英文原文
Given the head of a singly linked list, sort the list using insertion sort, and return the sorted list's head.
The steps of the insertion sort algorithm:
- Insertion sort iterates, consuming one input element each repetition and growing a sorted output list.
- At each iteration, insertion sort removes one element from the input data, finds the location it belongs within the sorted list and inserts it there.
- It repeats until no input elements remain.
The following is a graphical example of the insertion sort algorithm. The partially sorted list (black) initially contains only the first element in the list. One element (red) is removed from the input data and inserted in-place into the sorted list with each iteration.

Example 1:
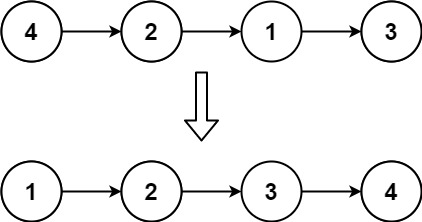
Input: head = [4,2,1,3] Output: [1,2,3,4]
Example 2:
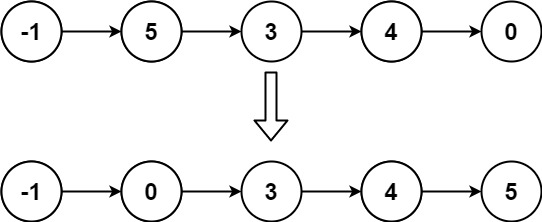
Input: head = [-1,5,3,4,0] Output: [-1,0,3,4,5]
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the list is in the range
[1, 5000]. -5000 <= Node.val <= 5000
中文题目
对链表进行插入排序。

插入排序的动画演示如上。从第一个元素开始,该链表可以被认为已经部分排序(用黑色表示)。
每次迭代时,从输入数据中移除一个元素(用红色表示),并原地将其插入到已排好序的链表中。
插入排序算法:
- 插入排序是迭代的,每次只移动一个元素,直到所有元素可以形成一个有序的输出列表。
- 每次迭代中,插入排序只从输入数据中移除一个待排序的元素,找到它在序列中适当的位置,并将其插入。
- 重复直到所有输入数据插入完为止。
示例 1:
输入: 4->2->1->3 输出: 1->2->3->4
示例 2:
输入: -1->5->3->4->0 输出: -1->0->3->4->5
通过代码
高赞题解
方法一:从前往后找插入点
插入排序的基本思想是,维护一个有序序列,初始时有序序列只有一个元素,每次将一个新的元素插入到有序序列中,将有序序列的长度增加 $1$,直到全部元素都加入到有序序列中。
如果是数组的插入排序,则数组的前面部分是有序序列,每次找到有序序列后面的第一个元素(待插入元素)的插入位置,将有序序列中的插入位置后面的元素都往后移动一位,然后将待插入元素置于插入位置。
