原文链接: https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/check-if-there-is-a-valid-path-in-a-grid
英文原文
grid. Each cell of the grid represents a street. The street of grid[i][j] can be:
- 1 which means a street connecting the left cell and the right cell.
- 2 which means a street connecting the upper cell and the lower cell.
- 3 which means a street connecting the left cell and the lower cell.
- 4 which means a street connecting the right cell and the lower cell.
- 5 which means a street connecting the left cell and the upper cell.
- 6 which means a street connecting the right cell and the upper cell.
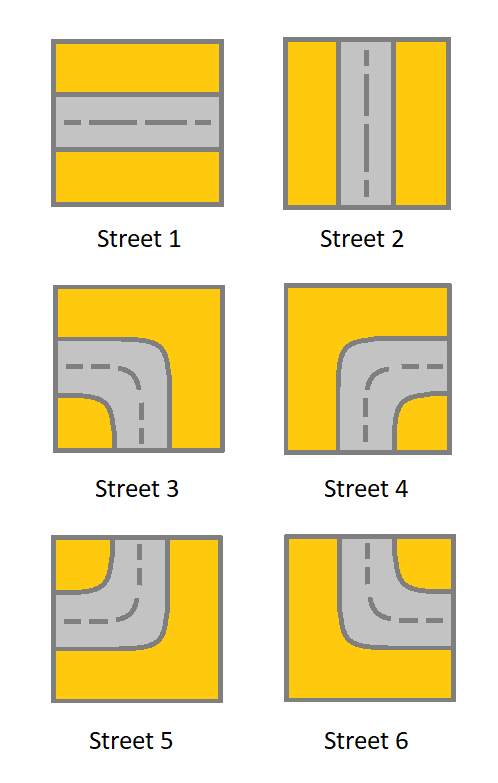
You will initially start at the street of the upper-left cell (0,0). A valid path in the grid is a path which starts from the upper left cell (0,0) and ends at the bottom-right cell (m - 1, n - 1). The path should only follow the streets.
Notice that you are not allowed to change any street.
Return true if there is a valid path in the grid or false otherwise.
Example 1:
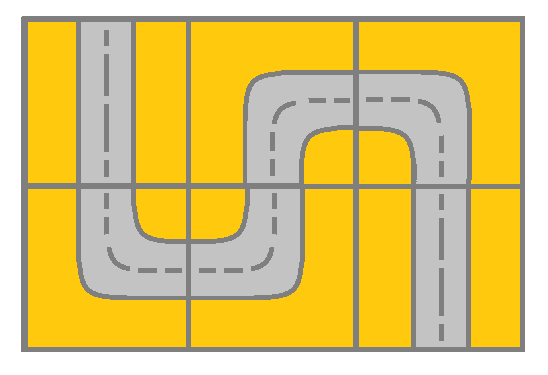
Input: grid = [[2,4,3],[6,5,2]] Output: true Explanation: As shown you can start at cell (0, 0) and visit all the cells of the grid to reach (m - 1, n - 1).
Example 2:
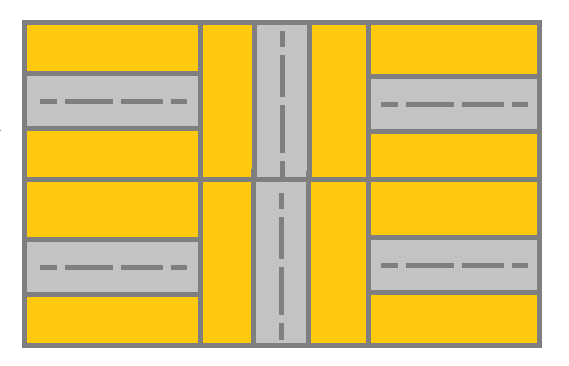
Input: grid = [[1,2,1],[1,2,1]] Output: false Explanation: As shown you the street at cell (0, 0) is not connected with any street of any other cell and you will get stuck at cell (0, 0)
Example 3:
Input: grid = [[1,1,2]] Output: false Explanation: You will get stuck at cell (0, 1) and you cannot reach cell (0, 2).
