原文链接: https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/longest-consecutive-sequence
英文原文
Given an unsorted array of integers nums, return the length of the longest consecutive elements sequence.
You must write an algorithm that runs in O(n) time.
Example 1:
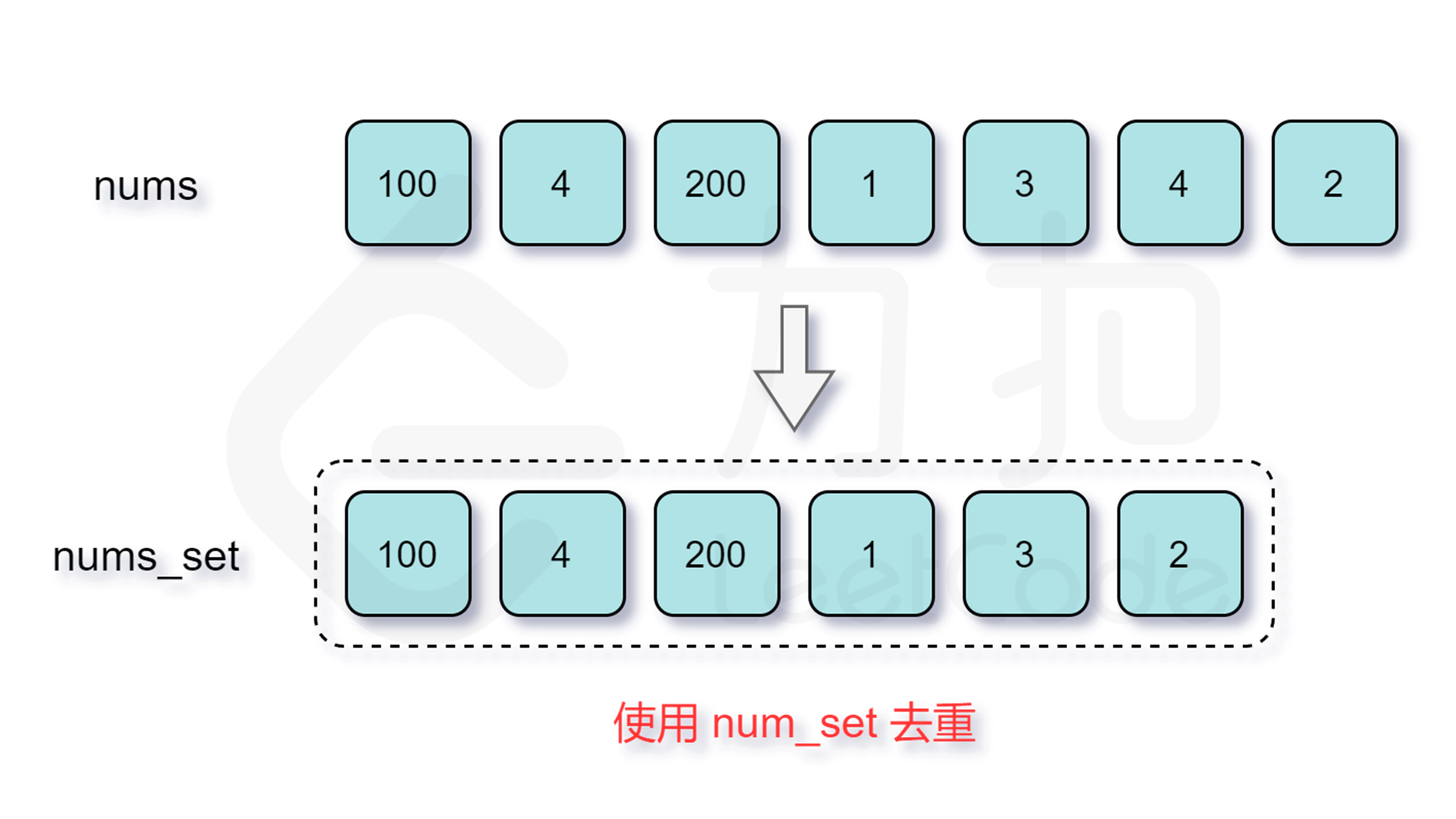
Input: nums = [100,4,200,1,3,2]
Output: 4
Explanation: The longest consecutive elements sequence is [1, 2, 3, 4]. Therefore its length is 4.
Example 2:
Input: nums = [0,3,7,2,5,8,4,6,0,1] Output: 9
Constraints:
0 <= nums.length <= 105-109 <= nums[i] <= 109