对于链表而言,插入元素时只要更新相邻节点的指针即可,不需要像数组一样将插入位置后面的元素往后移动,因此插入操作的时间复杂度是 $O(1)$,但是找到插入位置需要遍历链表中的节点,时间复杂度是 $O(n)$,因此链表插入排序的总时间复杂度仍然是 $O(n^2)$,其中 $n$ 是链表的长度。
对于单向链表而言,只有指向后一个节点的指针,因此需要从链表的头节点开始往后遍历链表中的节点,寻找插入位置。
对链表进行插入排序的具体过程如下。
首先判断给定的链表是否为空,若为空,则不需要进行排序,直接返回。
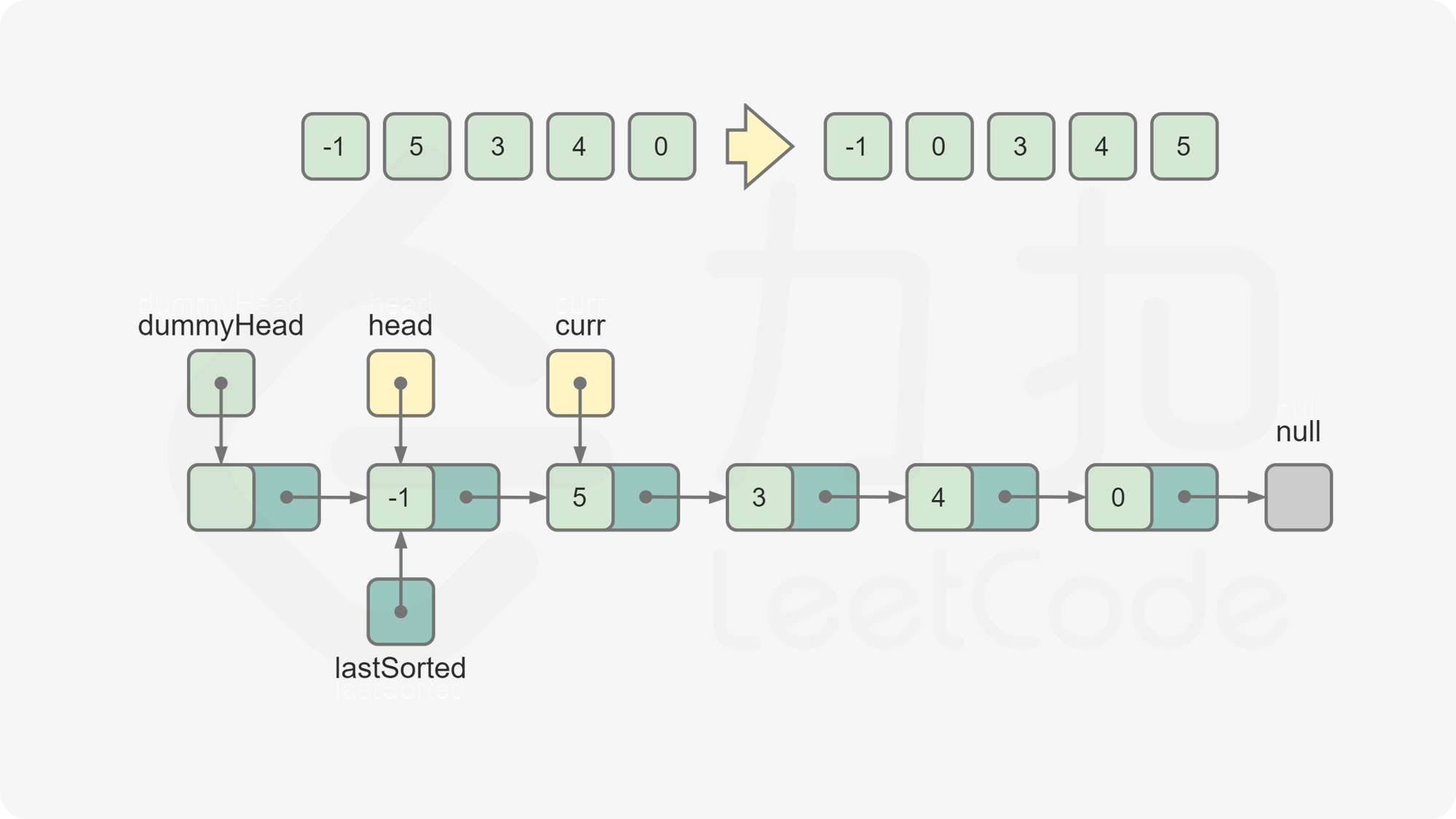
创建哑节点
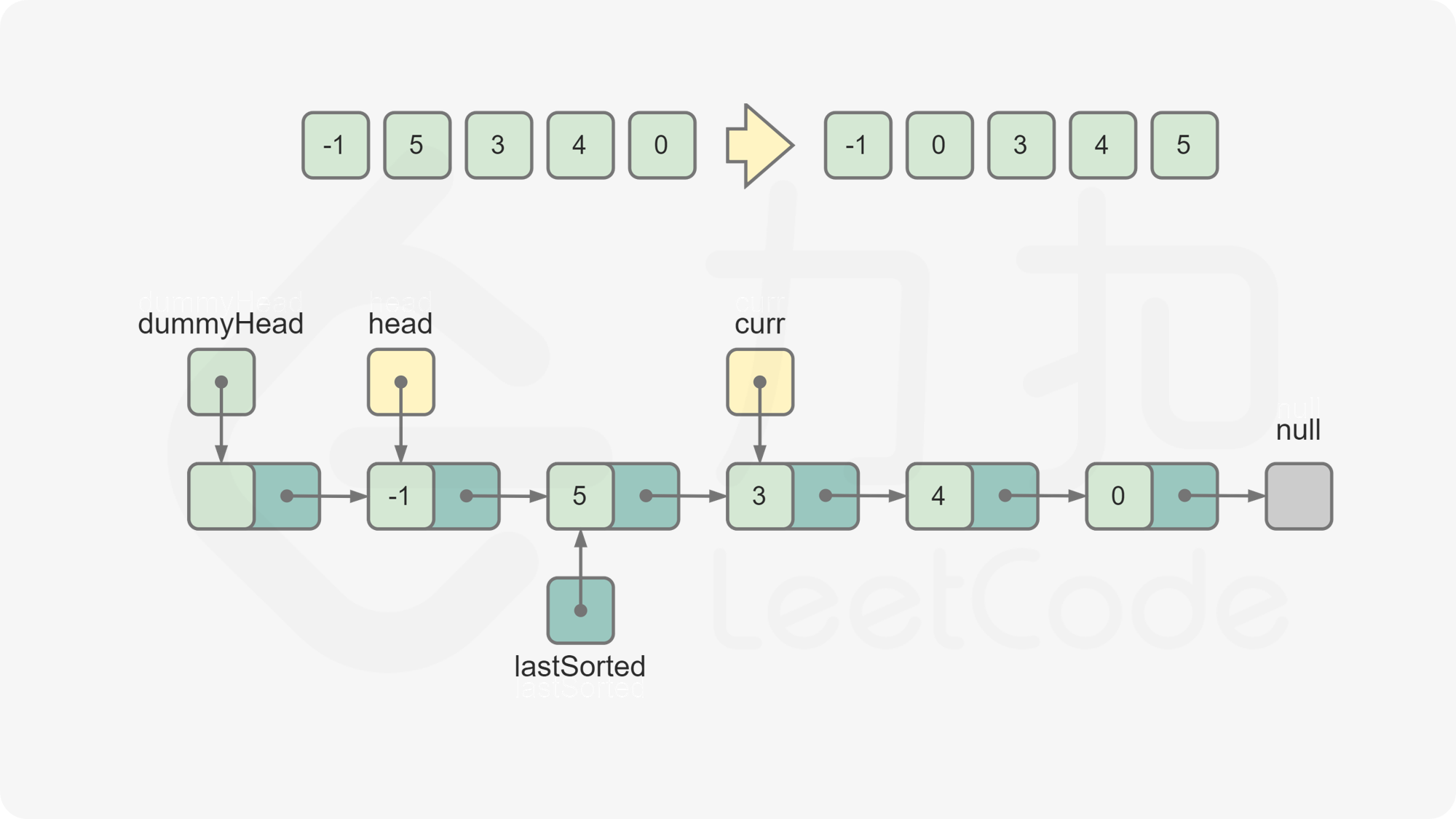
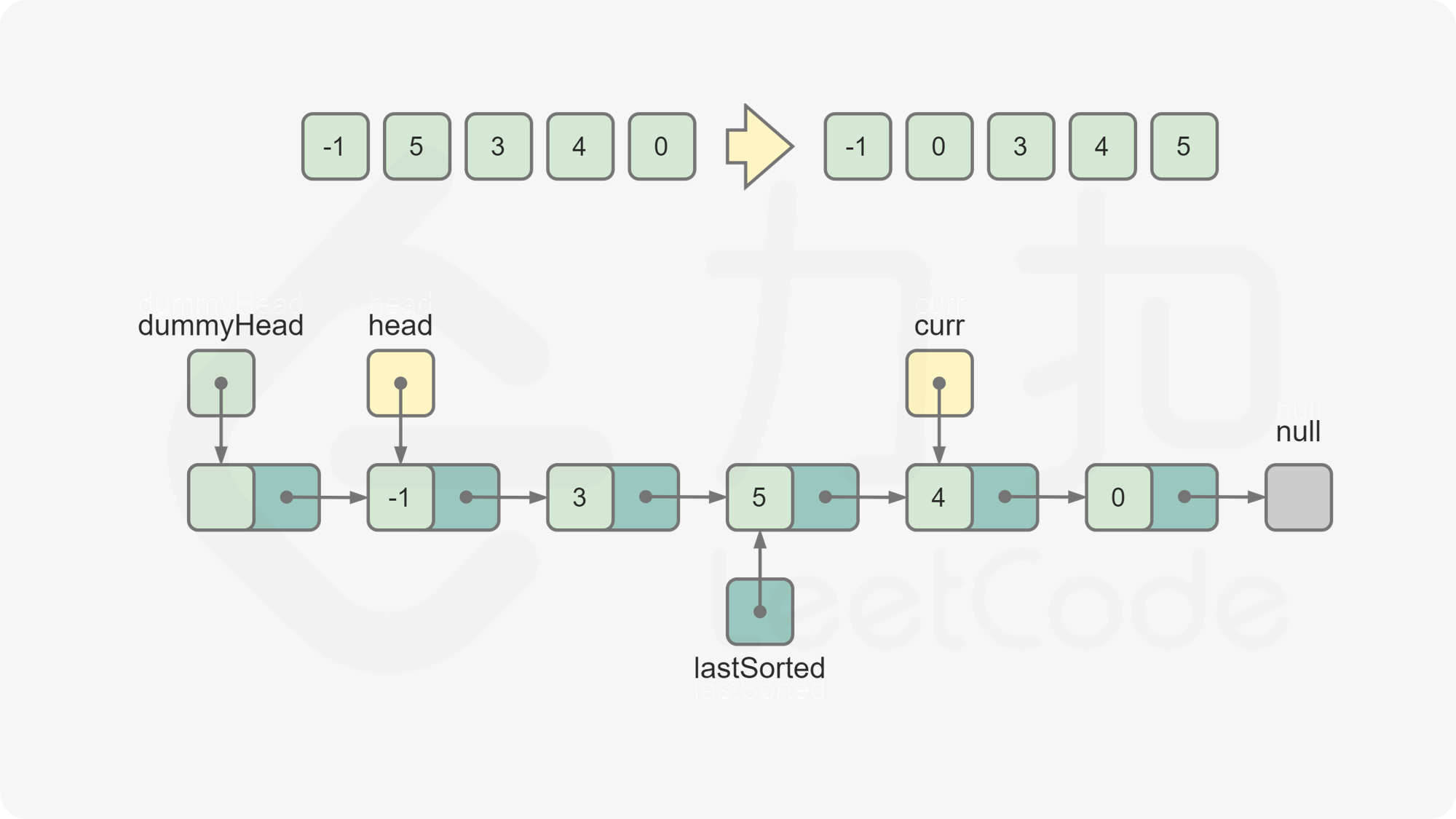
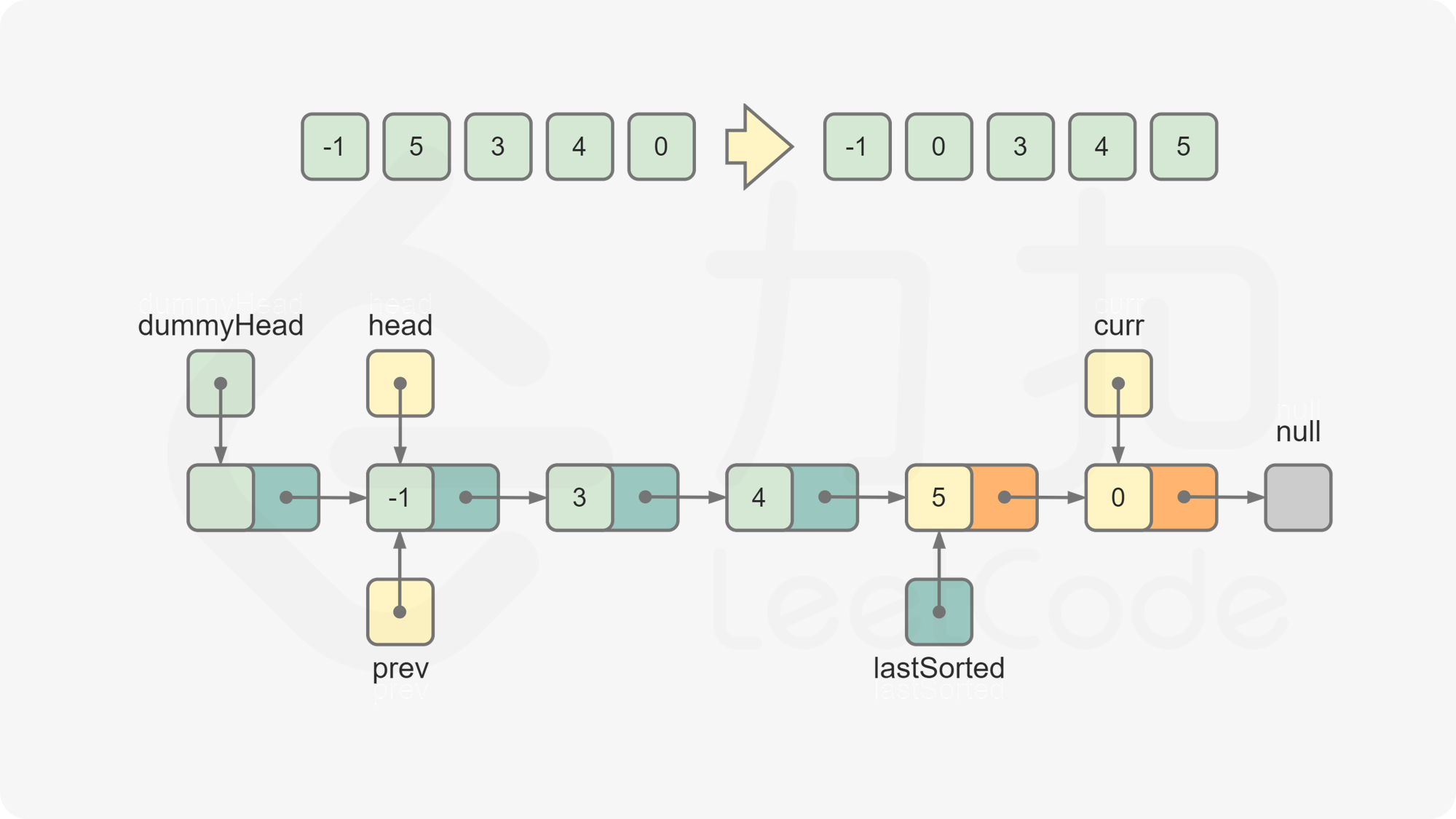
dummyHead,令dummyHead.next = head。引入哑节点是为了便于在head节点之前插入节点。维护
lastSorted为链表的已排序部分的最后一个节点,初始时lastSorted = head。维护
curr为待插入的元素,初始时curr = head.next。比较
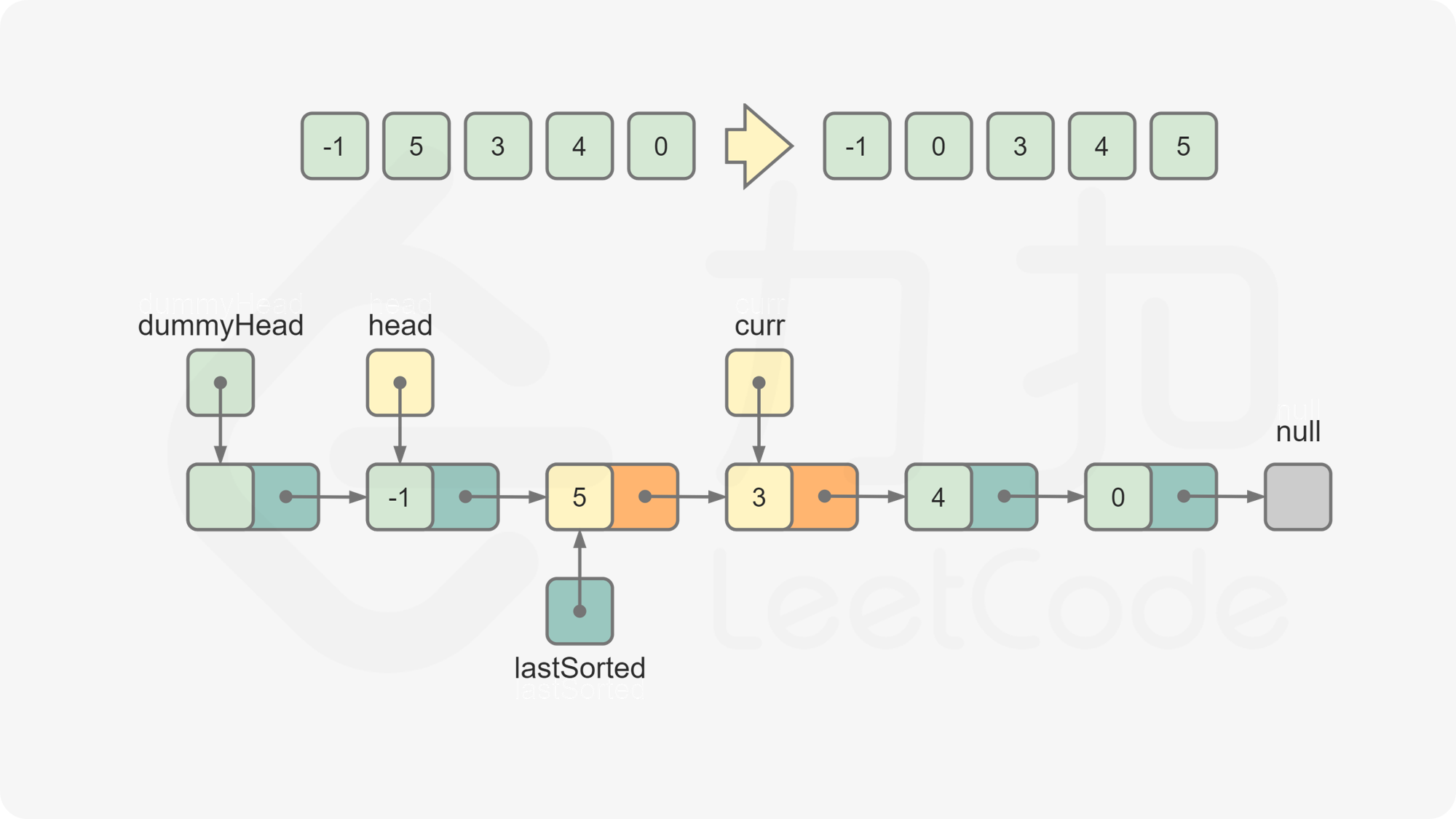
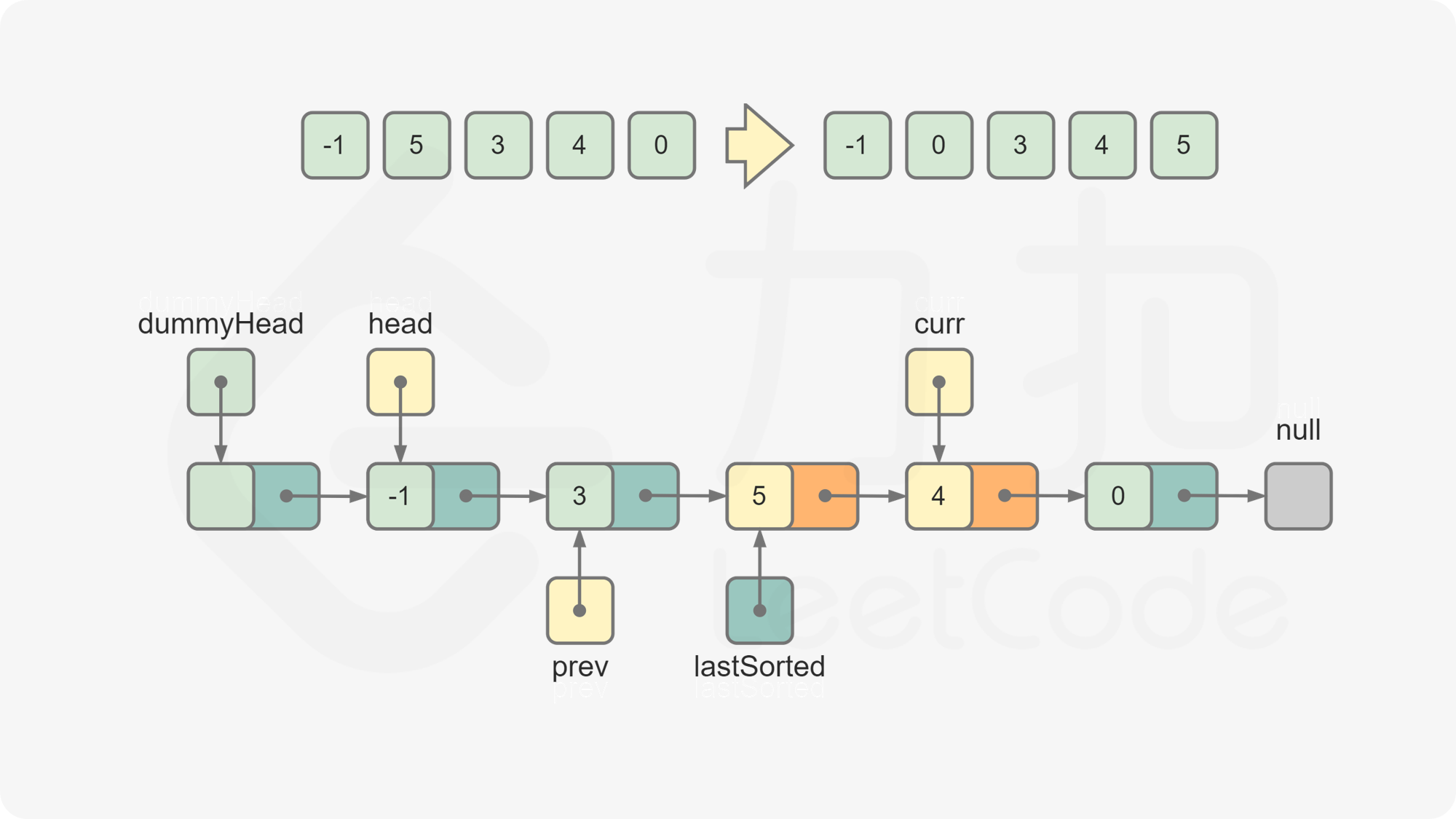
lastSorted和curr的节点值。若
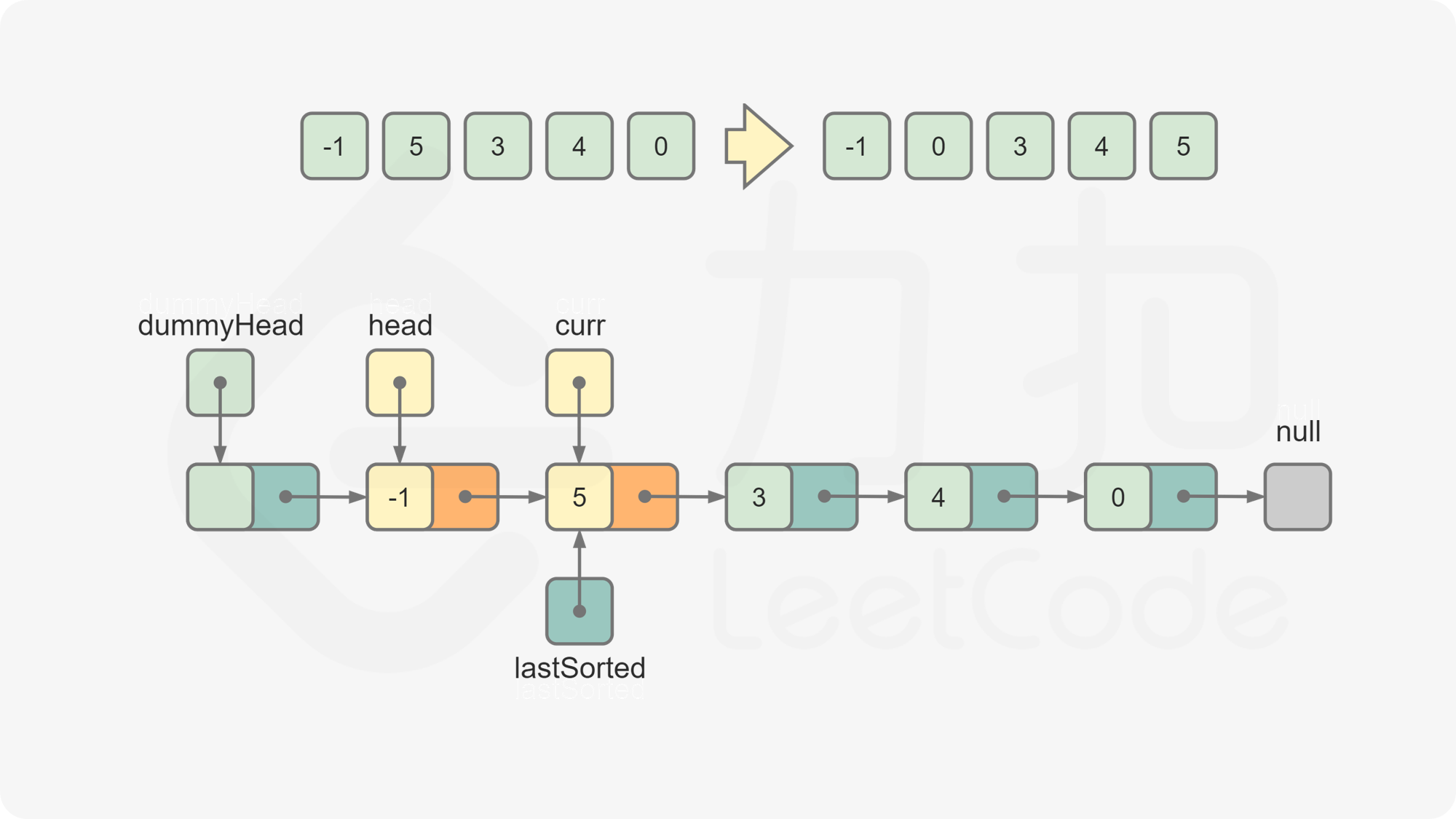
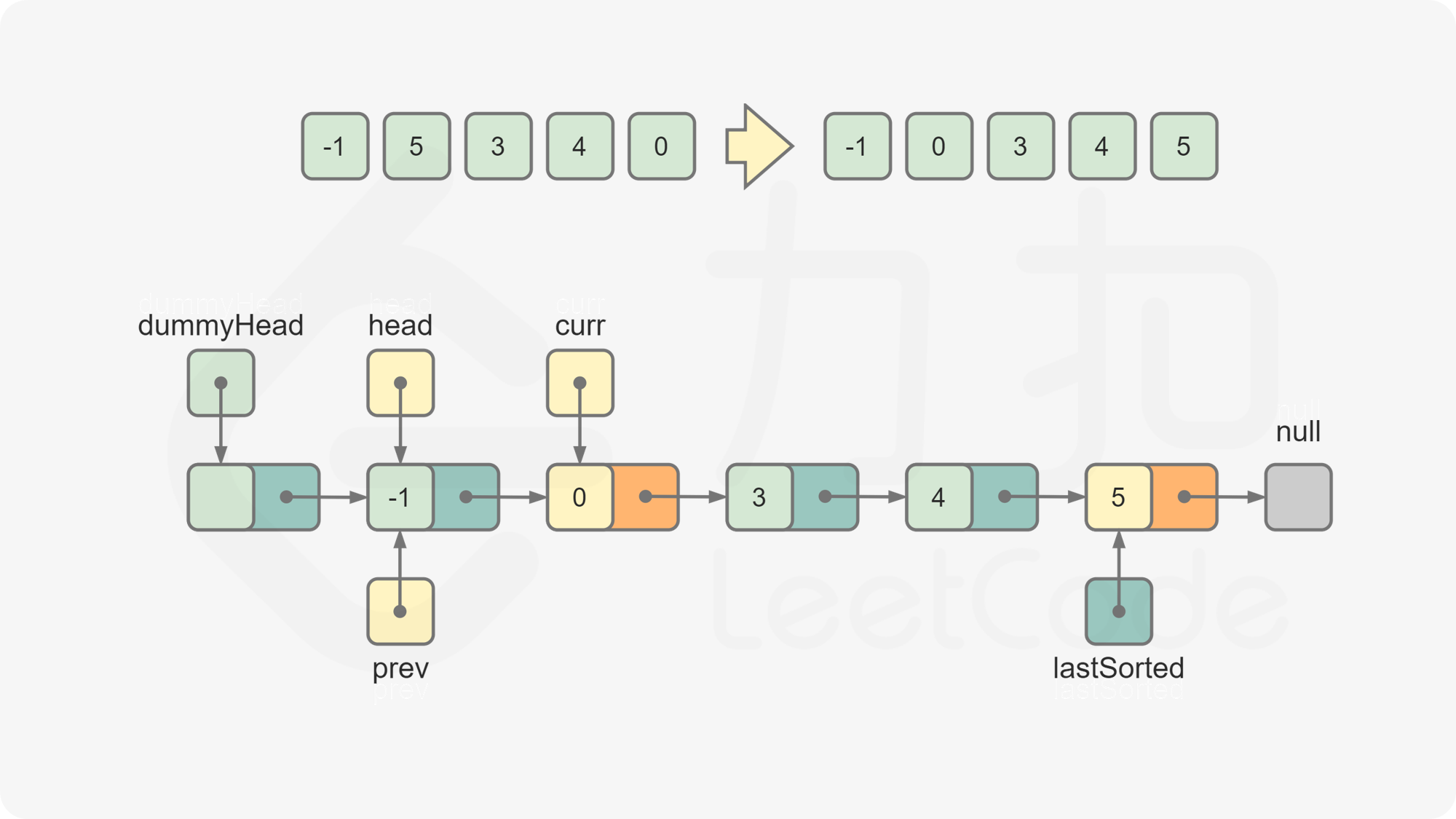
lastSorted.val <= curr.val,说明curr应该位于lastSorted之后,将lastSorted后移一位,curr变成新的lastSorted。否则,从链表的头节点开始往后遍历链表中的节点,寻找插入
