英文原文
There are n cities numbered from 0 to n-1. Given the array edges where edges[i] = [fromi, toi, weighti] represents a bidirectional and weighted edge between cities fromi and toi, and given the integer distanceThreshold.
Return the city with the smallest number of cities that are reachable through some path and whose distance is at most distanceThreshold, If there are multiple such cities, return the city with the greatest number.
Notice that the distance of a path connecting cities i and j is equal to the sum of the edges' weights along that path.
Example 1:
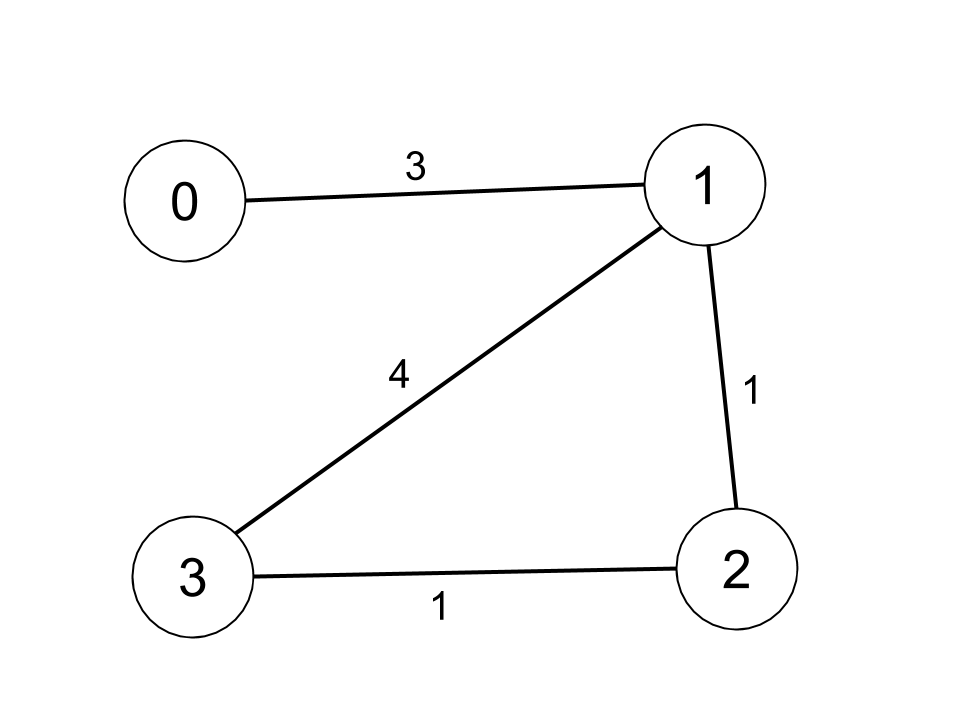
Input: n = 4, edges = [[0,1,3],[1,2,1],[1,3,4],[2,3,1]], distanceThreshold = 4 Output: 3 Explanation: The figure above describes the graph. The neighboring cities at a distanceThreshold = 4 for each city are: City 0 -> [City 1, City 2] City 1 -> [City 0, City 2, City 3] City 2 -> [City 0, City 1, City 3] City 3 -> [City 1, City 2] Cities 0 and 3 have 2 neighboring cities at a distanceThreshold = 4, but we have to return city 3 since it has the greatest number.
Example 2:
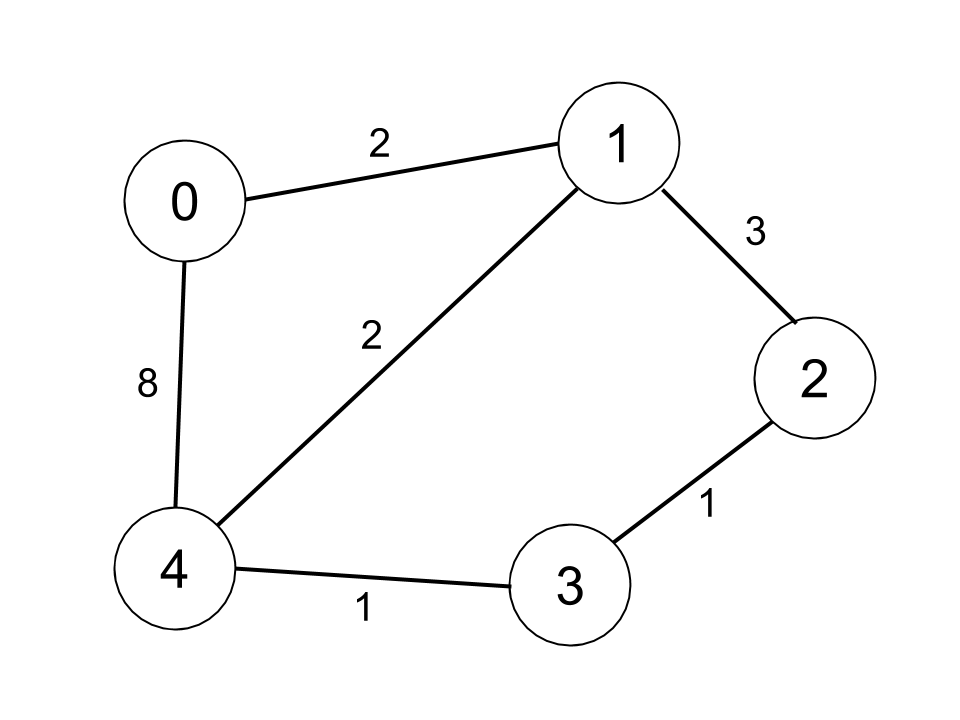
Input: n = 5, edges = [[0,1,2],[0,4,8],[1,2,3],[1,4,2],[2,3,1],[3,4,1]], distanceThreshold = 2 Output: 0 Explanation: The figure above describes the graph. The neighboring cities at a distanceThreshold = 2 for each city are: City 0 -> [City 1] City 1 -> [City 0, City 4] City 2 -> [City 3, City 4] City 3 -> [City 2, City 4] City 4 -> [City 1, City 2, City 3] The city 0 has 1 neighboring city at a distanceThreshold = 2.
