。树的根结点位于 (0, 0) 。
二叉树的 垂序遍历 从最左边的列开始直到最右边的列结束,按列索引每一列上的所有结点,形成一个按出现位置从上到下排序的有序列表。如果同行同列上有多个结点,则按结点的值从小到大进行排序。
返回二叉树的 垂序遍历 序列。
示例 1:

输入:root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7] 输出:[[9],[3,15],[20],[7]] 解释: 列 -1 :只有结点 9 在此列中。 列 0 :只有结点 3 和 15 在此列中,按从上到下顺序。 列 1 :只有结点 20 在此列中。 列 2 :只有结点 7 在此列中。
示例 2:

输入:root = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7]
输出:[[4],[2],[1,5,6],[3],[7]]
解释:
列 -2 :只有结点 4 在此列中。
列 -1 :只有结点 2 在此列中。
列 0 :结点 1 、5 和 6 都在此列中。
1 在上面,所以它出现在前面。
5 和 6 位置都是 (2, 0) ,所以按值从小到大排序,5 在 6 的前面。
列 1 :只有结点 3 在此列中。
列 2 :只有结点 7 在此列中。
示例 3:

输入:root = [1,2,3,4,6,5,7] 输出:[[4],[2],[1,5,6],[3],[7]] 解释: 这个示例实际上与示例 2 完全相同,只是结点 5 和 6 在树中的位置发生了交换。 因为 5 和 6 的位置仍然相同,所以答案保持不变,仍然按值从小到大排序。
提示:
- 树中结点数目总数在范围
[1, 1000]内 0 <= Node.val <= 1000
通过代码
高赞题解
DFS + 哈希表 + 排序
根据题意,我们需要按照优先级「“列号从小到大”,对于同列节点,“行号从小到大”,对于同列同行元素,“节点值从小到大”」进行答案构造。
因此我们可以对树进行遍历,遍历过程中记下这些信息 $(col, row, val)$,然后根据规则进行排序,并构造答案。
我们可以先使用「哈希表」进行存储,最后再进行一次性的排序。
代码:
[]class Solution { Map<TreeNode, int[]> map = new HashMap<>(); // col, row, val public List<List<Integer>> verticalTraversal(TreeNode root) { map.put(root, new int[]{0, 0, root.val}); dfs(root); List<int[]> list = new ArrayList<>(map.values()); Collections.sort(list, (a, b)->{ if (a[0] != b[0]) return a[0] - b[0]; if (a[1] != b[1]) return a[1] - b[1]; return a[2] - b[2]; }); int n = list.size(); List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList<>(); for (int i = 0; i < n; ) { int j = i; List<Integer> tmp = new ArrayList<>(); while (j < n && list.get(j)[0] == list.get(i)[0]) tmp.add(list.get(j++)[2]); ans.add(tmp); i = j; } return ans; } void dfs(TreeNode root) { if (root == null) return ; int[] info = map.get(root); int col = info[0], row = info[1], val = info[2]; if (root.left != null) { map.put(root.left, new int[]{col - 1, row + 1, root.left.val}); dfs(root.left); } if (root.right != null) { map.put(root.right, new int[]{col + 1, row + 1, root.right.val}); dfs(root.right); } } }
- 时间复杂度:令总节点数量为 $n$,填充哈希表时进行树的遍历,复杂度为 $O(n)$;构造答案时需要进行排序,复杂度为 $O(n\log{n})$。整体复杂度为 $O(n\log{n})$
- 空间复杂度:$O(n)$
DFS + 优先队列(堆)
显然,最终要让所有节点的相应信息有序,可以使用「优先队列(堆)」边存储边维护有序性。
代码:
[]class Solution { PriorityQueue<int[]> q = new PriorityQueue<>((a, b)->{ // col, row, val if (a[0] != b[0]) return a[0] - b[0]; if (a[1] != b[1]) return a[1] - b[1]; return a[2] - b[2]; }); public List<List<Integer>> verticalTraversal(TreeNode root) { int[] info = new int[]{0, 0, root.val}; q.add(info); dfs(root, info); List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList<>(); while (!q.isEmpty()) { List<Integer> tmp = new ArrayList<>(); int[] poll = q.peek(); while (!q.isEmpty() && q.peek()[0] == poll[0]) tmp.add(q.poll()[2]); ans.add(tmp); } return ans; } void dfs(TreeNode root, int[] fa) { if (root.left != null) { int[] linfo = new int[]{fa[0] - 1, fa[1] + 1, root.left.val}; q.add(linfo); dfs(root.left, linfo); } if (root.right != null) { int[] rinfo = new int[]{fa[0] + 1, fa[1] + 1, root.right.val}; q.add(rinfo); dfs(root.right, rinfo); } } }
