原文链接: https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/get-watched-videos-by-your-friends
英文原文
There are n people, each person has a unique id between 0 and n-1. Given the arrays watchedVideos and friends, where watchedVideos[i] and friends[i] contain the list of watched videos and the list of friends respectively for the person with id = i.
Level 1 of videos are all watched videos by your friends, level 2 of videos are all watched videos by the friends of your friends and so on. In general, the level k of videos are all watched videos by people with the shortest path exactly equal to k with you. Given your id and the level of videos, return the list of videos ordered by their frequencies (increasing). For videos with the same frequency order them alphabetically from least to greatest.
Example 1:
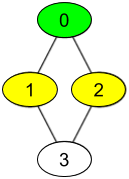
Input: watchedVideos = [["A","B"],["C"],["B","C"],["D"]], friends = [[1,2],[0,3],[0,3],[1,2]], id = 0, level = 1 Output: ["B","C"] Explanation: You have id = 0 (green color in the figure) and your friends are (yellow color in the figure): Person with id = 1 -> watchedVideos = ["C"] Person with id = 2 -> watchedVideos = ["B","C"] The frequencies of watchedVideos by your friends are: B -> 1 C -> 2
Example 2:
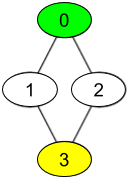
Input: watchedVideos = [["A","B"],["C"],["B","C"],["D"]], friends = [[1,2],[0,3],[0,3],[1,2]], id = 0, level = 2 Output: ["D"] Explanation: You have id = 0 (green color in the figure) and the only friend of your friends is the person with id = 3 (yellow color in the figure).
Constraints:
n == watchedVideos.length == friends.length2 <= n <= 1001 <= watchedVideos[i].length <= 1001 <= watchedVideos[i][j].length <= 80 <= friends[i].length < n0 <= friends[i][j] < n0 <= id < n1 <= level < n- if
friends[i]containsj, thenfriends[j]containsi
中文题目
有 n 个人,每个人都有一个 0 到 n-1 的唯一 id 。
给你数组 watchedVideos 和 friends ,其中 watchedVideos[i] 和 friends[i] 分别表示 id = i 的人观看过的视频列表和他的好友列表。
Level 1 的视频包含所有你好友观看过的视频,level 2 的视频包含所有你好友的好友观看过的视频,以此类推。一般的,Level 为 k 的视频包含所有从你出发,最短距离为 k 的好友观看过的视频。
给定你的 id 和一个 level 值,请你找出所有指定 level 的视频,并将它们按观看频率升序返回。如果有频率相同的视频,请将它们按字母顺序从小到大排列。
示例 1:
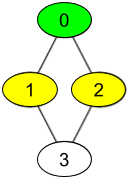
输入:watchedVideos = [["A","B"],["C"],["B","C"],["D"]], friends = [[1,2],[0,3],[0,3],[1,2]], id = 0, level = 1 输出:["B","C"] 解释: 你的 id 为 0(绿色),你的朋友包括(黄色): id 为 1 -> watchedVideos = ["C"] id 为 2 -> watchedVideos = ["B","C"] 你朋友观看过视频的频率为: B -> 1 C -> 2
示例 2:
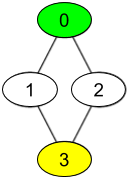
输入:watchedVideos = [["A","B"],["C"],["B","C"],["D"]], friends = [[1,2],[0,3],[0,3],[1,2]], id = 0, level = 2 输出:["D"] 解释: 你的 id 为 0(绿色),你朋友的朋友只有一个人,他的 id 为 3(黄色)。
提示:
n == watchedVideos.length == friends.length2 <= n <= 1001 <= watchedVideos[i].length <= 1001 <= watchedVideos[i][j].length <= 80 <= friends[i].length < n0 <= friends[i][j] < n0 <= id < n1 <= level < n- 如果
friends[i]包含j,那么friends[j]包含i
通过代码
高赞题解
广度优先遍历+优先级队列:
public List<String> watchedVideosByFriends(List<List<String>> watchedVideos, int[][] friends, int id, int level) {
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
Set<Integer> visited = new HashSet<>();
queue.offer(id);
visited.add(id);
int len = 0;
while (!queue.isEmpty() && len < level) {
int size = queue.size();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
Integer idd = queue.poll();
for (int j = 0; j < friends[idd].length; j++) {
if (!visited.contains(friends[idd][j])) {
queue.add(friends[idd][j]);
visited.add(friends[idd][j]);
}
}
}
len++;
}
Map<String, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
Integer idd = queue.poll();
for (int i = 0; i < watchedVideos.get(idd).size(); i++) {
map.put(watchedVideos.get(idd).get(i), map.getOrDefault(watchedVideos.get(idd).get(i), 0) + 1);
}
}
PriorityQueue<Pair<String, Integer>> priorityQueue = new PriorityQueue<>((t1, t2) -> {
if (t1.getValue().equals(t2.getValue())) {
return t1.getKey().compareTo(t2.getKey());
} else {
return t1.getValue().compareTo(t2.getValue());
}
});
map.forEach((key, value) -> priorityQueue.add(new Pair<>(key, value)));
List<String> ans = new ArrayList<>();
while (!priorityQueue.isEmpty()) {
ans.add(priorityQueue.poll().getKey());
}
return ans;
}统计信息
| 通过次数 | 提交次数 | AC比率 |
|---|---|---|
| 5811 | 15195 | 38.2% |
提交历史
| 提交时间 | 提交结果 | 执行时间 | 内存消耗 | 语言 |
|---|