Constraints:
2 <= n <= 1001 <= edges.length <= n * (n - 1) / 2edges[i].length == 30 <= fromi < toi < n1 <= weighti, distanceThreshold <= 10^4- All pairs
(fromi, toi)are distinct.
中文题目
有 n 个城市,按从 0 到 n-1 编号。给你一个边数组 edges,其中 edges[i] = [fromi, toi, weighti] 代表 fromi 和 toi 两个城市之间的双向加权边,距离阈值是一个整数 distanceThreshold。
返回能通过某些路径到达其他城市数目最少、且路径距离 最大 为 distanceThreshold 的城市。如果有多个这样的城市,则返回编号最大的城市。
注意,连接城市 i 和 j 的路径的距离等于沿该路径的所有边的权重之和。
示例 1:
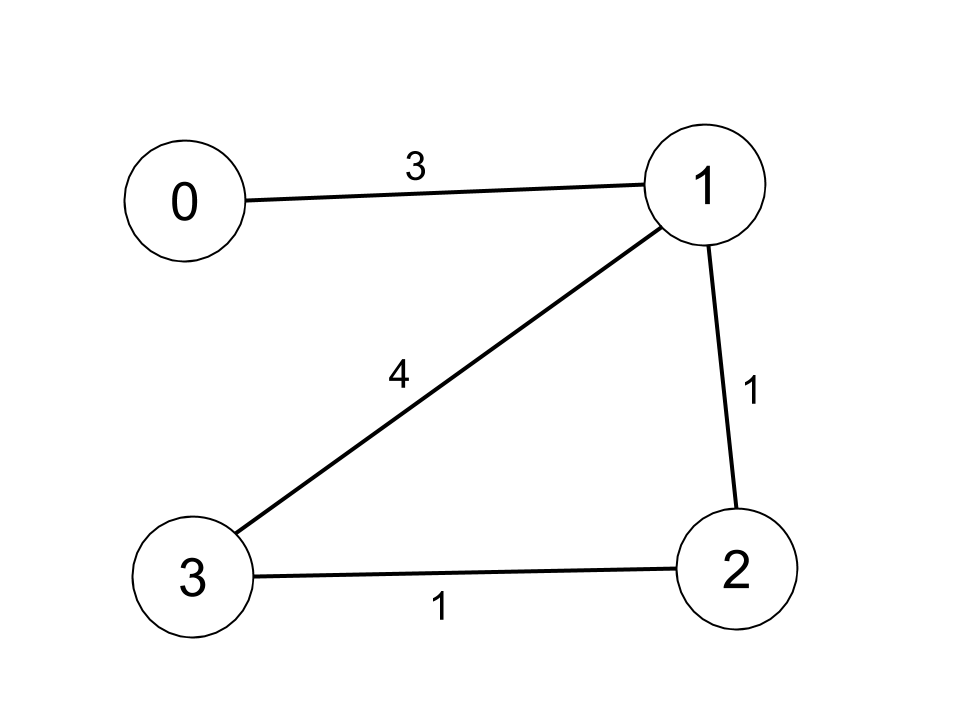
输入:n = 4, edges = [[0,1,3],[1,2,1],[1,3,4],[2,3,1]], distanceThreshold = 4 输出:3 解释:城市分布图如上。 每个城市阈值距离 distanceThreshold = 4 内的邻居城市分别是: 城市 0 -> [城市 1, 城市 2] 城市 1 -> [城市 0, 城市 2, 城市 3] 城市 2 -> [城市 0, 城市 1, 城市 3] 城市 3 -> [城市 1, 城市 2] 城市 0 和 3 在阈值距离 4 以内都有 2 个邻居城市,但是我们必须返回城市 3,因为它的编号最大。
示例 2:
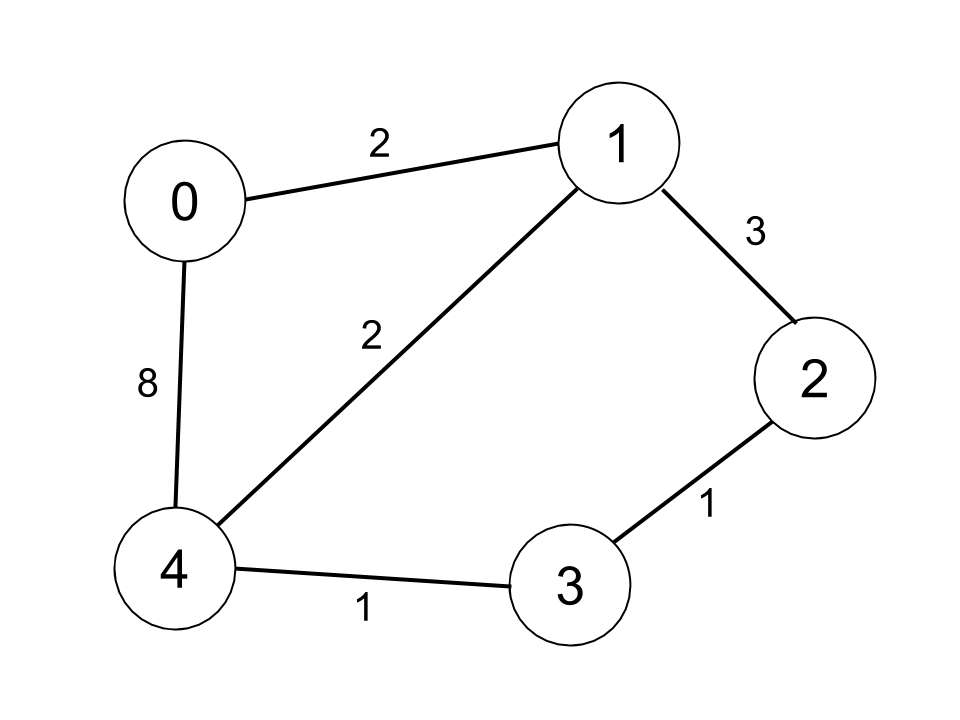
输入:n = 5, edges = [[0,1,2],[0,4,8],[1,2,3],[1,4,2],[2,3,1],[3,4,1]], distanceThreshold = 2 输出:0 解释:城市分布图如上。 每个城市阈值距离 distanceThreshold = 2 内的邻居城市分别是: 城市 0 -> [城市 1] 城市 1 -> [城市 0, 城市 4] 城市 2 -> [城市 3, 城市 4] 城市 3 -> [城市 2, 城市 4] 城市 4 -> [城市 1, 城市 2, 城市 3] 城市 0 在阈值距离 2 以内只有 1 个邻居城市。
提示:
2 <= n <= 1001 <= edges.length <= n * (n - 1) / 2edges[i].length == 30 <= fromi < toi < n1 <= weighti, distanceThreshold <= 10^4- 所有
(fromi, toi)都是不同的。
通过代码
高赞题解
$Floyd$ 算法
$Floyd$ 算法又称插点法,其中算法的核心思想是动态规划。
算法步骤
通过已知条件初始化距离矩阵 $D[n][n]$ ,其中 $D[i][j]$ 表示,顶点 $i$ 到顶点 $j$ 的距离。
$n$ 个顶点依次作为插入点,例如,$k$ 为其中一个顶点,$D[i][k] + D[k][j] < D[i][j]$ ,那说明顶点 $i$ 经过顶点 $k$ 再到达 $j$ ,比直接到达 $j$ 要近。所以更新 $D[i][j]:$ $D[i][j] = D[i][k] + D[k][j]$ 。
可以归纳得到状态转移方程:$D[i][j] = min(D[i,k]+D[k,j],D[i,j])$ 。
$Floyd$ 核心代码:
// Floyd算法
for (int k = 0; k < n; k++) {
