原文链接: https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/reverse-substrings-between-each-pair-of-parentheses
英文原文
You are given a string s that consists of lower case English letters and brackets.
Reverse the strings in each pair of matching parentheses, starting from the innermost one.
Your result should not contain any brackets.
Example 1:
Input: s = "(abcd)" Output: "dcba"
Example 2:
Input: s = "(u(love)i)" Output: "iloveu" Explanation: The substring "love" is reversed first, then the whole string is reversed.
Example 3:
Input: s = "(ed(et(oc))el)" Output: "leetcode" Explanation: First, we reverse the substring "oc", then "etco", and finally, the whole string.
Example 4:
Input: s = "a(bcdefghijkl(mno)p)q" Output: "apmnolkjihgfedcbq"
Constraints:
0 <= s.length <= 2000sonly contains lower case English characters and parentheses.- It's guaranteed that all parentheses are balanced.
中文题目
给出一个字符串 s(仅含有小写英文字母和括号)。
请你按照从括号内到外的顺序,逐层反转每对匹配括号中的字符串,并返回最终的结果。
注意,您的结果中 不应 包含任何括号。
示例 1:
输入:s = "(abcd)" 输出:"dcba"
示例 2:
输入:s = "(u(love)i)" 输出:"iloveu" 解释:先反转子字符串 "love" ,然后反转整个字符串。
示例 3:
输入:s = "(ed(et(oc))el)" 输出:"leetcode" 解释:先反转子字符串 "oc" ,接着反转 "etco" ,然后反转整个字符串。
示例 4:
输入:s = "a(bcdefghijkl(mno)p)q" 输出:"apmnolkjihgfedcbq"
提示:
0 <= s.length <= 2000s中只有小写英文字母和括号- 题目测试用例确保所有括号都是成对出现的
通过代码
高赞题解
方法一:栈
思路及算法
本题要求按照从括号内到外的顺序进行处理。如字符串 $\texttt{(u(love)i)}$,首先处理内层括号,变为 $\texttt{(uevoli)}$,然后处理外层括号,变为 $\texttt{iloveu}$。
对于括号序列相关的题目,通用的解法是使用递归或栈。本题中我们将使用栈解决。
我们从左到右遍历该字符串,使用字符串 $\textit{str}$ 记录当前层所遍历到的小写英文字母。对于当前遍历的字符:
如果是左括号,将 $\textit{str}$ 插入到栈中,并将 $\textit{str}$ 置为空,进入下一层;
如果是右括号,则说明遍历完了当前层,需要将 $\textit{str}$ 反转,返回给上一层。具体地,将栈顶字符串弹出,然后将反转后的 $\textit{str}$ 拼接到栈顶字符串末尾,将结果赋值给 $\textit{str}$。
如果是小写英文字母,将其加到 $\textit{str}$ 末尾。
注意到我们仅在遇到右括号时才进行字符串处理,这样可以保证我们是按照从括号内到外的顺序处理字符串。
代码
[sol1-C++]class Solution { public: string reverseParentheses(string s) { stack<string> stk; string str; for (auto &ch : s) { if (ch == '(') { stk.push(str); str = ""; } else if (ch == ')') { reverse(str.begin(), str.end()); str = stk.top() + str; stk.pop(); } else { str.push_back(ch); } } return str; } };
[sol1-Java]class Solution { public String reverseParentheses(String s) { Deque<String> stack = new LinkedList<String>(); StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer(); for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) { char ch = s.charAt(i); if (ch == '(') { stack.push(sb.toString()); sb.setLength(0); } else if (ch == ')') { sb.reverse(); sb.insert(0, stack.pop()); } else { sb.append(ch); } } return sb.toString(); } }
[sol1-C#]public class Solution { public string ReverseParentheses(string s) { Stack<string> stack = new Stack<string>(); StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(); foreach (char ch in s) { if (ch == '(') { stack.Push(sb.ToString()); sb.Length = 0; } else if (ch == ')') { char[] arr = sb.ToString().ToCharArray(); sb.Length = 0; for (int i = arr.Length - 1; i >= 0; i--) { sb.Append(arr[i]); } sb.Insert(0, stack.Pop()); } else { sb.Append(ch); } } return sb.ToString(); } }