中文题目
给定一个未排序的整数数组 nums ,找出数字连续的最长序列(不要求序列元素在原数组中连续)的长度。
请你设计并实现时间复杂度为 O(n) 的算法解决此问题。
示例 1:
输入:nums = [100,4,200,1,3,2]
输出:4
解释:最长数字连续序列是 [1, 2, 3, 4]。它的长度为 4。
示例 2:
输入:nums = [0,3,7,2,5,8,4,6,0,1] 输出:9
提示:
0 <= nums.length <= 105-109 <= nums[i] <= 109
通过代码
高赞题解
方法一:哈希表
思路和算法
我们考虑枚举数组中的每个数 $x$,考虑以其为起点,不断尝试匹配 $x+1, x+2, \cdots$ 是否存在,假设最长匹配到了 $x+y$,那么以 $x$ 为起点的最长连续序列即为 $x, x+1, x+2, \cdots, x+y$,其长度为 $y+1$,我们不断枚举并更新答案即可。
对于匹配的过程,暴力的方法是 $O(n)$ 遍历数组去看是否存在这个数,但其实更高效的方法是用一个哈希表存储数组中的数,这样查看一个数是否存在即能优化至 $O(1)$ 的时间复杂度。
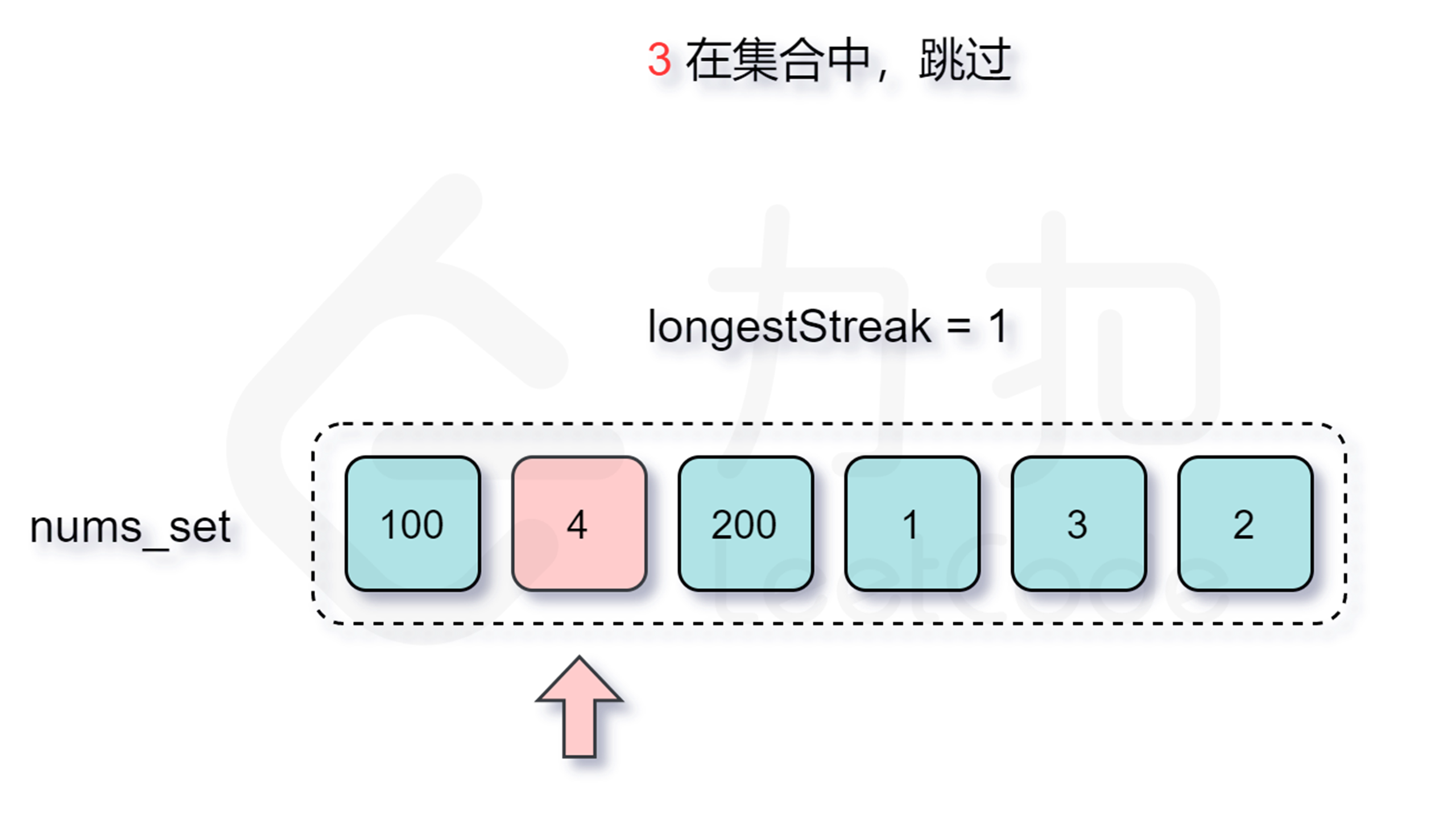
仅仅是这样我们的算法时间复杂度最坏情况下还是会达到 $O(n^2)$(即外层需要枚举 $O(n)$ 个数,内层需要暴力匹配 $O(n)$ 次),无法满足题目的要求。但仔细分析这个过程,我们会发现其中执行了很多不必要的枚举,如果已知有一个 $x, x+1, x+2, \cdots, x+y$ 的连续序列,而我们却重新从 $x+1$,$x+2$ 或者是 $x+y$ 处开始尝试匹配,那么得到的结果肯定不会优于枚举 $x$ 为起点的答案,因此我们在外层循环的时候碰到这种情况跳过即可。
那么怎么判断是否跳过呢?由于我们要枚举的数 $x$ 一定是在数组中不存在前驱数 $x-1$ 的,不然按照上面的分析我们会从 $x-1$ 开始尝试匹配,因此我们每次在哈希表中检查是否存在 $x-1$ 即能判断是否需要跳过了。
<
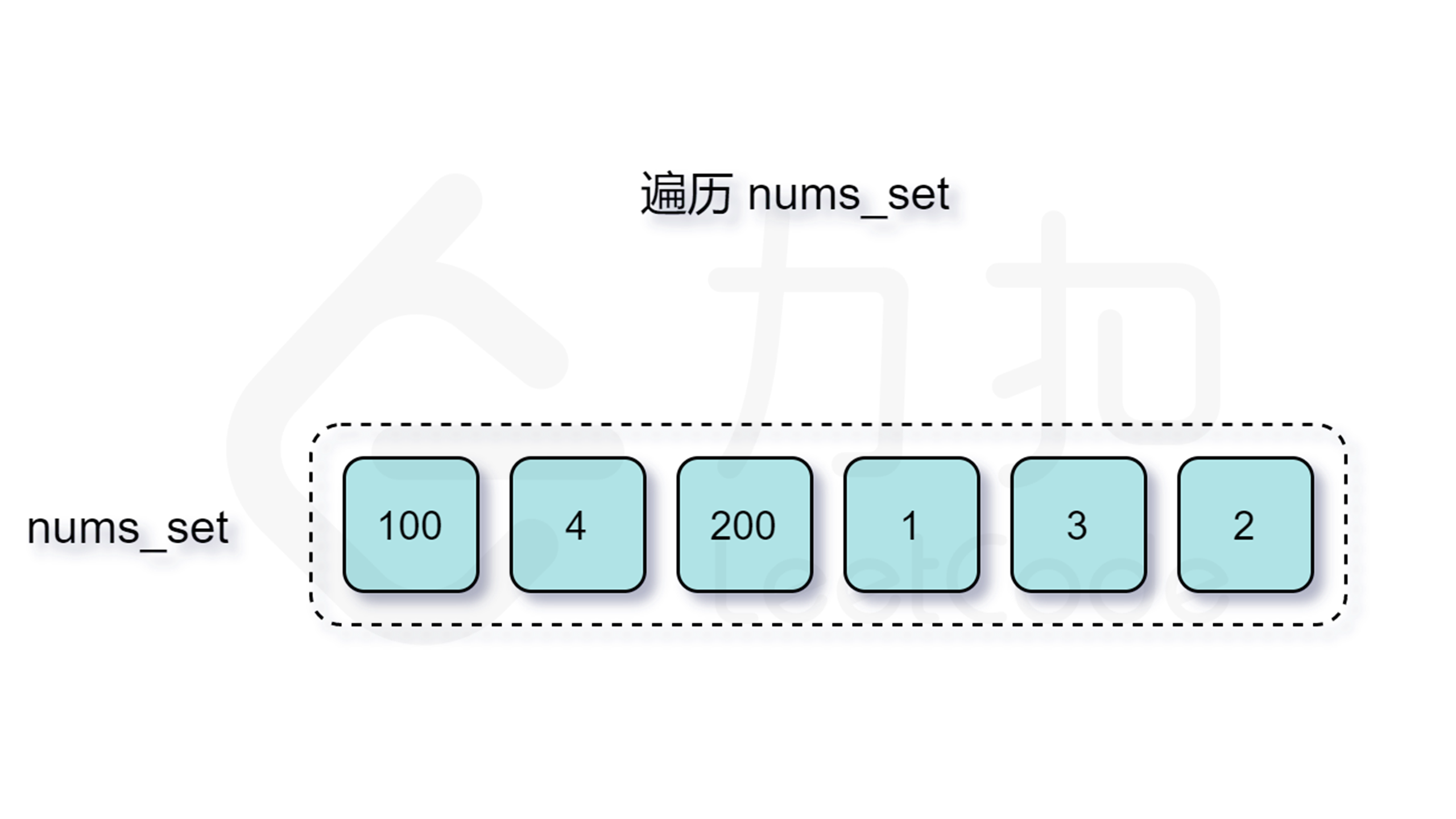
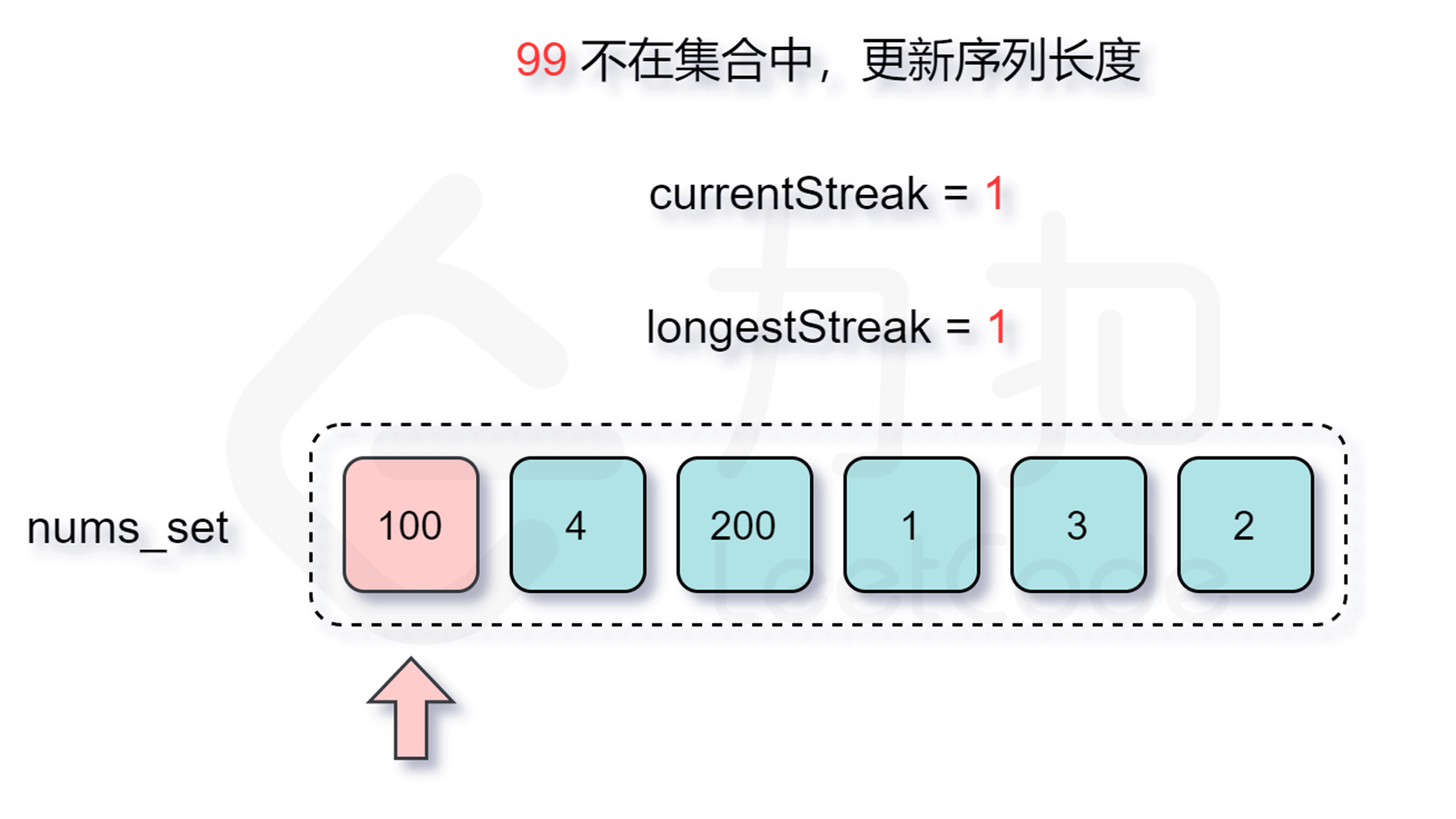
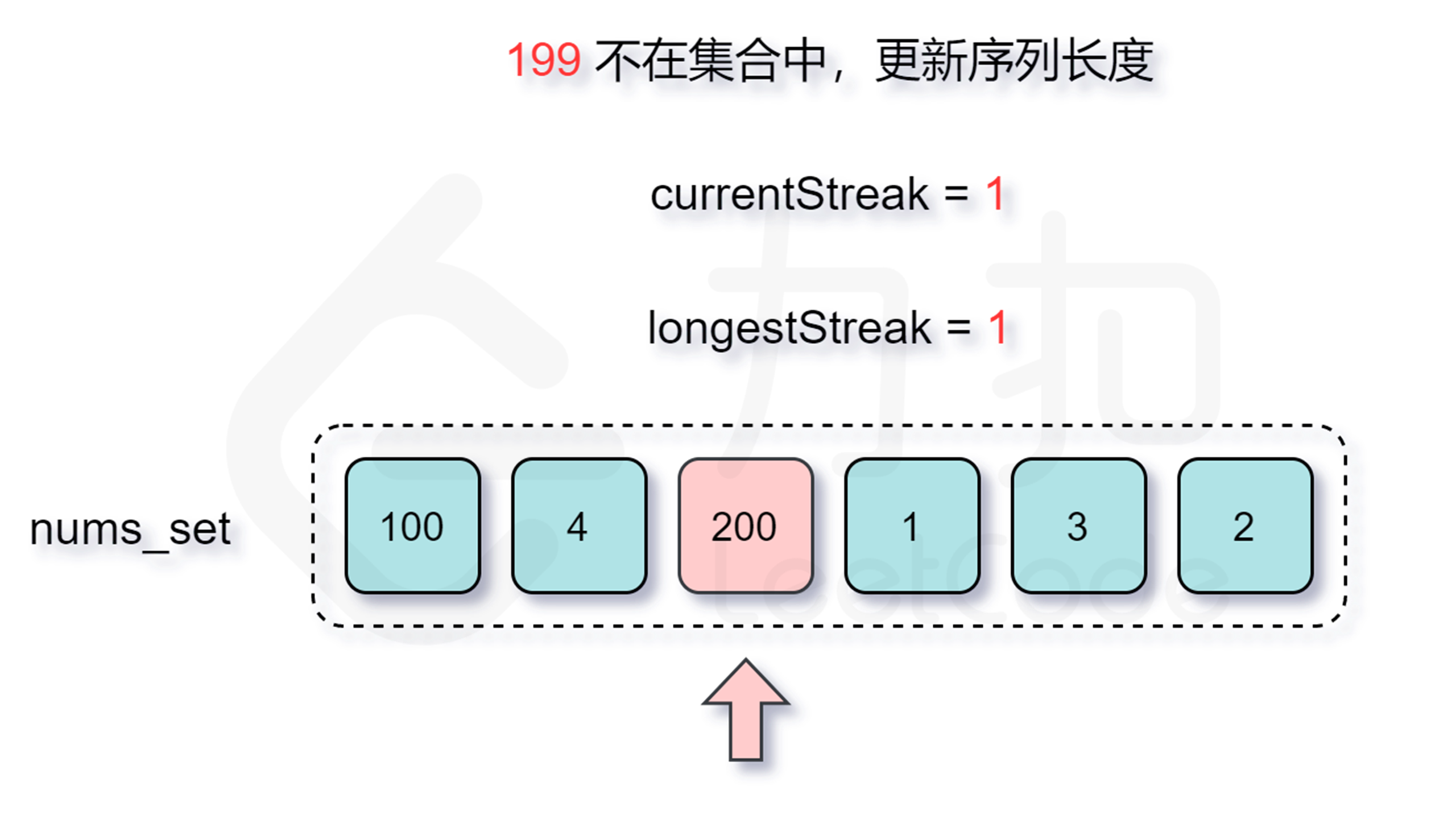
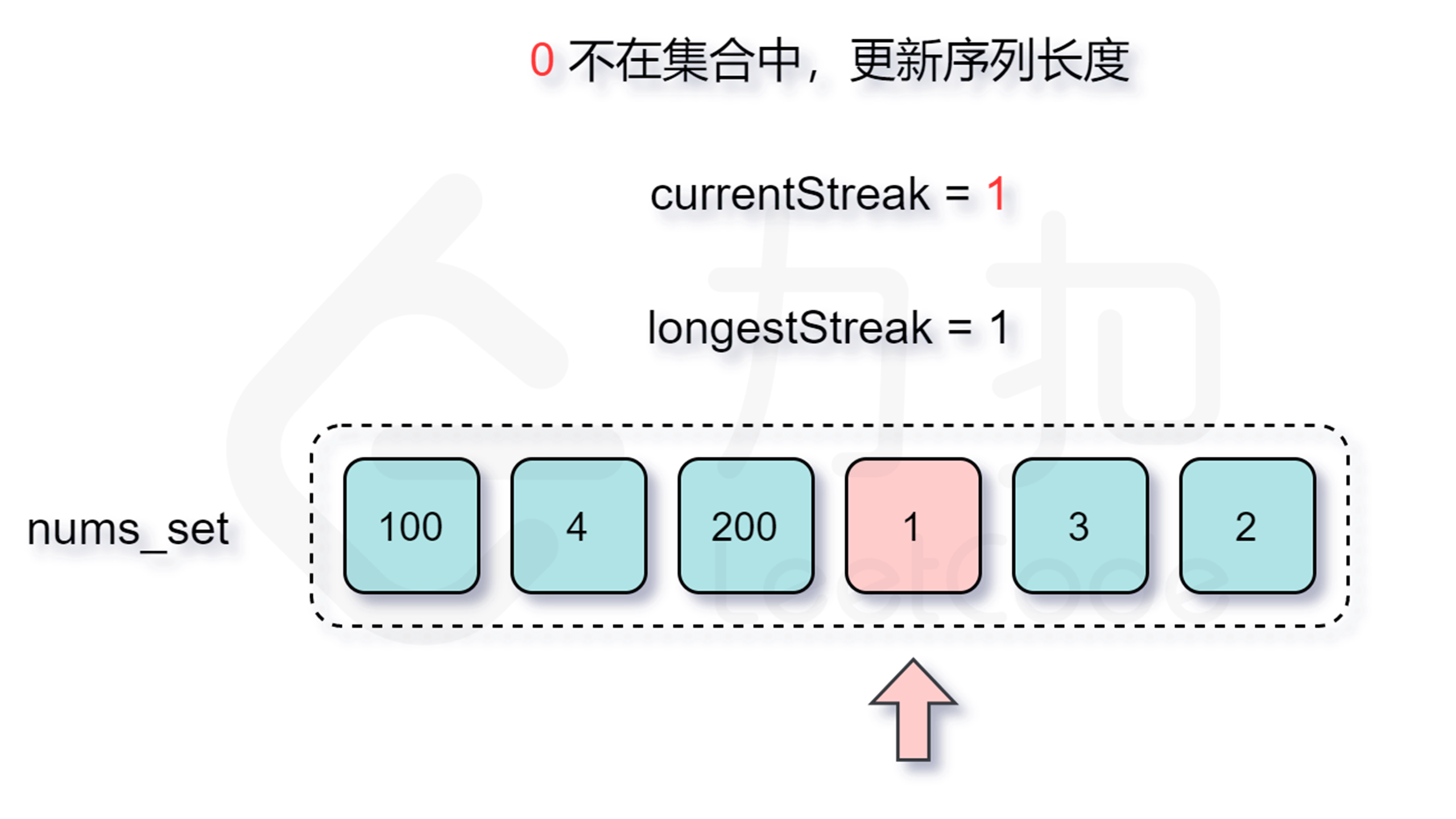