// n个顶点依次作为插入点
// 注意插点k是放在第一层循环,后面会解释原因
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
// 遍历各个顶点之间的距离,并用插入点进行更新
D[i][j] = min(D[i][k]+D[k][j], D[i][j]);
}
}
}题目解析
使用 $Floyd$ 算法求出各个城市到其它城市的距离,保存在矩阵 $D[n][n]$ 中。
遍历 $D[n][n]$ ,统计各个城市在距离不超过 $distanceThreshold$ 的情况下,能到达的其它城市的数量。
返回能到达其它城市最少的城市 $ret$ 。
解题代码
class Solution {
public:
int findTheCity(int n, vector <vector<int>> &edges, int distanceThreshold) {
// 定义邻接矩阵D,并初始化各个城市间距离为INT_MAX(无穷)
vector <vector<int>> D(n, vector<int>(n, INT_MAX));
// 根据edges[][]初始化D[][]
for (auto &e : edges) {
// 无向图两个城市间的两个方向距离相同
D[e[0]][e[1]] = e[2];
D[e[1]][e[0]] = e[2];
}
// Floyd算法
for (int k = 0; k < n; k++) {
// n个顶点依次作为插入点
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (i == j || D[i][k] == INT_MAX || D[k][j] == INT_MAX) {
// 这些情况都不符合下一行的if条件,
// 单独拿出来只是为了防止两个INT_MAX相加导致溢出
continue;
}
D[i][j] = min(D[i][k] + D[k][j], D[i][j]);
}
}
}
// 选择出能到达其它城市最少的城市ret
int ret;
int minNum = INT_MAX;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int cnt = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (i != j && D[i][j] <= distanceThreshold) {
cnt++;
}
}
if (cnt <= minNum) {
minNum = cnt;
ret = i;
}
}
return ret;
}
};答疑:为什么遍历插入点k是放在第一层循环?
这个源自 $Floyd$ 的核心思想–动态规划,代码中的二维状态转移方程 $D[i][j] = min(D[i,k]+D[k,j],D[i,j]);$ ,其实是从三维简化得到的。
我们不妨从最初的三维说起:
首先定义状态数组(也就是距离矩阵)$D[n][n][n]$,其中 $D[k][i][j]$ 表示顶点 $i$, 顶点 $j$ 通过前 $k$ 个顶点得到的最短距离。
$D[k][i][j]$ 是从 $D[k-1][i][j]$ 和 $D[k-1][i][k] + D[k-1][k][j]$ 两者中值较小的一个转移得到的,也就是说要在前 $k-1$ 个顶点已经插入,更新距离矩阵状态之后,第 $k$ 个顶点才能作为插入顶点。
归纳得到状态转移方程:$D[k][i][j] = min(D[k-1][i][j], D[k-1][i][k] + D[k-1][k][j])$。
其中 $k$ 的作用是标志到达了第几个插入点,也就是状态数组到达了哪个状态,不用刻意记录,于是减去第一维就变成了二维。