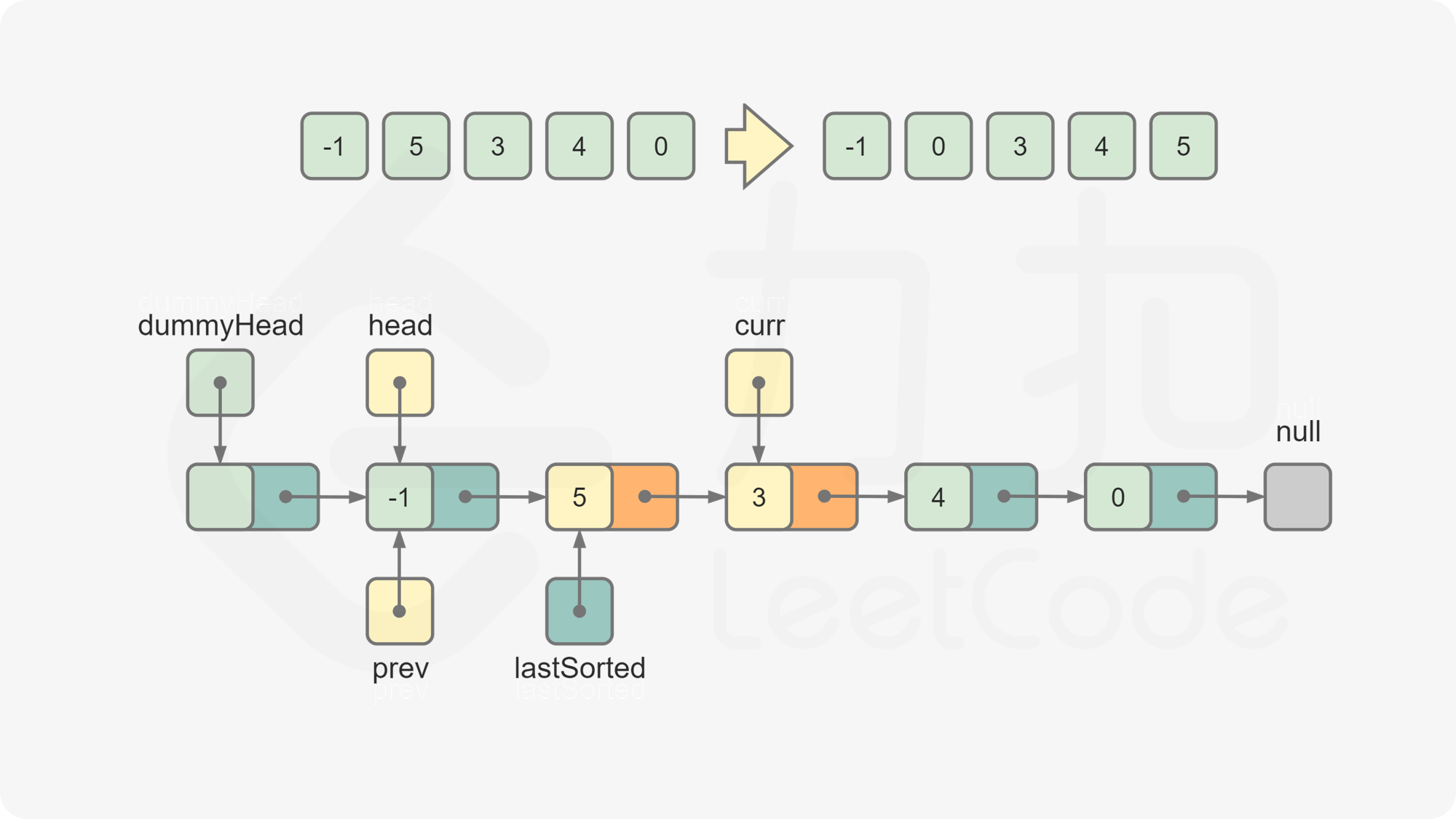
curr的位置。令prev为插入curr的位置的前一个节点,进行如下操作,完成对curr的插入:
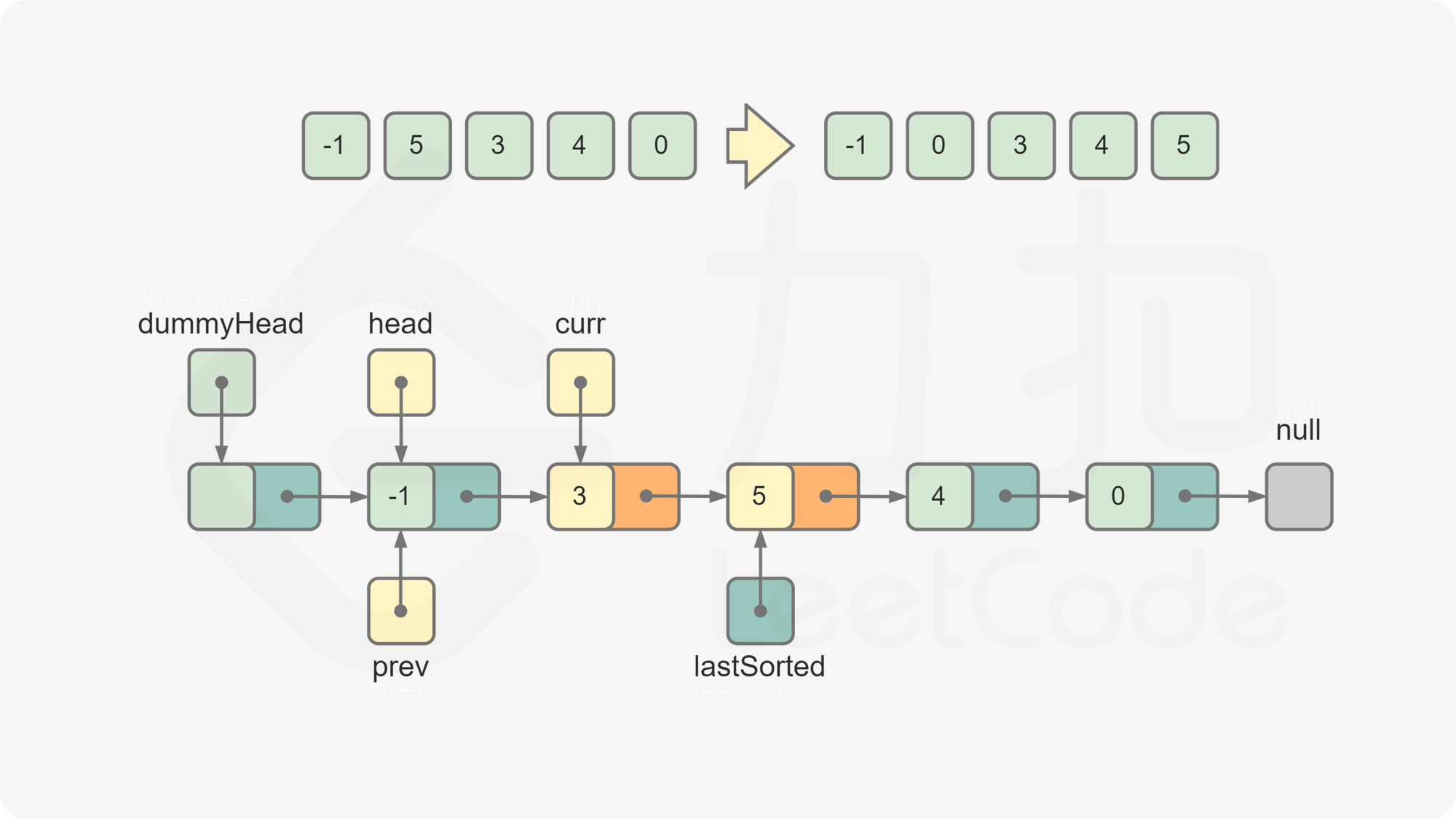
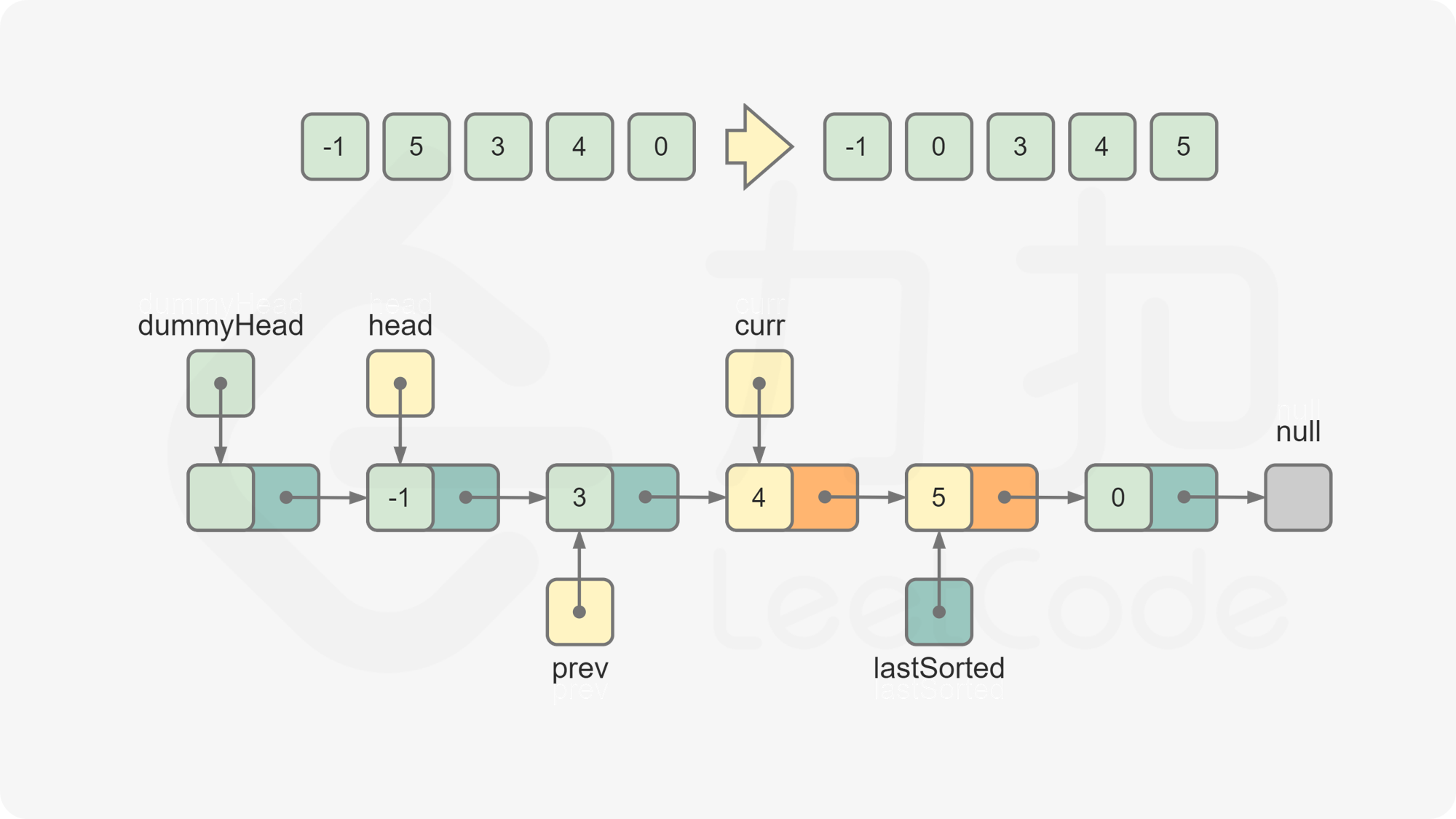
lastSorted.next = curr.next curr.next = prev.next prev.next = curr令
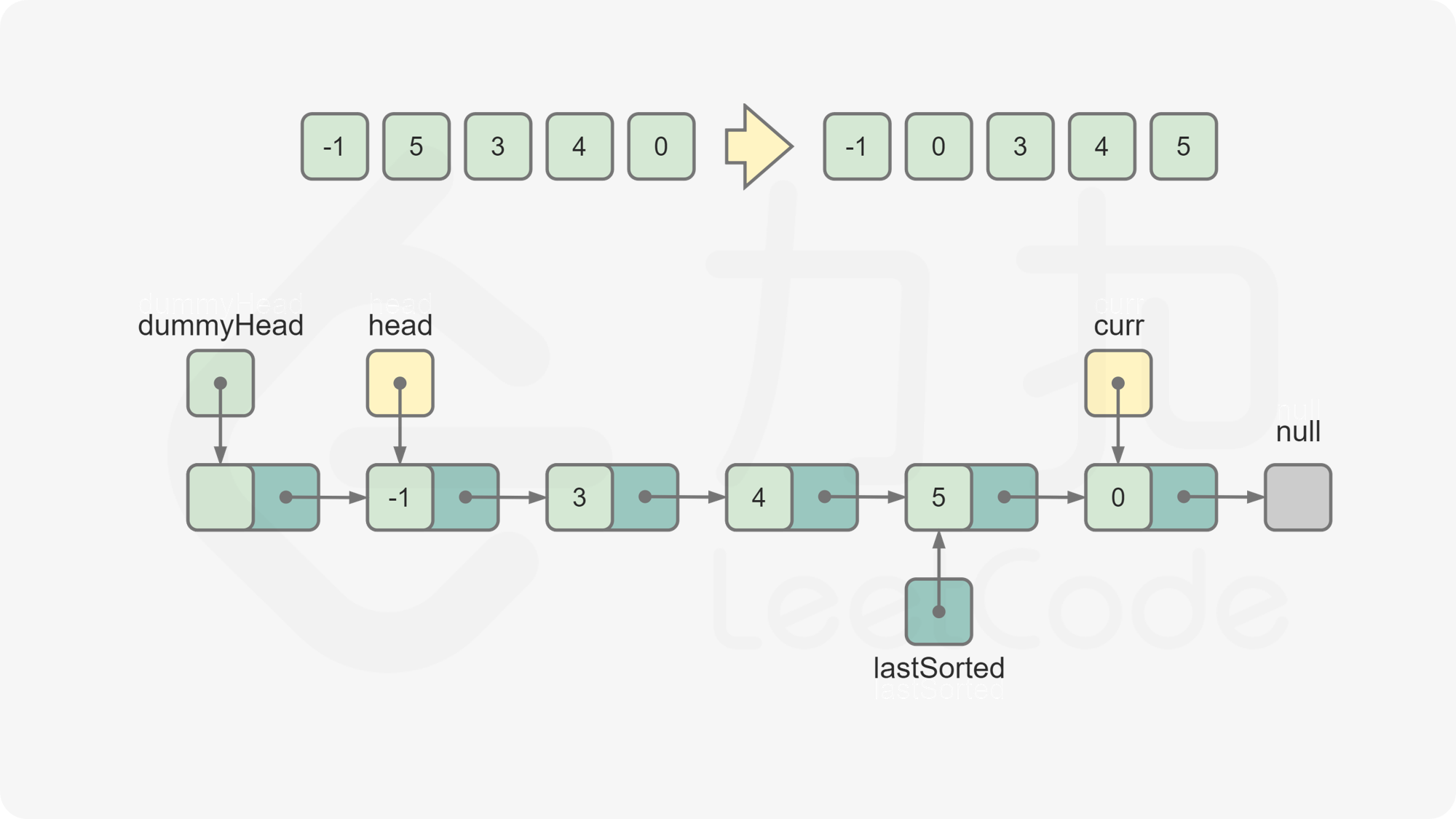
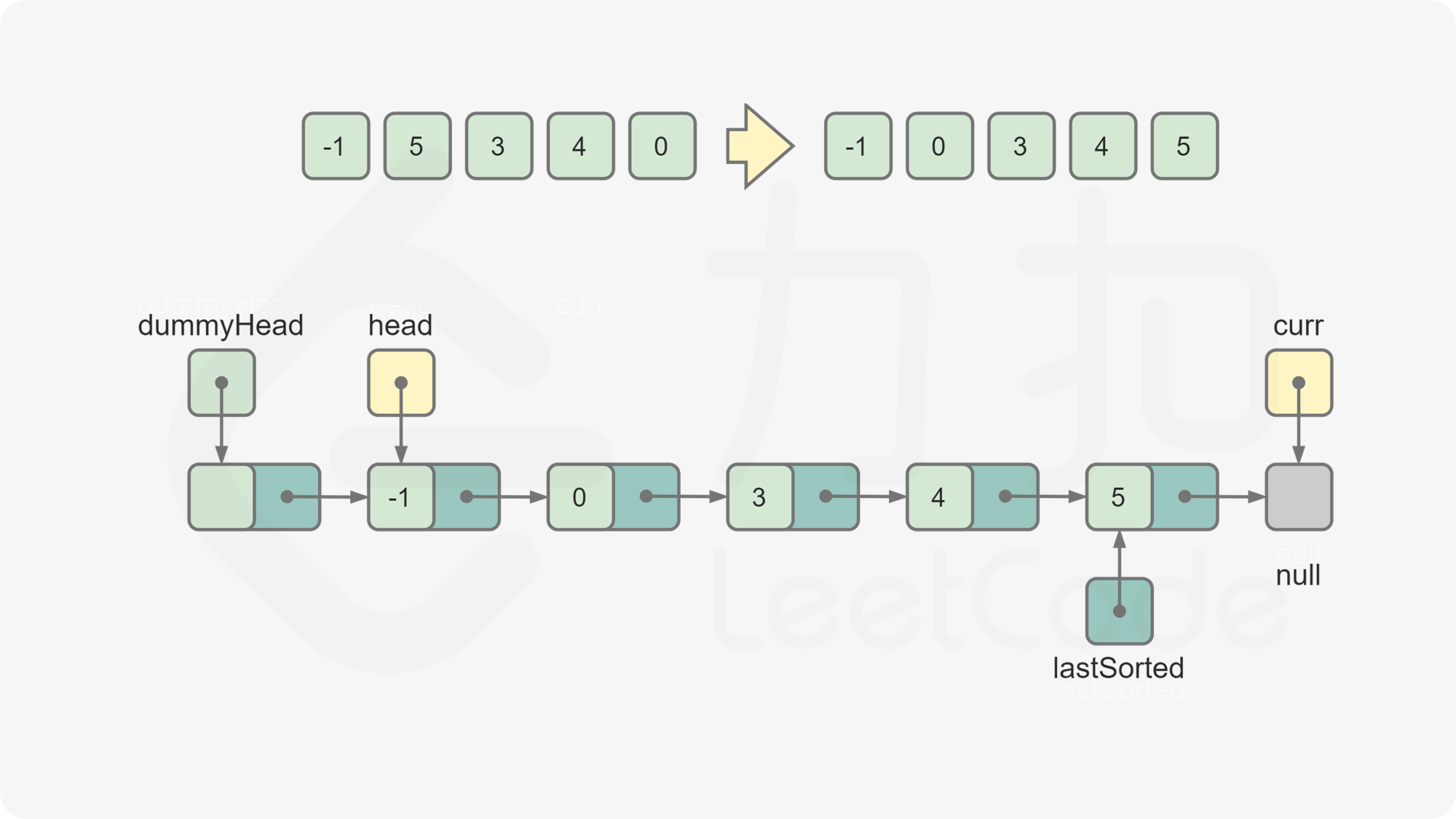
curr = lastSorted.next,此时curr为下一个待插入的元素。重复第 5 步和第 6 步,直到
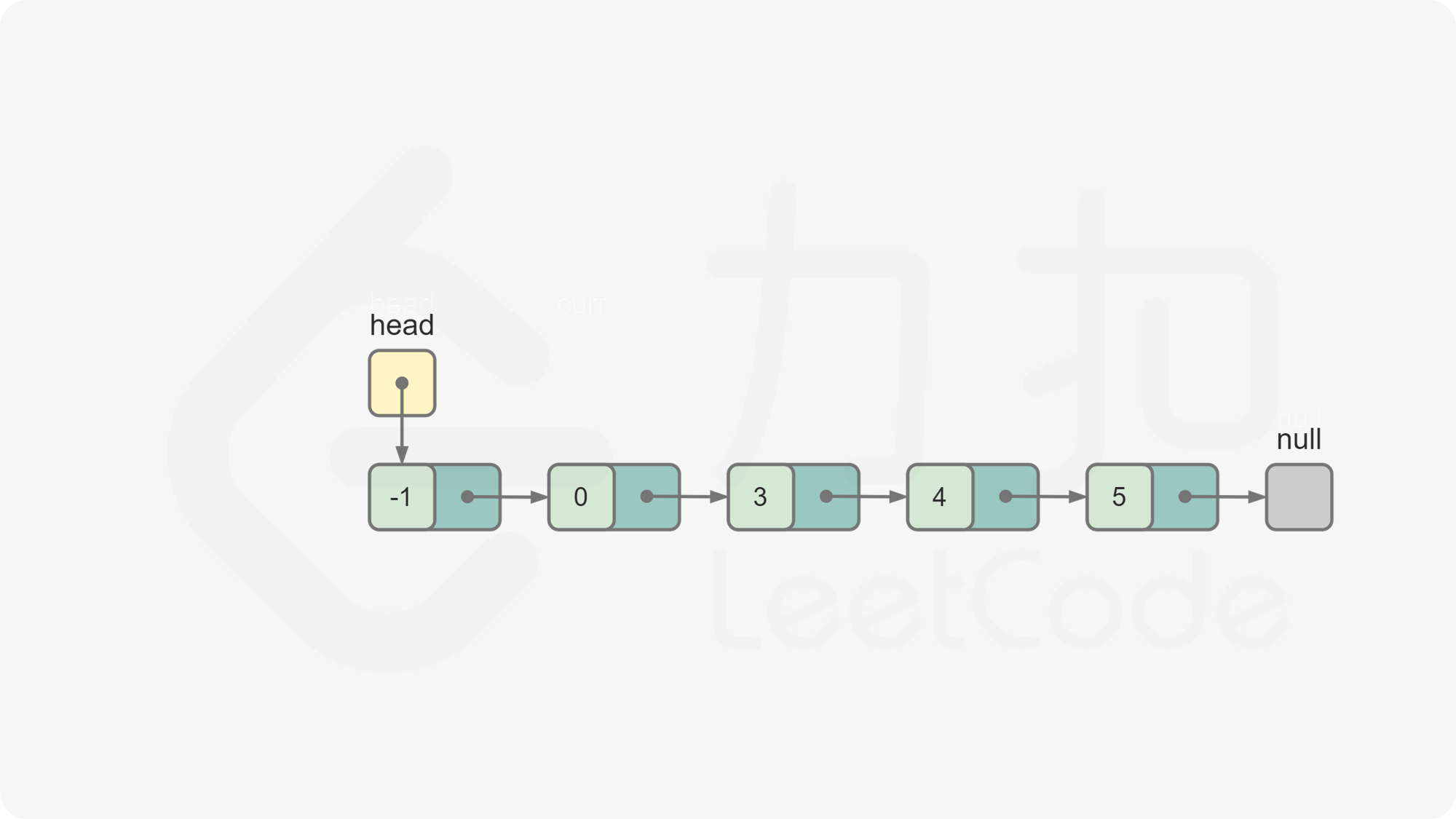
curr变成空,排序结束。返回
dummyHead.next,为排序后的链表的头节点。
< ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, >
>
[sol1-Java]class Solution { public ListNode insertionSortList(ListNode head) { if (head == null) { return head; } ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode(0); dummyHead.next = head; ListNode