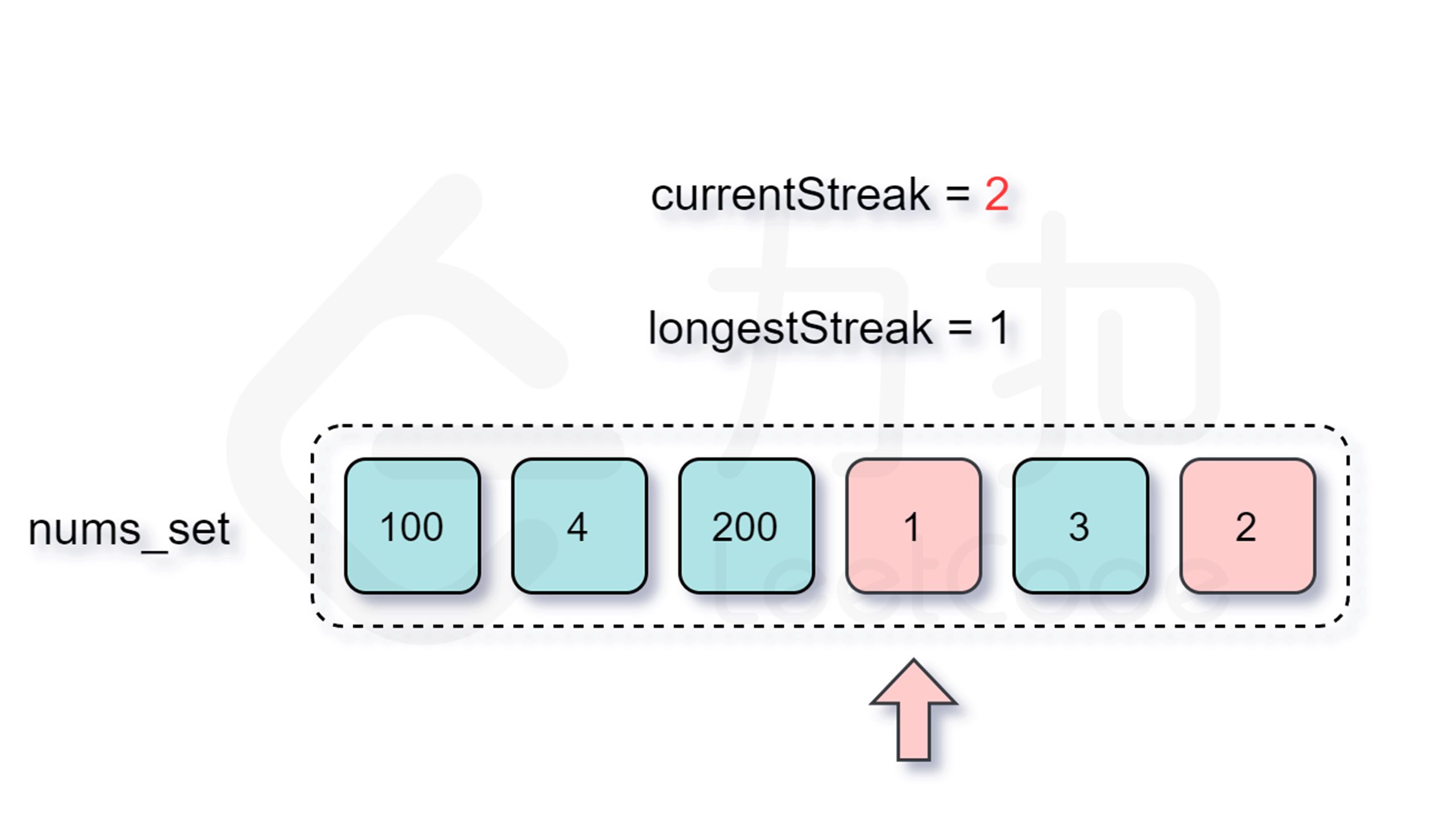
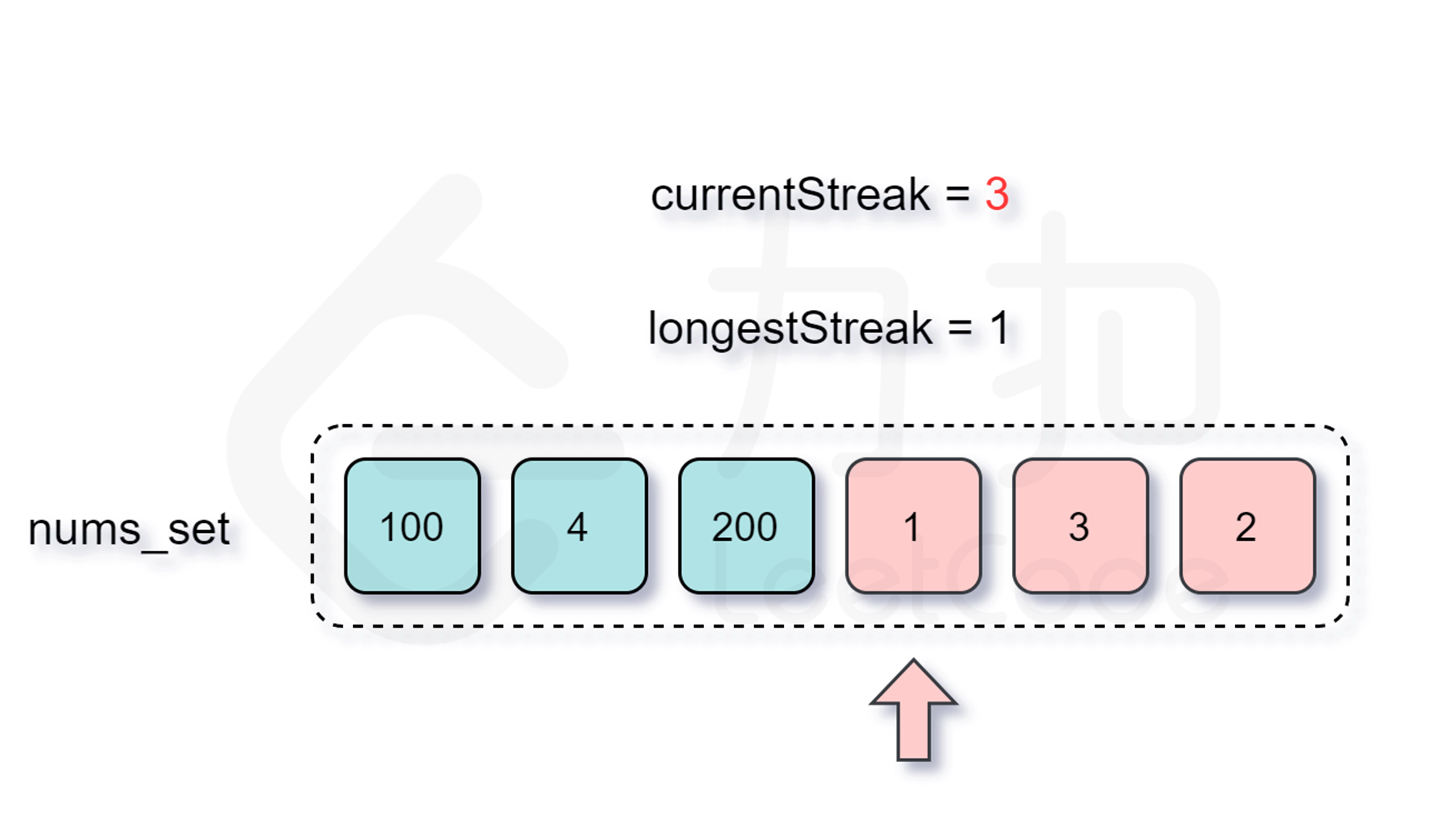
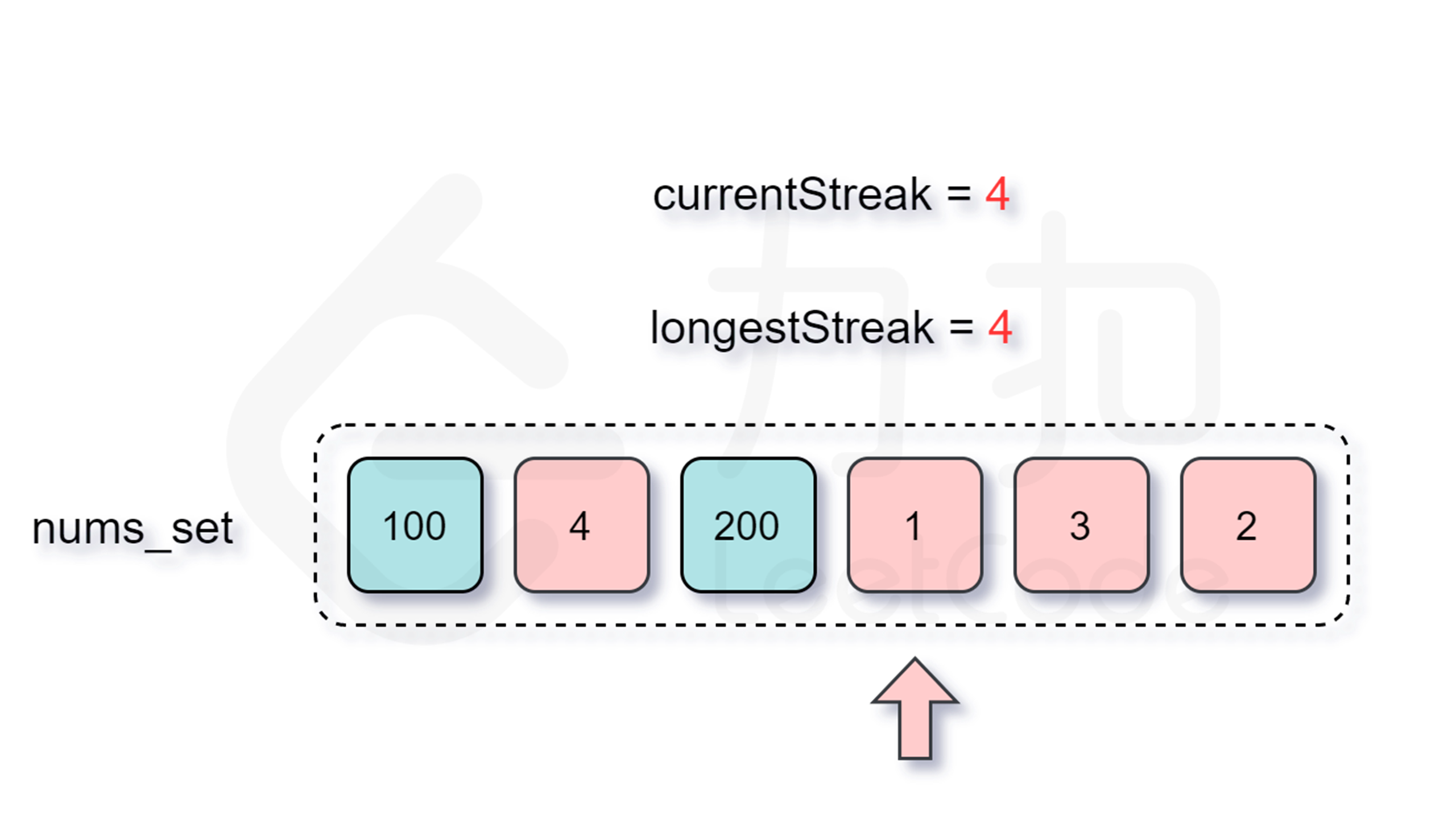
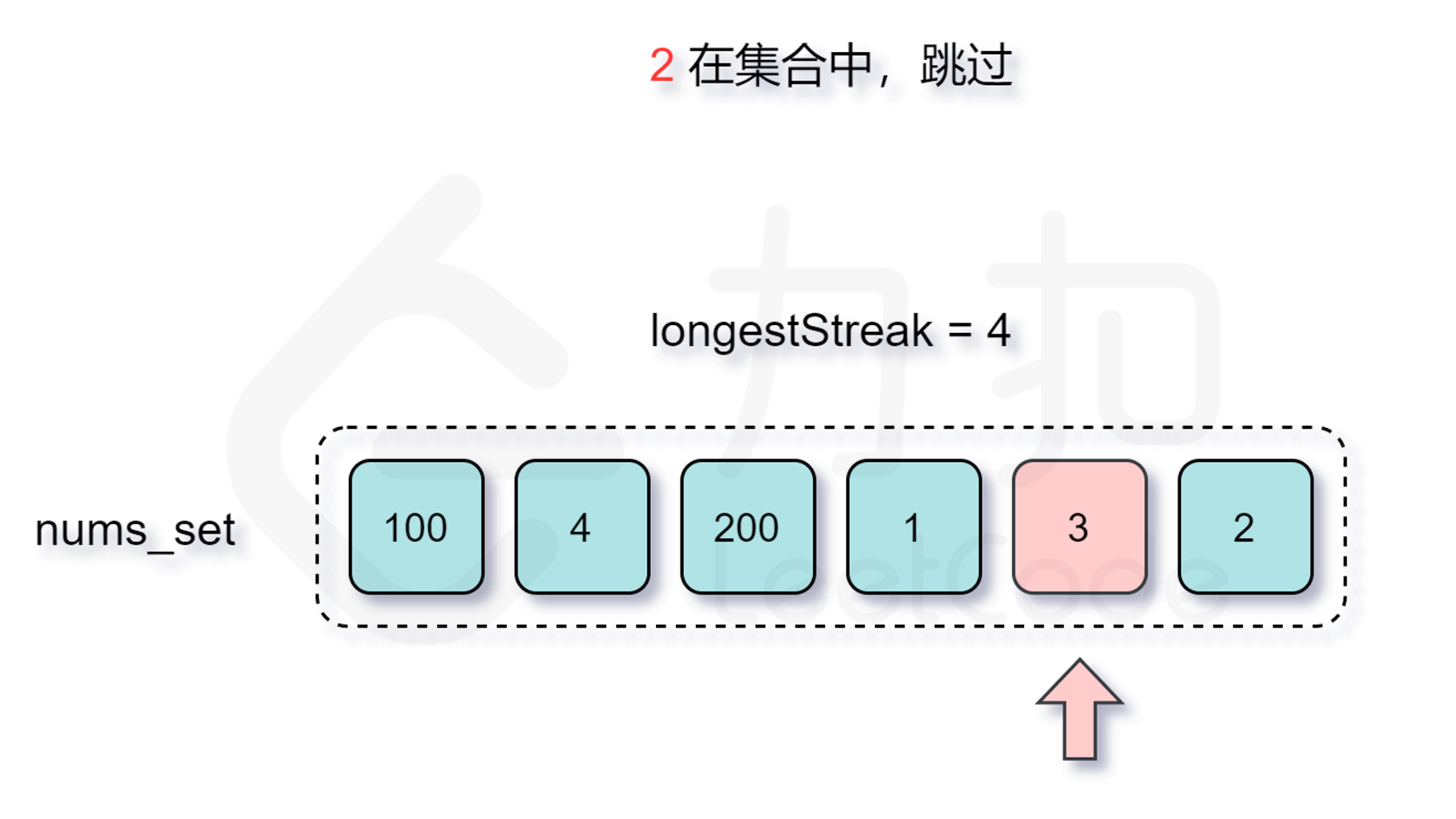
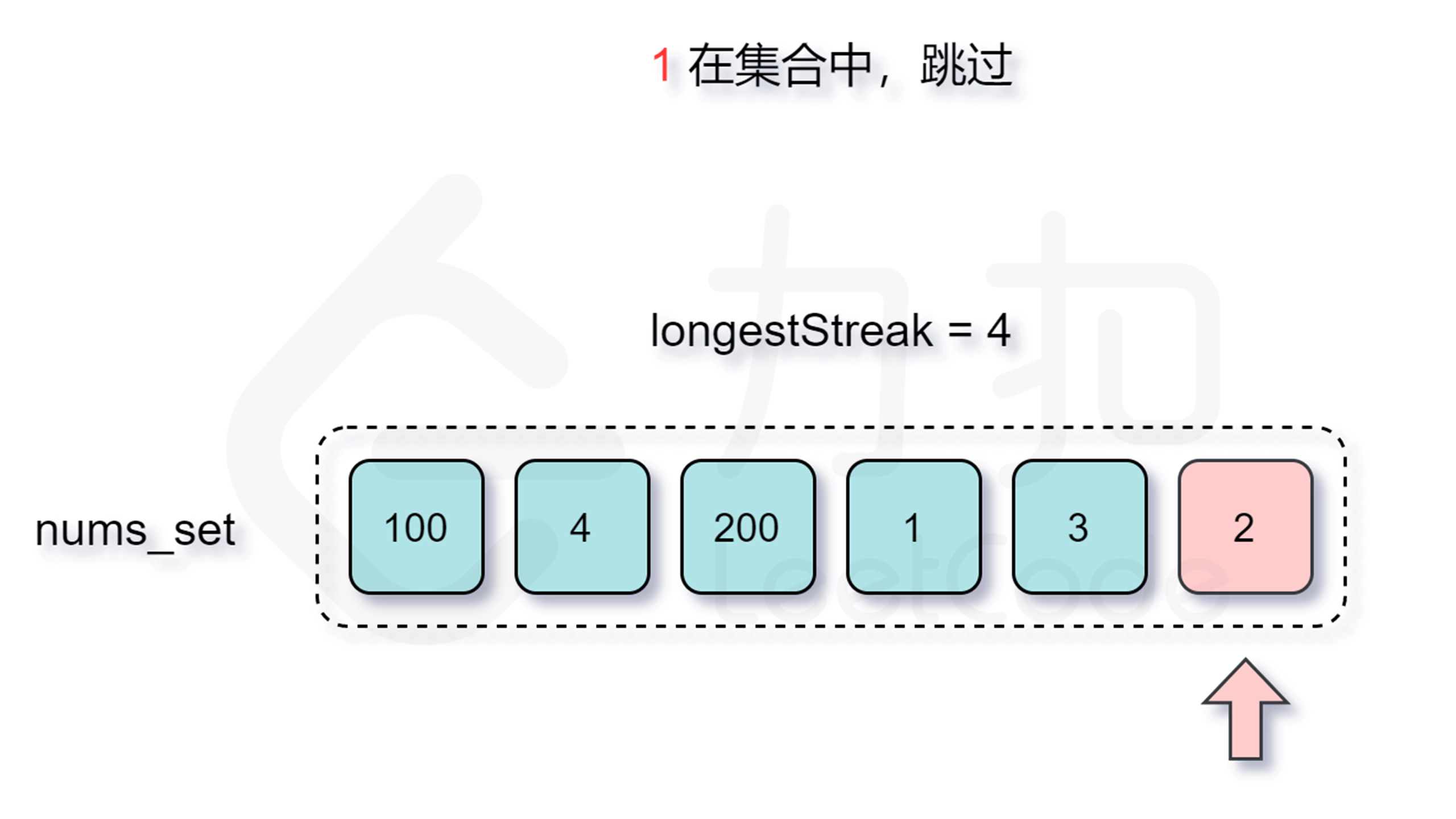
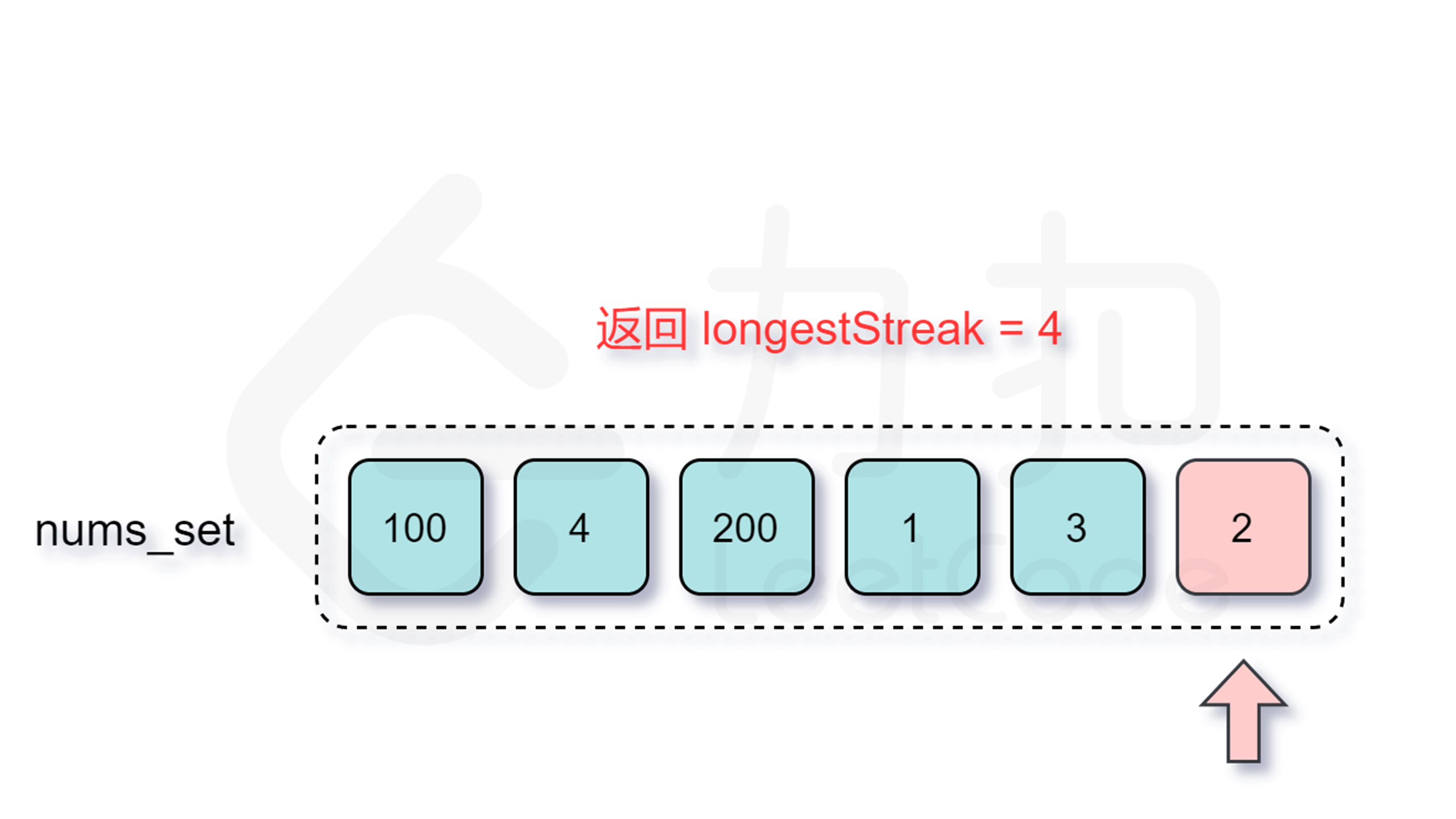
增加了判断跳过的逻辑之后,时间复杂度是多少呢?外层循环需要 $O(n)$ 的时间复杂度,只有当一个数是连续序列的第一个数的情况下才会进入内层循环,然后在内层循环中匹配连续序列中的数,因此数组中的每个数只会进入内层循环一次。根据上述分析可知,总时间复杂度为 $O(n)$,符合题目要求。
[sol1-Java]class Solution { public int longestConsecutive(int[] nums) { Set<Integer> num_set = new HashSet<Integer>(); for (int num : nums) { num_set.add(num); } int