原文链接: https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/maximum-level-sum-of-a-binary-tree
英文原文
Given the root of a binary tree, the level of its root is 1, the level of its children is 2, and so on.
Return the smallest level x such that the sum of all the values of nodes at level x is maximal.
Example 1:

Input: root = [1,7,0,7,-8,null,null] Output: 2 Explanation: Level 1 sum = 1. Level 2 sum = 7 + 0 = 7. Level 3 sum = 7 + -8 = -1. So we return the level with the maximum sum which is level 2.
Example 2:
Input: root = [989,null,10250,98693,-89388,null,null,null,-32127] Output: 2
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[1, 104]. -105 <= Node.val <= 105
中文题目
给你一个二叉树的根节点 root。设根节点位于二叉树的第 1 层,而根节点的子节点位于第 2 层,依此类推。
请你找出层内元素之和 最大 的那几层(可能只有一层)的层号,并返回其中 最小 的那个。
示例 1:
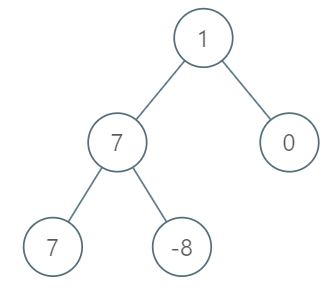
输入:root = [1,7,0,7,-8,null,null] 输出:2 解释: 第 1 层各元素之和为 1, 第 2 层各元素之和为 7 + 0 = 7, 第 3 层各元素之和为 7 + -8 = -1, 所以我们返回第 2 层的层号,它的层内元素之和最大。
示例 2:
输入:root = [989,null,10250,98693,-89388,null,null,null,-32127] 输出:2
提示:
- 树中的节点数介于
1和10^4之间 -10^5 <= node.val <= 10^5
通过代码
官方题解
概述
遍历树的两种通用策略:
深度优先遍历(
DFS)这种方法以深度
depth优先为策略,从根节点开始一直遍历到某个叶子节点,然后回到根节点,再遍历另外一个分支。根据根节点,左子节点和右子节点的访问顺序又可以将 DFS 细分为先序遍历
preorder,中序遍历inorder和后序遍历postorder。DFS 遍历通常有三种实现方式:递归
recursion,迭代iteration,Morris,其中最简单的是递归。
 {:width=500}
{:width=500}
广度优先遍历(
BFS)按照高度顺序,从上往下逐层遍历节点。先遍历上层节点再遍历下层节点。
最标准的实现方法是使用队列进行迭代。
下图中按照不同的方法遍历对应子树,得到的遍历顺序都是 1-2-3-4-5。根据不同子树结构比较不同遍历方法的特点。
 {:width=500}
{:width=500}
本题可以使用两种策略解决:DFS 和 BFS。这里使用 DFS 的中序遍历和队列实现的 BFS 解答。
方法一:DFS:递归实现的中序遍历
递归实现的中序遍历非常简单:遵循 Left->Node->Right 的顺序。例如:首先递归访问 左孩子,然后访问父节点,再递归访问 右孩子。
遍历时需要记录当前层节点之和。由于 Java 中 HashMap 的性能问题,在 Java 中使用数组,在 Python 中使用 hashmap。
算法
创建方法
inorder(node, level),实现递归的中序遍历。该方法输入当前节点和当前节点层级,然后递归更新level_sum[level]。返回数组
level_sum的最大值。
[solution1-Pyhton]from collections import defaultdict class Solution: def maxLevelSum(self, root: TreeNode) -> int: def inorder(node, level): if node: inorder(node.left, level + 1) level_sum[level] += node.val inorder(node.right, level + 1) level_sum = defaultdict(int) inorder(root, 1) return max(level_sum, key = level_sum.get)
[solution1-Java]class Solution { int n = 10000; int[] levelSum = new int[n]; public void inorder(TreeNode node, int level) { if (node != null) { inorder(node.left, level + 1); levelSum[level] += node.val; inorder(node.right, level + 1); } } public int maxLevelSum(TreeNode root) { inorder(root, 1); int maxIdx = 0; for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) maxIdx = levelSum[i] > levelSum[maxIdx] ? i : maxIdx; return maxIdx; } }
复杂度分析
时间复杂度:$\mathcal{O}(N)$,中序遍历每个节点只访问一次,然后遍历
level_sum。空间复杂度:$\mathcal{O}(10000) = \mathcal{O}(1)$ 为 Java 中
level_sum的空间。$\mathcal{O}(D)$ 为 Python 的空间,其中 $D$ 是树的深度。树是平衡的情况下,空间复杂度为 $\mathcal{O}(\log N)$ ,最坏情况下为 $\mathcal{O}(N)$。
