英文原文
Given a reference of a node in a connected undirected graph.
Return a deep copy (clone) of the graph.
Each node in the graph contains a value (int) and a list (List[Node]) of its neighbors.
class Node {
public int val;
public List<Node> neighbors;
}
Test case format:
For simplicity, each node's value is the same as the node's index (1-indexed). For example, the first node with val == 1, the second node with val == 2, and so on. The graph is represented in the test case using an adjacency list.
An adjacency list is a collection of unordered lists used to represent a finite graph. Each list describes the set of neighbors of a node in the graph.
The given node will always be the first node with val = 1. You must return the copy of the given node as a reference to the cloned graph.
Example 1:
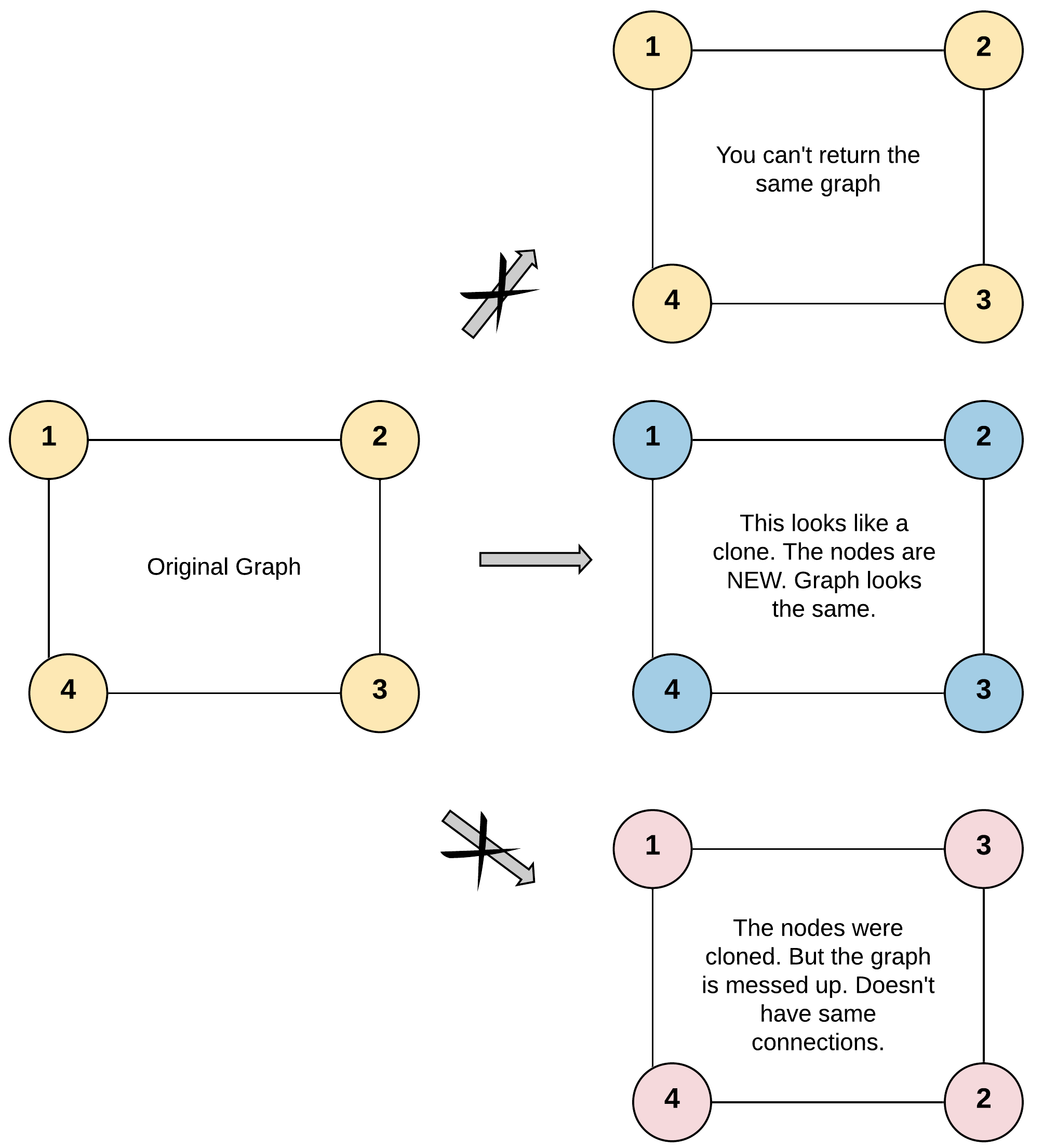
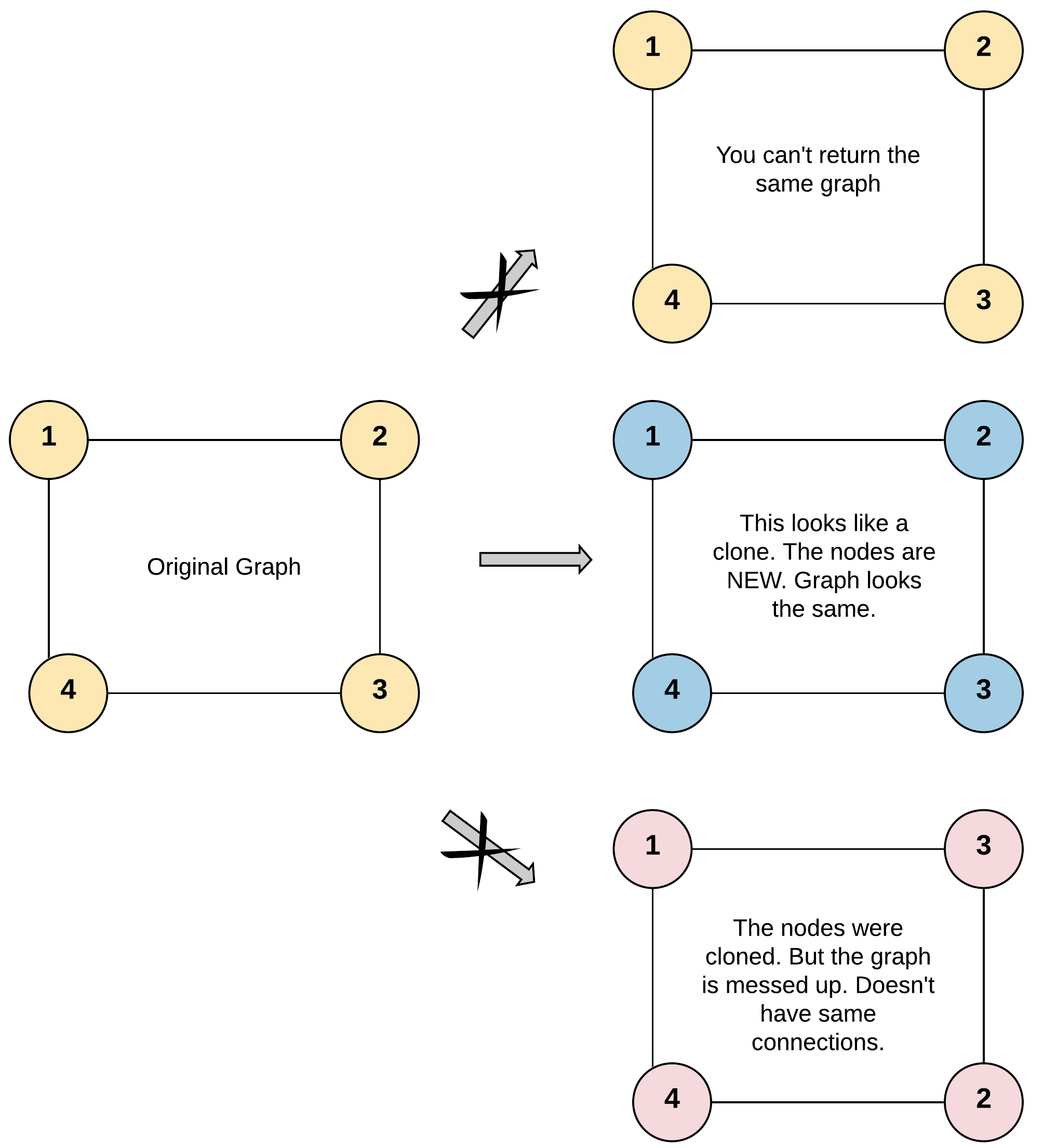
Input: adjList = [[2,4],[1,3],[2,4],[1,3]] Output: [[2,4],[1,3],[2,4],[1,3]] Explanation: There are 4 nodes in the graph. 1st node (val = 1)'s neighbors are 2nd node (val = 2) and 4th node (val = 4). 2nd node (val = 2)'s neighbors are 1st node (val = 1) and 3rd node (val = 3). 3rd node (val = 3)'s neighbors are 2nd node (val = 2) and 4th node (val = 4). 4th node (val = 4)'s neighbors are 1st node (val = 1) and 3rd node (val = 3).
Example 2:
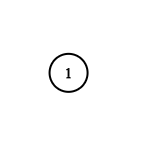
Input: adjList = [[]] Output: [[]] Explanation: Note that the input contains one empty list. The graph consists of only one node with val = 1 and it does not have any neighbors.
Example 3:
Input: adjList = [] Output: [] Explanation: This an empty graph, it does not have any nodes.
Example 4:
Input: adjList = [[2],[1]] Output: [[2],[1]]
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the graph is in the range
[0, 100]. 1 <= Node.val <= 100Node.valis unique for each node.- There are no repeated edges and no self-loops in the graph.
- The Graph is connected and all nodes can be visited starting from the given node.