Example 4:
Input: grid = [[1,1,1,1,1,1,3]] Output: true
Example 5:
Input: grid = [[2],[2],[2],[2],[2],[2],[6]] Output: true
Constraints:
m == grid.lengthn == grid[i].length1 <= m, n <= 3001 <= grid[i][j] <= 6
中文题目
给你一个 m x n 的网格 grid。网格里的每个单元都代表一条街道。grid[i][j] 的街道可以是:
- 1 表示连接左单元格和右单元格的街道。
- 2 表示连接上单元格和下单元格的街道。
- 3 表示连接左单元格和下单元格的街道。
- 4 表示连接右单元格和下单元格的街道。
- 5 表示连接左单元格和上单元格的街道。
- 6 表示连接右单元格和上单元格的街道。
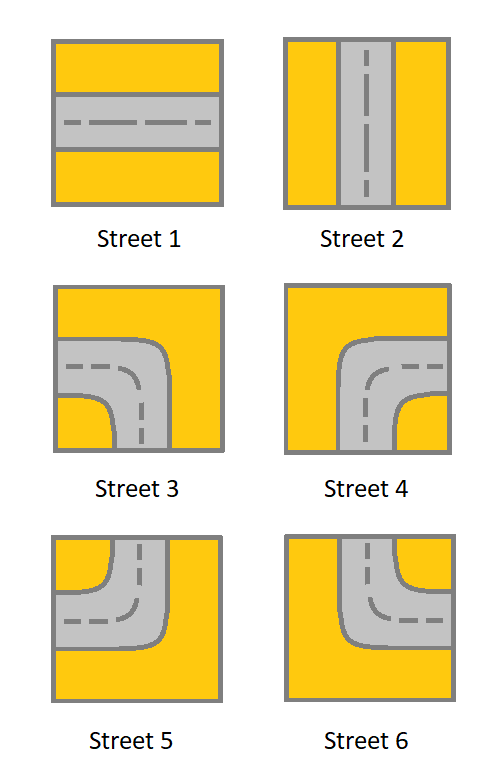
你最开始从左上角的单元格 (0,0) 开始出发,网格中的「有效路径」是指从左上方的单元格 (0,0) 开始、一直到右下方的 (m-1,n-1) 结束的路径。该路径必须只沿着街道走。
注意:你 不能 变更街道。
如果网格中存在有效的路径,则返回 true,否则返回 false 。
示例 1:
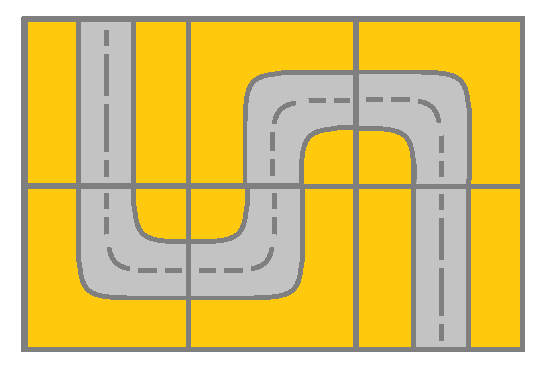
输入:grid = [[2,4,3],[6,5,2]] 输出:true 解释:如图所示,你可以从 (0, 0) 开始,访问网格中的所有单元格并到达 (m - 1, n - 1) 。
示例 2:
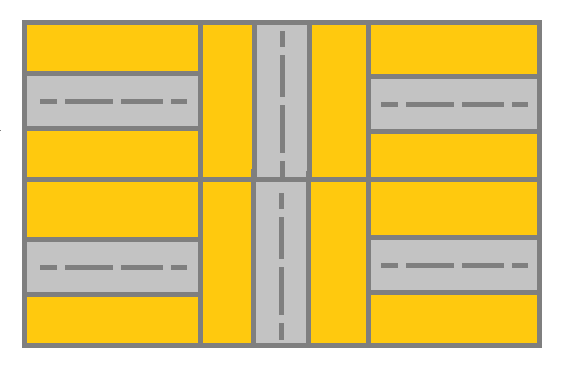
输入:grid = [[1,2,1],[1,2,1]] 输出:false 解释:如图所示,单元格 (0, 0) 上的街道没有与任何其他单元格上的街道相连,你只会停在 (0, 0) 处。
示例 3:
输入:grid = [[1,1,2]] 输出:false 解释:你会停在 (0, 1),而且无法到达 (0, 2) 。
示例 4:
输入:grid = [[1,1,1,1,1,1,3]] 输出:true
示例 5:
输入:grid = [[2],[2],[2],[2],[2],[2],[6]] 输出:true
提示:
m == grid.lengthn == grid[i].length1 <= m, n <= 3001 <= grid[i][j] <= 6
通过代码
高赞题解
解题思路:
通过构建pipe数组,将每个拼图转化为四个方向上的移动限制图。
例:
pipe[3][2]=3,代表3号拼图可以由向上的方向进入其中,并转向左方向继续前进。
pipe[5][3]=-1,代表5号拼图不可以由向左的方向进入其中。
其中0代表向下、1代表向右、2代表向上、3代表向左、-1代表不可走

这之后问题就变成了一个简单的DFS了
class Solution {
int m,n,dx[4]={1,0,-1,0},dy[4]={0,1,0,-1};//0下、1右、2上、3左
int pipe[7][4]={{-1,-1,-1,-1},{-1,1,-1,3},{0,-1,2,-1},{-1,0,3,-1},{-1,-1,1,0},{3,2,-1,-1},{1,-1,-1,2}};
//记录各个拼图块路径的方向,0、1、2、3代表方向,-1代表不可走。
bool dfs(int x,int y,int dir,vector<vector<int>>& grid){//(x,y,当前方向,地图)
if(x==m-1&&y==n-1) return 1;//到达终点
int xx=x+dx[dir];