longestStreak = 0; for (int num : num_set) { if (!num_set.contains(num - 1)) { int currentNum = num; int currentStreak = 1; while (num_set.contains(currentNum + 1)) { currentNum += 1; currentStreak += 1; } longestStreak = Math.max(longestStreak, currentStreak); } } return longestStreak; } }
[sol1-Python3]class Solution: def longestConsecutive(self, nums: List[int]) -> int: longest_streak = 0 num_set = set(nums) for num in num_set: if num - 1 not in num_set: current_num = num current_streak = 1 while current_num + 1 in num_set: current_num += 1 current_streak += 1 longest_streak = max(longest_streak, current_streak) return longest_streak
[sol1-C++]class Solution { public: int longestConsecutive(vector<int>& nums) { unordered_set<int> num_set; for (const int& num : nums) { num_set.insert(num); } int longestStreak = 0; for (const int& num : num_set) { if (!num_set.count(num - 1)) { int currentNum = num; int currentStreak = 1; while (num_set.count(currentNum + 1)) { currentNum += 1; currentStreak += 1; } longestStreak = max(longestStreak, currentStreak); } } return longestStreak; } };
[sol1-TypeScript]var longestConsecutive = function(nums: number[]): number { let num_set: Set<number> = new Set(); for (const num of nums) { num_set.add(num); } let longestStreak = 0; for (const num of num_set) { if (!num_set.has(num - 1)) { let currentNum = num; let currentStreak = 1; while (num_set.has(currentNum + 1)) { currentNum += 1; currentStreak += 1; } longestStreak = Math.max(longestStreak, currentStreak); } } return longestStreak; };
[sol1-Golang]func longestConsecutive(nums []int) int { numSet := map[int]bool{} for _, num := range nums { numSet[num] = true } longestStreak := 0 for num := range numSet { if !numSet[num-1] { currentNum := num currentStreak := 1 for numSet[currentNum+1] { currentNum++ currentStreak++ } if longestStreak < currentStreak { longestStreak = currentStreak } } } return longestStreak }
复杂度分析
时间复杂度:$O(n)$,其中 $n$ 为数组的长度。具体分析已在上面正文中给出。
空间复杂度:$O(n)$。哈希表存储数组中所有的数需要 $O(n)$ 的空间。
统计信息
| 通过次数 | 提交次数 | AC比率 |
|---|---|---|
| 188465 | 346490 | 54.4% |
提交历史
| 提交时间 | 提交结果 | 执行时间 | 内存消耗 | 语言 |
|---|
相似题目
| 题目 | 难度 |
|---|---|
| 二叉树最长连续序列 | 中等 |




