原文链接: https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/number-of-nodes-in-the-sub-tree-with-the-same-label
英文原文
Given a tree (i.e. a connected, undirected graph that has no cycles) consisting of n nodes numbered from 0 to n - 1 and exactly n - 1 edges. The root of the tree is the node 0, and each node of the tree has a label which is a lower-case character given in the string labels (i.e. The node with the number i has the label labels[i]).
The edges array is given on the form edges[i] = [ai, bi], which means there is an edge between nodes ai and bi in the tree.
Return an array of size n where ans[i] is the number of nodes in the subtree of the ith node which have the same label as node i.
A subtree of a tree T is the tree consisting of a node in T and all of its descendant nodes.
Example 1:
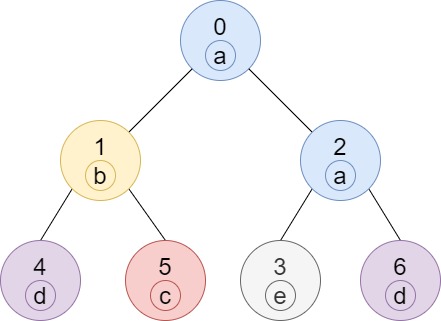
Input: n = 7, edges = [[0,1],[0,2],[1,4],[1,5],[2,3],[2,6]], labels = "abaedcd" Output: [2,1,1,1,1,1,1] Explanation: Node 0 has label 'a' and its sub-tree has node 2 with label 'a' as well, thus the answer is 2. Notice that any node is part of its sub-tree. Node 1 has a label 'b'. The sub-tree of node 1 contains nodes 1,4 and 5, as nodes 4 and 5 have different labels than node 1, the answer is just 1 (the node itself).
Example 2:
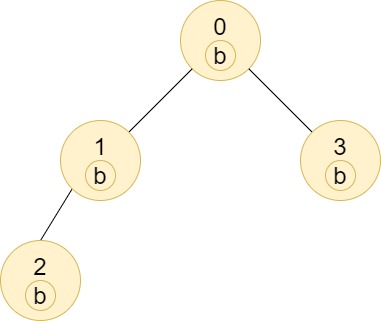
Input: n = 4, edges = [[0,1],[1,2],[0,3]], labels = "bbbb" Output: [4,2,1,1] Explanation: The sub-tree of node 2 contains only node 2, so the answer is 1. The sub-tree of node 3 contains only node 3, so the answer is 1. The sub-tree of node 1 contains nodes 1 and 2, both have label 'b', thus the answer is 2. The sub-tree of node 0 contains nodes 0, 1, 2 and 3, all with label 'b', thus the answer is 4.
Example 3:
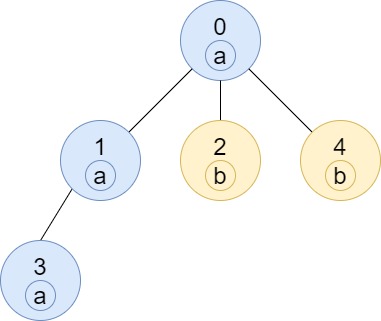
Input: n = 5, edges = [[0,1],[0,2],[1,3],[0,4]], labels = "aabab" Output: [3,2,1,1,1]
Example 4:
Input: n = 6, edges = [[0,1],[0,2],[1,3],[3,4],[4,5]], labels = "cbabaa" Output: [1,2,1,1,2,1]
Example 5:
Input: n = 7, edges = [[0,1],[1,2],[2,3],[3,4],[4,5],[5,6]], labels = "aaabaaa" Output: [6,5,4,1,3,2,1]
Constraints:
1 <= n <= 10^5edges.length == n - 1edges[i].length == 20 <= ai, bi < nai != bilabels.length == nlabelsis consisting of only of lower-case English letters.