int yy=y+dy[dir];//得到下一个准备走的坐标
if(xx<0||yy<0||xx>=m||yy>=n)return 0;//越界
int nxt=grid[xx][yy];//得到下一块拼图的编号
if(pipe[nxt][dir]!=-1)return dfs(xx,yy,pipe[nxt][dir],grid);//如果当前方向可走,则方向改变,继续走。
return 0;//无法走,返回0
}
public:
bool hasValidPath(vector<vector<int>>& grid) {
m=grid.size();
n=grid[0].size();
int sta=grid[0][0];//起点的拼图编号
for(int i=0;i<4;++i)//朝着四个方向都试一下
if(pipe[sta][i]!=-1)//当前方向可以走
if(dfs(0,0,pipe[sta][i],grid))//沿着当前方向搜索
return 1;//拼图都有两个方向可以走,只要沿着一个初始方向走通就可以。
return 0;
}
};3.23 updata
之前是加了vis数组判断是否访问过的,之后感觉没啥用,就删掉了,发现也能过题目,便没再多想。
这里很感谢@study11 @xm9304同学的质疑
同时很感谢@mapleking同学的指正。
之后,再@LeetCode加一下测试用例。
class Solution {
int m,n,dx[4]={1,0,-1,0},dy[4]={0,1,0,-1};//0下、1右、2上、3左
int pipe[7][4]={
{-1,-1,-1,-1},
{-1,1,-1,3},
{0,-1,2,-1},
{-1,0,3,-1},
{-1,-1,1,0},
{3,2,-1,-1},
{1,-1,-1,2}
};
//记录各个拼图块路径的方向,0、1、2、3代表方向,-1代表不可走。
bool vis[302][302];
bool dfs(int x,int y,int dir,vector<vector<int>>& grid){//(x,y,当前方向,地图)
vis[x][y]=1;
if(x==m-1&&y==n-1) return 1;//到达终点
int xx=x+dx[dir];
int yy=y+dy[dir];//得到下一个准备走的坐标
if(xx<0||yy<0||xx>=m||yy>=n)return 0;//越界
int nxt=grid[xx][yy];//得到下一块拼图的编号
if(pipe[nxt][dir]!=-1&&!vis[xx][yy])
return dfs(xx,yy,pipe[nxt][dir],grid);//如果当前方向可走,则方向改变,继续走。
return 0;//无法走,返回0
}
public:
bool hasValidPath(vector<vector<int>>& grid) {
m=grid.size();
n=grid[0].size();
memset(vis,0,sizeof(vis));
int sta=grid[0][0];//起点的拼图编号
for(int i=0;i<4;++i)//朝着四个方向都试一下
if(pipe[sta][i]!=-1)//当前方向可以走
if(dfs(0,0,pipe[sta][i],grid))//沿着当前方向搜索
return 1;//拼图都有两个方向可以走,只要沿着一个初始方向走通就可以。
return 0;
}
};统计信息
| 通过次数 | 提交次数 | AC比率 |
|---|---|---|
| 6860 | 17077 | 40.2% |
提交历史
| 提交时间 | 提交结果 | 执行时间 | 内存消耗 | 语言 |
|---|