- 时间复杂度:令总节点数量为 $n$,将节点信息存入优先队列(堆)复杂度为 $O(n\log{n})$;构造答案复杂度为 $O(n\log{n})$。整体复杂度为 $O(n\log{n})$
- 空间复杂度:$O(n)$
DFS + 哈希嵌套 + 排序
当然,如果想锻炼一下自己的代码能力,不使用三元组 $(col, row, val)$ 进行存储,而是使用哈希表嵌套,也是可以的。
用三个「哈希表」来记录相关信息:
使用
node2row和node2col分别用来记录「节点到行」&「节点到列」的映射关系,并实现dfs1对树进行遍历,目的是为了记录下相关的映射关系;使用
col2row2nodes记录「从列到行,从行到节点集」的映射关系,具体的存储格式为{col : {row : [node1, node2, ... ]}},实现dfs2再次进行树的遍历,配合之前node2row和node2col信息,填充col2row2nodes的映射关系;按照题意,按「列号从小到大」,对于同列节点,按照「行号从小到大」,对于同列同行元素,按照「节点值从小到大」的规则,使用
col2row2nodes+ 排序 构造答案。
注意:本解法可以只进行一次树的遍历,分两步主要是不想
dfs操作过于复杂,加大读者的阅读难度,于是在拆开不影响复杂度上界的情况,选择了分两步。
代码:
[]class Solution { Map<TreeNode, Integer> node2col = new HashMap<>(), node2row = new HashMap<>(); Map<Integer, Map<Integer, List<Integer>>> col2row2nodes = new HashMap<>(); public List<List<Integer>> verticalTraversal(TreeNode root) { List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList<>(); node2col.put(root, 0); node2row.put(root, 0); dfs1(root); dfs2(root); List<Integer> cols = new ArrayList<>(col2row2nodes.keySet()); Collections.sort(cols); for (int col : cols) { Map<Integer, List<Integer>> row2nodes = col2row2nodes.get(col); List<Integer> rows = new ArrayList<>(row2nodes.keySet()); Collections.sort(rows); List<Integer> cur = new ArrayList<>(); for (int row : rows) { List<Integer> nodes = row2nodes.get(row); Collections.sort(nodes); cur.addAll(nodes); } ans.add(cur); } return ans; } // 树的遍历,根据「节点到列」&「节点到行」的映射关系,构造出「从列到行,从行到节点集」的映射关系 void dfs2(TreeNode root) { if (root == null) return ; int col = node2col.get(root), row = node2row.get(root); Map<Integer, List<Integer>> row2nodes = col2row2nodes.getOrDefault(col, new HashMap<>()); List<Integer> nodes = row2nodes.getOrDefault(row, new ArrayList<>()); nodes.add(root.val); row2nodes.put(row, nodes); col2row2nodes.put(col, row2nodes); dfs2(root.left); dfs2(root.right); } // 树的遍历,记录下「节点到列」&「节点到行」的映射关系 void dfs1(TreeNode root) { if (root == null) return ; if (root.left != null) { int col = node2col.get(root); node2col.put(root.left, col - 1); int row = node2row.get(root); node2row.put(root.left, row + 1); dfs1(root.left); } if (root.right != null) { int col = node2col.get(root); node2col.put(root.right, col + 1); int row = node2row.get(root); node2row.put(root.right, row + 1); dfs1(root.right); } } }
- 时间复杂度:令总的节点数量为 $n$,填充几个哈希表的复杂度为 $O(n)$;构造答案时需要对行号、列号和节点值进行排序,总的复杂度上界为 $O(n\log{n})$。整体复杂度为 $O(n\log{n})$
- 空间复杂度:$O(n)$
最后
如果有帮助到你,请给题解点个赞和收藏,让更多的人看到 ~ (“▔□▔)/
也欢迎你 关注我 和 加入我们的「组队打卡」小群 ,提供写「证明」&「思路」的高质量题解。
所有题解已经加入 刷题指南,欢迎 star 哦 ~
统计信息
| 通过次数 | 提交次数 | AC比率 |
|---|---|---|
| 23969 | 44944 | 53.3% |
提交历史
| 提交时间 | 提交结果 | 执行时间 | 内存消耗 | 语言 |
|---|