中文题目
给你一棵树(即,一个连通的无环无向图),这棵树由编号从 0 到 n - 1 的 n 个节点组成,且恰好有 n - 1 条 edges 。树的根节点为节点 0 ,树上的每一个节点都有一个标签,也就是字符串 labels 中的一个小写字符(编号为 i 的 节点的标签就是 labels[i] )
边数组 edges 以 edges[i] = [ai, bi] 的形式给出,该格式表示节点 ai 和 bi 之间存在一条边。
返回一个大小为 n 的数组,其中 ans[i] 表示第 i 个节点的子树中与节点 i 标签相同的节点数。
树 T 中的子树是由 T 中的某个节点及其所有后代节点组成的树。
示例 1:
输入:n = 7, edges = [[0,1],[0,2],[1,4],[1,5],[2,3],[2,6]], labels = "abaedcd" 输出:[2,1,1,1,1,1,1] 解释:节点 0 的标签为 'a' ,以 'a' 为根节点的子树中,节点 2 的标签也是 'a' ,因此答案为 2 。注意树中的每个节点都是这棵子树的一部分。 节点 1 的标签为 'b' ,节点 1 的子树包含节点 1、4 和 5,但是节点 4、5 的标签与节点 1 不同,故而答案为 1(即,该节点本身)。
示例 2:
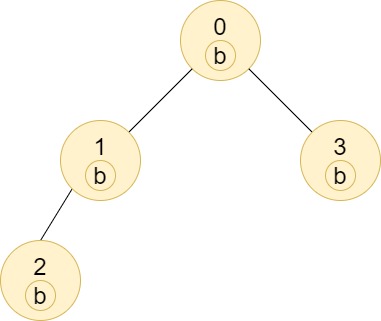
输入:n = 4, edges = [[0,1],[1,2],[0,3]], labels = "bbbb" 输出:[4,2,1,1] 解释:节点 2 的子树中只有节点 2 ,所以答案为 1 。 节点 3 的子树中只有节点 3 ,所以答案为 1 。 节点 1 的子树中包含节点 1 和 2 ,标签都是 'b' ,因此答案为 2 。 节点 0 的子树中包含节点 0、1、2 和 3,标签都是 'b',因此答案为 4 。
示例 3:
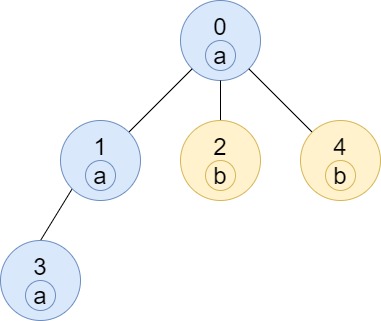
输入:n = 5, edges = [[0,1],[0,2],[1,3],[0,4]], labels = "aabab" 输出:[3,2,1,1,1]
示例 4:
输入:n = 6, edges = [[0,1],[0,2],[1,3],[3,4],[4,5]], labels = "cbabaa" 输出:[1,2,1,1,2,1]
示例 5:
输入:n = 7, edges = [[0,1],[1,2],[2,3],[3,4],[4,5],[5,6]], labels = "aaabaaa" 输出:[6,5,4,1,3,2,1]
提示:
1 <= n <= 10^5edges.length == n - 1edges[i].length == 20 <= ai, bi < nai != bilabels.length == nlabels仅由小写英文字母组成
通过代码
高赞题解
题目说明
给你一棵树, 但实际上一个连通的无环无向图,注意,这是一个无向图,可以看做以 0 作为根节点的树(后面有个错误,就是关于 0 是根节点这个问题)
以某个点 i 为根节点,得到 i 的子树中与 i 具有相同标签的子树个数
由于我们需要知道子树的情况,再将子树情况返回给根节点,因此我们使用后序遍历,将子树处理完,将所有的子节点的所有标签 组成数组 返回给根节点
由于只存在 26 个字母,因此我们可以使用一个 26 大小的 int 型数组存储标签
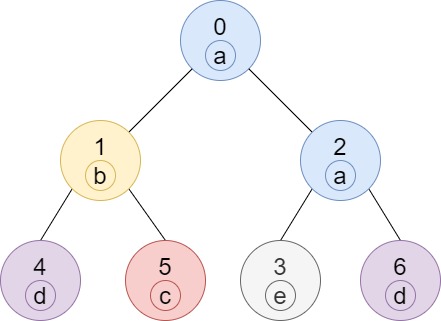
上图的 4 节点,它是叶子节点,因此它的子树加上它所有存在的标签结果是
a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y z
0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0将这个数组返回给 1 节点
上图的 5 节点,它是叶子节点,因此它的子树加上它所有存在的标签结果是
a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y z
0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0将这个数组返回给 1 节点
比如上图的 1 节点,我们接收它的子节点,即 4 和 5 返回的数组,综合它们的结果,然后加上自身标签,得到的数组就是
a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y z
0 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0将这个数组,返回给 1 的父节点 0
代码
class Solution {
public int[] countSubTrees(int n, int[][] edges, String labels) {
/*
后序遍历
*/
List<Integer>[] points = new List[n];
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
points[i] = new ArrayList<>();
}
//记录某个节点的子节点
for(int[] p : edges){
//单向添加,只需要知道某个节点的子节点即可
points[p[0]].add(p[1]);
}