明白了 $Floyd$ 的三维 $dp$ 思想,根据状态转移方程在编码时就很自然的会将 $k$ 放在第一层循环,而将 $k$ 放在最后一层则是错误的编码。
补充一个 $dijkstra$ 的代码
class Solution {
public:
void dijkstra(int graph[101][101], int dist[101], int v, int n) {
// 初始化 dist
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
dist[i] = graph[v][i];
}
// 标记当前点是否已经加入集合
bool m[101];
memset(m, 0, sizeof(m));
m[v] = true;
// 每次都找离集合最近的一个点,一共要找 n-1 次
for (int k = 0; k < n-1; k ++) {
int minv = INT_MAX;
int next = v;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++) {
if (!m[i] && dist[i] < minv) {
minv = dist[i];
next = i;
}
}
m[next] = true;
// 每次找到最近的点,并用它更新其它点到集合的距离,
// 也就是更新dist数组
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++) {
if (m[i] || graph[next][i] == INT_MAX) {
continue;
}
dist[i] = min(dist[i], dist[next] + graph[next][i]);
}
}
}
int findTheCity(int n, vector<vector<int>>& edges, int distanceThreshold) {
// 定义并初始化邻接矩阵 graph
int graph[101][101];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j ++) {
graph[i][j] = INT_MAX;
}
}
for (auto& edge : edges) {
graph[edge[0]][edge[1]] = edge[2];
graph[edge[1]][edge[0]] = edge[2];
}
int mincnt = INT_MAX;
int ret = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++) {
// 使用单源最短路径dijkstra算法生成:
// 以i为源点到其它各点的最短路径数组dist
int dist[101];
dijkstra(graph, dist, i, n);
int cnt = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < n; j ++) {
if (dist[j] <= distanceThreshold) {
cnt ++;
}
}
if (cnt <= mincnt) {
mincnt = cnt;
ret = i;
}
}
return ret;
}
};最后
感谢您的观看!欢迎大家留言,一起讨论交流。
统计信息
| 通过次数 | 提交次数 | AC比率 |
|---|---|---|
| 6073 | 12226 | 49.7% |
提交历史
| 提交时间 | 提交结果 | 执行时间 | 内存消耗 | 语言 |
|---|