lastSorted = head, curr = head.next; while (curr != null) { if (lastSorted.val <= curr.val) { lastSorted = lastSorted.next; } else { ListNode prev = dummyHead; while (prev.next.val <= curr.val) { prev = prev.next; } lastSorted.next = curr.next; curr.next = prev.next; prev.next = curr; } curr = lastSorted.next; } return dummyHead.next; } }
[sol1-JavaScript]var insertionSortList = function(head) { if (head === null) { return head; } const dummyHead = new ListNode(0); dummyHead.next = head; let lastSorted = head, curr = head.next; while (curr !== null) { if (lastSorted.val <= curr.val) { lastSorted = lastSorted.next; } else { let prev = dummyHead; while (prev.next.val <= curr.val) { prev = prev.next; } lastSorted.next = curr.next; curr.next = prev.next; prev.next = curr; } curr = lastSorted.next; } return dummyHead.next; };
[sol1-C++]class Solution { public: ListNode* insertionSortList(ListNode* head) { if (head == nullptr) { return head; } ListNode* dummyHead = new ListNode(0); dummyHead->next = head; ListNode* lastSorted = head; ListNode* curr = head->next; while (curr != nullptr) { if (lastSorted->val <= curr->val) { lastSorted = lastSorted->next; } else { ListNode *prev = dummyHead; while (prev->next->val <= curr->val) { prev = prev->next; } lastSorted->next = curr->next; curr->next = prev->next; prev->next = curr; } curr = lastSorted->next; } return dummyHead->next; } };
[sol1-Python3]class Solution: def insertionSortList(self, head: ListNode) -> ListNode: if not head: return head dummyHead = ListNode(0) dummyHead.next = head lastSorted = head curr = head.next while curr: if lastSorted.val <= curr.val: lastSorted = lastSorted.next else: prev = dummyHead while prev.next.val <= curr.val: prev = prev.next lastSorted.next = curr.next curr.next = prev.next prev.next = curr curr = lastSorted.next return dummyHead.next
[sol1-Golang]func insertionSortList(head *ListNode) *ListNode { if head == nil { return nil } dummyHead := &ListNode{Next: head} lastSorted, curr := head, head.Next for curr != nil { if lastSorted.Val <= curr.Val { lastSorted = lastSorted.Next } else { prev := dummyHead for prev.Next.Val <= curr.Val { prev = prev.Next } lastSorted.Next = curr.Next curr.Next = prev.Next prev.Next = curr } curr = lastSorted.Next } return dummyHead.Next }
[sol1-C]struct ListNode *insertionSortList(struct ListNode *head) { if (head == NULL) { return head; } struct ListNode *dummyHead = malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode)); dummyHead->val = 0; dummyHead->next = head; struct ListNode *lastSorted = head; struct ListNode *curr = head->next; while (curr != NULL) { if (lastSorted->val <= curr->val) { lastSorted = lastSorted->next; } else { struct ListNode *prev = dummyHead; while (prev->next->val <= curr->val) { prev = prev->next; } lastSorted->next = curr->next; curr->next = prev->next; prev->next = curr; } curr = lastSorted->next; } return dummyHead->next; }
复杂度分析
时间复杂度:$O(n^2)$,其中 $n$ 是链表的长度。
空间复杂度:$O(1)$。
统计信息
| 通过次数 | 提交次数 | AC比率 |
|---|---|---|
| 104983 | 153675 | 68.3% |
提交历史
| 提交时间 | 提交结果 | 执行时间 | 内存消耗 | 语言 |
|---|
相似题目
| 题目 | 难度 |
|---|---|
| 排序链表 | 中等 |
| 循环有序列表的插入 | 中等 |