方法二:BFS:使用队列实现的层序遍历
DFS 的缺点是必须保存所有层节点之和,BFS 逐层计算之和不需要同时保存每层之和:
初始
max_sum = 0。使用 BFS 逐层遍历,计算每层的累加和
curr_sum,在每层结束时更新max_sum = max(max_sum, curr_sum)。
使用队列(先进先出结构)实现 BFS:
把当前层所有的节点压入队列。
遍历队列。每从队列中弹出一个节点,就将该节点的子节点压入队列。
 {:width=500}
{:width=500}
这种方法可以从根节点逐层遍历到叶节点,不过需要设置标记在每层末尾计算该层节点的累加和。
面试技巧。可以使用 标记 分离队列/链表/树中的节点。
例子:LRU Cache。
这里使用空节点作为每层结束的标记。
算法
初始化变量:
- 令当前层级与最大累加和层级为 1。
- 令当前累加和为 0,最大累加和为根节点的值。
- 使用空节点作为标记,初始化队列:压入根节点和标记节点,标记当前层数为 1。
当前队列长度大于 1:
- 从队列左端弹出一个节点。
- 如果它不是标记节点,则在当前层继续:
- 更新当前层累加和。
- 将该节点的子节点压入队列右端。
- 如果它是标记节点,则当前层结束。
- 根据当前层累加和更新最大和。
- 设置当前累加和为 0。
- 层数加 1,向队列中压入标记节点,表示下一层节点结束。
返回最大累加和层序号。
[solution2-Python]from collections import deque class Solution: def maxLevelSum(self, root: TreeNode) -> int: curr_level = max_level = 1 max_sum = float('-inf') curr_sum = 0 marker = None queue = deque([root, marker]) while len(queue) > 1: x = queue.popleft() # continue current level if x != marker: curr_sum += x.val if x.left: queue.append(x.left) if x.right: queue.append(x.right) # end of current level, go to the next level else: if curr_sum > max_sum: max_sum, max_level = curr_sum, curr_level curr_sum = 0 curr_level += 1 queue.append(marker) return max_level
[solution2-Java]class Solution { public int maxLevelSum(TreeNode root) { int currLevel = 1, maxLevel = 1; int maxSum = root.val, currSum = 0; LinkedList<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList(); TreeNode marker = null, x = root; queue.addLast(root); queue.addLast(marker); while (queue.size() > 1) { x = queue.removeFirst(); // continue current level if (x != marker) { currSum += x.val; if (x.left != null) queue.addLast(x.left); if (x.right != null) queue.addLast(x.right); } // end of current level, go to the next level else { if (currSum > maxSum) { maxSum = currSum; maxLevel = currLevel; } currSum = 0; currLevel++; queue.addLast(marker); } } return maxLevel; } }
复杂度分析
时间复杂度:$\mathcal{O}(N)$,每个节点只被访问两次,入队列和出队列。
空间复杂度:$\mathcal{O}(N)$,队列的存储空间。任意时刻,队列最多只包含一层的所有节点。完美树中一层节点最多有 $(N + 1)/2$ 个。
方法三:BFS:简洁的 Python 解法
重写方法二中 Python 代码。
[solution3-Python]class Solution: def maxLevelSum(self, root: TreeNode) -> int: curr_level = max_level = 1 max_sum = float('-inf') queue = [root, ] while queue: # sum up all the nodes on the current level curr_sum = sum([x.val for x in queue]) # update max_sum if curr_sum > max_sum: max_sum, max_level = curr_sum, curr_level # build next level queue = [y for x in queue for y in [x.left, x.right] if y] curr_level += 1 return max_level
复杂度分析
时间复杂度:$\mathcal{O}(N)$。
空间复杂度:$\mathcal{O}(N)$,队列的存储空间。任意时刻,队列最多只包含一层的所有节点。完美树中一层节点最多有 $(N + 1)/2$ 个。
统计信息
| 通过次数 | 提交次数 | AC比率 |
|---|---|---|
| 10975 | 17340 | 63.3% |
提交历史
| 提交时间 | 提交结果 | 执行时间 | 内存消耗 | 语言 |
|---|