[sol1-JavaScript]var reverseParentheses = function(s) { const stk = []; let str = ''; for (const ch of s) { if (ch === '(') { stk.push(str); str = ''; } else if (ch === ')') { str = str.split("").reverse().join(""); str = stk[stk.length - 1] + str; stk.pop(); } else { str += ch; } } return str; };
[sol1-Golang]func reverseParentheses(s string) string { stack := [][]byte{} str := []byte{} for i := range s { if s[i] == '(' { stack = append(stack, str) str = []byte{} } else if s[i] == ')' { for j, n := 0, len(str); j < n/2; j++ { str[j], str[n-1-j] = str[n-1-j], str[j] } str = append(stack[len(stack)-1], str...) stack = stack[:len(stack)-1] } else { str = append(str, s[i]) } } return string(str) }
[sol1-C]void reverse(char* str, int strSize) { for (int j = 0; j < strSize / 2; j++) { char tmp = str[j]; str[j] = str[strSize - j - 1], str[strSize - j - 1] = tmp; } } char* reverseParentheses(char* s) { int n = strlen(s); char* stk[n]; int top = 0; char* str = malloc(sizeof(char) * (n + 1)); str[0] = '\0'; int strSize = 0; for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { if (s[i] == '(') { stk[top] = malloc(sizeof(char) * (strSize + 1)); memcpy(stk[top], str, sizeof(char) * (strSize + 1)); top++; str[0] = '\0'; strSize = 0; } else if (s[i] == ')') { reverse(str, strSize); int len = strlen(stk[top - 1]); for (int j = strSize; j >= 0; j--) { str[j + len] = str[j]; } memcpy(str, stk[top - 1], sizeof(char) * len); strSize += len; top--; } else { str[strSize++] = s[i]; str[strSize] = '\0'; } } return str; }
复杂度分析
时间复杂度:$O(n^2)$,其中 $n$ 为字符串的长度。栈的最大深度为 $O(n)$,每一层处理的时间复杂度主要为反转的时间复杂度,为 $O(n)$,因此总时间复杂度为 $O(n^2)$。
空间复杂度:$O(n)$,其中 $n$ 为字符串的长度。对于任意时刻,字符串中的任意一个字符至多只被栈中的一个位置包含一次。
方法二:预处理括号
思路及算法
我们可以将括号的反转理解为逆序地遍历括号,如下图:
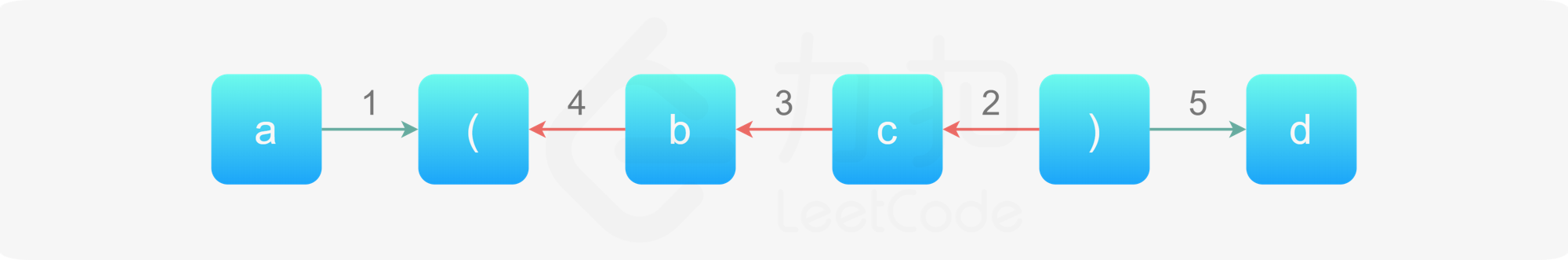
- 第一步我们向右移动到左括号,此时我们跳跃到该左括号对应的右括号(进入了更深一层);
- 第二到第三步我们在括号内部向左移动(完成了更深层的遍历);
- 第四步我们向左移动到左括号,此时我们跳跃到该左括号对应的右括号(返回到上一层);
- 第五步我们在括号外向右移动(继续遍历)。
读者们可以自行尝试模拟两层乃至多层括号嵌套的移动方案,规律可以从当前的单层括号中总结出来。
假设我们沿着某个方向移动,此时遇到了括号,那么我们只需要首先跳跃到该括号对应的另一个括号所在处,然后改变我们的移动方向即可。这个方案同时适用于遍历时进入更深一层,以及完成当前层的遍历后返回到上一层的方案。
在实际代码中,我们需要预处理出每一个括号对应的另一个括号所在的位置,这一部分我们可以使用栈解决。当我们预处理完成后,即可在线性时间内完成遍历,遍历的字符串顺序即为反转后的字符串。
代码
[sol2-C++]class Solution { public: string reverseParentheses(string s) { int n = s.length(); vector<int> pair(n); stack<int> stk; for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { if (s[i] == '(') { stk.push(i); } else if (s[i] == ')') { int j = stk.top(); stk.pop(); pair[i] = j, pair[j] = i; } } string ret; int index = 0, step = 1; while (index < n) { if (s[index] == '(' || s[index] == ')') { index = pair[index]; step = -step; } else { ret.push_back(s[index]); } index += step; } return ret; } };