中文题目
给你无向 连通 图中一个节点的引用,请你返回该图的 深拷贝(克隆)。
图中的每个节点都包含它的值 val(int) 和其邻居的列表(list[Node])。
class Node {
public int val;
public List<Node> neighbors;
}
测试用例格式:
简单起见,每个节点的值都和它的索引相同。例如,第一个节点值为 1(val = 1),第二个节点值为 2(val = 2),以此类推。该图在测试用例中使用邻接列表表示。
邻接列表 是用于表示有限图的无序列表的集合。每个列表都描述了图中节点的邻居集。
给定节点将始终是图中的第一个节点(值为 1)。你必须将 给定节点的拷贝 作为对克隆图的引用返回。
示例 1:
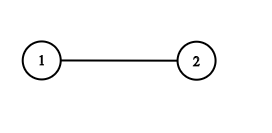
输入:adjList = [[2,4],[1,3],[2,4],[1,3]] 输出:[[2,4],[1,3],[2,4],[1,3]] 解释: 图中有 4 个节点。 节点 1 的值是 1,它有两个邻居:节点 2 和 4 。 节点 2 的值是 2,它有两个邻居:节点 1 和 3 。 节点 3 的值是 3,它有两个邻居:节点 2 和 4 。 节点 4 的值是 4,它有两个邻居:节点 1 和 3 。
示例 2:
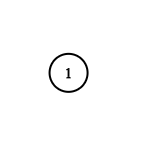
输入:adjList = [[]] 输出:[[]] 解释:输入包含一个空列表。该图仅仅只有一个值为 1 的节点,它没有任何邻居。
示例 3:
输入:adjList = [] 输出:[] 解释:这个图是空的,它不含任何节点。
示例 4:
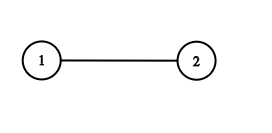
输入:adjList = [[2],[1]] 输出:[[2],[1]]
提示:
- 节点数不超过 100 。
- 每个节点值
Node.val都是唯一的,1 <= Node.val <= 100。 - 无向图是一个简单图,这意味着图中没有重复的边,也没有自环。
- 由于图是无向的,如果节点 p 是节点 q 的邻居,那么节点 q 也必须是节点 p 的邻居。
- 图是连通图,你可以从给定节点访问到所有节点。
通过代码
高赞题解
解题思路:
这道题就是遍历整个图,所以遍历时候要记录已经访问点,我们用一个字典记录。
所以,遍历方法就有两种。
思路一:DFS (深度遍历)
思路二:BFS (广度遍历)
!!! 大家重点掌握,后面图遍历都和这个有关系!
代码:
思路一:
[1]class Solution: def cloneGraph(self, node: 'Node') -> 'Node': lookup = {} def dfs(node): #print(node.val) if not node: return if node in lookup: return lookup[node] clone = Node(node.val, []) lookup[node] = clone for n in node.neighbors: clone.neighbors.append(dfs(n)) return clone return dfs(node)
[1]class Solution { public Node cloneGraph(Node node) { Map<Node, Node> lookup = new HashMap<>(); return dfs(node, lookup); } private Node dfs(Node node, Map<Node,Node> lookup) { if (node == null) return null; if (lookup.containsKey(node)) return lookup.get(node); Node clone = new Node(node.val, new ArrayList<>()); lookup.put(node, clone); for (Node n : node.neighbors)clone.neighbors.add(dfs(n,lookup)); return clone; } }
思路二:
[2]class Solution: def cloneGraph(self, node: 'Node') -> 'Node': from collections import deque lookup = {} def bfs(node): if not node: return clone = Node(node.val, []) lookup[node] = clone queue = deque() queue.appendleft(node) while queue: tmp = queue.pop() for n in tmp.neighbors: if n not in lookup: lookup[n] = Node(n.val, []) queue.appendleft(n) lookup[tmp].neighbors.append(lookup[n]) return clone return bfs(node)
[2]class Solution { public Node cloneGraph(Node node) { if (node == null) return null; Map<Node, Node> lookup = new HashMap<>(); Node clone = new Node(node.val, new ArrayList<>()); lookup.put(node, clone); Deque<Node> queue = new LinkedList<>(); queue.offer(node); while (!queue.isEmpty()) { Node tmp = queue.poll(); for (Node n : tmp.neighbors) { if (!lookup.containsKey(n)) { lookup.put(n, new Node(n.val, new ArrayList<>())); queue.offer(n); } lookup.get(tmp).neighbors.add(lookup.get(n)); } } return clone; } }
统计信息
| 通过次数 | 提交次数 | AC比率 |
|---|---|---|
| 77338 | 114126 | 67.8% |
提交历史
| 提交时间 | 提交结果 | 执行时间 | 内存消耗 | 语言 |
|---|
相似题目
| 题目 | 难度 |
|---|---|
| 复制带随机指针的链表 | 中等 |