//记录每个节点对应的标签
int[] ls = new int[n];
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
ls[i] = labels.charAt(i) - 'a';
}
res = new int[n];
//0 是根节点,从 0 出发
dfs(0, points, ls);
return res;
}
int[] res;
private int[] dfs(int i, List<Integer>[] points, int[] ls){
int[] curLs = new int[26];
//自身标签数 + 1
curLs[ls[i]]++;
for(int child : points[i]){
int[] childLs = dfs(child, points, ls);
for(int k = 0; k < 26; k++){
curLs[k] += childLs[k];
}
}
res[i] = curLs[ls[i]];
//将标签结果返回给父节点
return curLs;
}
}错误产生
当然,本来以为上面可以过了,不过出现了这么一个用例
输入:
4
[[0,2],[0,3],[1,2]]
"aeed"
输出:
[1,0,1,1]
预期:
[1,1,2,1]我们可以看出,它的图形是这样的
即这样看的话, 2 存在两个父节点,0 和 1,我们上面只添加了每个节点的子节点,然后默认一个节点只有一个父节点,从 0 开始 dfs
所以导致 1 节点对应的结果为 0,因为我们没有遍历到 1
然后继续修改代码,不再只是遍历 0 号节点,而是遍历所有节点
当某个节点的结果为 0 时,表示它没有遍历过(因为如果遍历过了,那么结果至少为 1,即它本身)
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
if(res[i] == 0){
dfs(i, points, ls);
}
}但还是错在原来那个用例
输入:
4
[[0,2],[0,3],[1,2]]
"aeed"
输出:
[1,2,1,1]
预期:
[1,1,2,1]这次 1 节点 和 2 节点的结果反了, 节点 2 的结果为 2, 而 节点 1 的结果为 1
这表示 2 是把 1 当作子节点的,即
因此,我们不能再单单按照 [1, 2] 的顺序将 1 当作 2 的父节点
题目说的无向图的意思就出来了,[1, 2] 不意味着 1 是 2 的父节点,而是存在一条连通的路
这里是 0 能到 2,所以我们应该从 2 出发,真正的路径是 2 -> 1
因此,我们需要进行双向添加
for(int[] p : edges){
points[p[0]].add(p[1]);
points[p[1]].add(p[0]);
}使用一个 visited 数组,记录遍历过程中判断节点是否已经遍历过
最终代码
class Solution {
public int[] countSubTrees(int n, int[][] edges, String labels) {
/*
后序遍历
*/
List<Integer>[] points = new List[n];
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
points[i] = new ArrayList<>();
}
for(int[] p : edges){
points[p[0]].add(p[1]);
points[p[1]].add(p[0]);
}
int[] ls = new int[n];
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
ls[i] = labels.charAt(i) - 'a';
}
res = new int[n];
visited = new boolean[n];
visited[0] = true;
dfs(0, points, ls);
return res;
}
int[] res;
boolean[] visited;
private int[] dfs(int i, List<Integer>[] points, int[] ls){
int[] curLs = new int[26];
//添加自身节点
curLs[ls[i]]++;
for(int child : points[i]){
/*
判断是否已经遍历过该节点,如果遍历过,那么跳过
因为这是无向图, 1 可以到 2,2 也可以到 1,因此,当 1 到 2 的时候,我们需要记录 1 已经访问
这样,从 2 出发,就不会再到 1 了
*/
if(visited[child]){
continue;
}
visited[child] = true;
int[] childLs = dfs(child, points, ls);
for(int k = 0; k < 26; k++){
curLs[k] += childLs[k];
}
}
res[i] = curLs[ls[i]];
return curLs;
}
}统计信息
| 通过次数 | 提交次数 | AC比率 |
|---|---|---|
| 5628 | 18784 | 30.0% |
提交历史
| 提交时间 | 提交结果 | 执行时间 | 内存消耗 | 语言 |
|---|