[sol2-Java]class Solution { public String reverseParentheses(String s) { int n = s.length(); int[] pair = new int[n]; Deque<Integer> stack = new LinkedList<Integer>(); for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { if (s.charAt(i) == '(') { stack.push(i); } else if (s.charAt(i) == ')') { int j = stack.pop(); pair[i] = j; pair[j] = i; } } StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer(); int index = 0, step = 1; while (index < n) { if (s.charAt(index) == '(' || s.charAt(index) == ')') { index = pair[index]; step = -step; } else { sb.append(s.charAt(index)); } index += step; } return sb.toString(); } }
[sol2-C#]public class Solution { public string ReverseParentheses(string s) { int n = s.Length; int[] pair = new int[n]; Stack<int> stack = new Stack<int>(); for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { if (s[i] == '(') { stack.Push(i); } else if (s[i] == ')') { int j = stack.Pop(); pair[i] = j; pair[j] = i; } } StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(); int index = 0, step = 1; while (index < n) { if (s[index] == '(' || s[index] == ')') { index = pair[index]; step = -step; } else { sb.Append(s[index]); } index += step; } return sb.ToString(); } }
[sol2-JavaScript]var reverseParentheses = function(s) { const n = s.length; const pair = new Array(n).fill(0); const stack = []; for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) { if (s[i] === '(') { stack.push(i); } else if (s[i] == ')') { const j = stack.pop(); pair[i] = j; pair[j] = i; } } const sb = []; let index = 0, step = 1; while (index < n) { if (s[index] === '(' || s[index] === ')') { index = pair[index]; step = -step; } else { sb.push(s[index]); } index += step; } return sb.join(''); };
[sol2-Golang]func reverseParentheses(s string) string { n := len(s) pair := make([]int, n) stack := []int{} for i, b := range s { if b == '(' { stack = append(stack, i) } else if b == ')' { j := stack[len(stack)-1] stack = stack[:len(stack)-1] pair[i], pair[j] = j, i } } ans := []byte{} for i, step := 0, 1; i < n; i += step { if s[i] == '(' || s[i] == ')' { i = pair[i] step = -step } else { ans = append(ans, s[i]) } } return string(ans) }
[sol2-C]char* reverseParentheses(char* s) { int n = strlen(s); int pair[n]; memset(pair, 0, sizeof(pair)); int stk[n], top = 0; for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { if (s[i] == '(') { stk[top++] = i; } else if (s[i] == ')') { int j = stk[--top]; pair[i] = j, pair[j] = i; } } char* ret = malloc(sizeof(char) * (n + 1)); int retSize = 0; int index = 0, step = 1; while (index < n) { if (s[index] == '(' || s[index] == ')') { index = pair[index]; step = -step; } else { ret[retSize++] = s[index]; } index += step; } ret[retSize] = '\0'; return ret; }
复杂度分析
时间复杂度:$O(n)$,其中 $n$ 为字符串的长度。预处理出括号的对应关系的序列的时间复杂度为 $O(n)$,遍历字符串的时间复杂度同样为 $O(n)$。
空间复杂度:$O(n)$,其中 $n$ 为字符串的长度。栈的大小不会超过 $n$,以及我们需要 $O(n)$ 的空间记录括号的对应关系。
统计信息
| 通过次数 | 提交次数 | AC比率 |
|---|---|---|
| 46270 | 71126 | 65.1% |
提交历史
| 提交时间 | 提交结果 | 执行时间 | 内存消耗 | 语言 |
|---|




