英文原文
You are given a tree with n nodes numbered from 0 to n - 1 in the form of a parent array parent where parent[i] is the parent of the ith node. The root of the tree is node 0, so parent[0] = -1 since it has no parent. You want to design a data structure that allows users to lock, unlock, and upgrade nodes in the tree.
The data structure should support the following functions:
- Lock: Locks the given node for the given user and prevents other users from locking the same node. You may only lock a node using this function if the node is unlocked.
- Unlock: Unlocks the given node for the given user. You may only unlock a node using this function if it is currently locked by the same user.
- Upgrade: Locks the given node for the given user and unlocks all of its descendants regardless of who locked it. You may only upgrade a node if all 3 conditions are true:
- The node is unlocked,
- It has at least one locked descendant (by any user), and
- It does not have any locked ancestors.
Implement the LockingTree class:
LockingTree(int[] parent)initializes the data structure with the parent array.lock(int num, int user)returnstrueif it is possible for the user with iduserto lock the nodenum, orfalseotherwise. If it is possible, the nodenumwill become locked by the user with iduser.unlock(int num, int user)returnstrueif it is possible for the user with iduserto unlock the nodenum, orfalseotherwise. If it is possible, the nodenumwill become unlocked.upgrade(int num, int user)returnstrueif it is possible for the user with iduserto upgrade the nodenum, orfalseotherwise. If it is possible, the nodenumwill be upgraded.
Example 1:
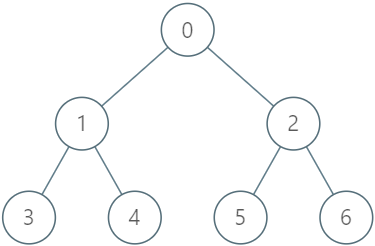
Input ["LockingTree", "lock", "unlock", "unlock", "lock", "upgrade", "lock"] [[[-1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 2, 2]], [2, 2], [2, 3], [2, 2], [4, 5], [0, 1], [0, 1]] Output [null, true, false, true, true, true, false]Explanation
LockingTree lockingTree = new LockingTree([-1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 2, 2]);
lockingTree.lock(2, 2); // return true because node 2 is unlocked.
// Node 2 will now be locked by user 2.
lockingTree.unlock(2, 3); // return false because user 3 cannot unlock a node locked by user 2.
lockingTree.unlock(2, 2); // return true because node 2 was previously locked by user 2.
// Node 2 will now be unlocked.
lockingTree.lock(4, 5); // return true because node 4 is unlocked.
// Node 4 will now be locked by user 5.
lockingTree.upgrade(0, 1); // return true because node 0 is unlocked and has at least one locked descendant (node 4).
// Node 0 will now be locked by user 1 and node 4 will now be unlocked.
lockingTree.lock(0, 1); // return false because node 0 is already locked.
Constraints:
n == parent.length2 <= n <= 20000 <= parent[i] <= n - 1fori != 0parent[0] == -10 <= num <= n - 11 <= user <= 104parentrepresents a valid tree.- At most
2000calls in total will be made tolock,unlock, andupgrade.
中文题目
给你一棵 n 个节点的树,编号从 0 到 n - 1 ,以父节点数组 parent 的形式给出,其中 parent[i] 是第 i 个节点的父节点。树的根节点为 0 号节点,所以 parent[0] = -1 ,因为它没有父节点。你想要设计一个数据结构实现树里面对节点的加锁,解锁和升级操作。
数据结构需要支持如下函数:
- Lock:指定用户给指定节点 上锁 ,上锁后其他用户将无法给同一节点上锁。只有当节点处于未上锁的状态下,才能进行上锁操作。
- Unlock:指定用户给指定节点 解锁 ,只有当指定节点当前正被指定用户锁住时,才能执行该解锁操作。
- Upgrade:指定用户给指定节点 上锁 ,并且将该节点的所有子孙节点 解锁 。只有如下 3 个条件 全部 满足时才能执行升级操作:
- 指定节点当前状态为未上锁。
- 指定节点至少有一个上锁状态的子孙节点(可以是 任意 用户上锁的)。
- 指定节点没有任何上锁的祖先节点。
请你实现 LockingTree 类:
LockingTree(int[] parent)用父节点数组初始化数据结构。lock(int num, int user)如果 id 为user的用户可以给节点num上锁,那么返回true,否则返回false。如果可以执行此操作,节点num会被 id 为user的用户 上锁 。unlock(int num, int user)如果 id 为user的用户可以给节点num解锁,那么返回true,否则返回false。如果可以执行此操作,节点num变为 未上锁 状态。upgrade(int num, int user)如果 id 为user的用户可以给节点num升级,那么返回true,否则返回false。如果可以执行此操作,节点num会被 升级 。
示例 1:

输入:
["LockingTree", "lock", "unlock", "unlock", "lock", "upgrade", "lock"]
[[[-1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 2, 2]], [2, 2], [2, 3], [2, 2], [4, 5], [0, 1], [0, 1]]
输出:
[null, true, false, true, true, true, false]
解释:
LockingTree lockingTree = new LockingTree([-1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 2, 2]);
lockingTree.lock(2, 2); // 返回 true ,因为节点 2 未上锁。
// 节点 2 被用户 2 上锁。
lockingTree.unlock(2, 3); // 返回 false ,因为用户 3 无法解锁被用户 2 上锁的节点。
lockingTree.unlock(2, 2); // 返回 true ,因为节点 2 之前被用户 2 上锁。
// 节点 2 现在变为未上锁状态。
lockingTree.lock(4, 5); // 返回 true ,因为节点 4 未上锁。
// 节点 4 被用户 5 上锁。
lockingTree.upgrade(0, 1); // 返回 true ,因为节点 0 未上锁且至少有一个被上锁的子孙节点(节点 4)。
// 节点 0 被用户 1 上锁,节点 4 变为未上锁。
lockingTree.lock(0, 1); // 返回 false ,因为节点 0 已经被上锁了。
提示:
n == parent.length2 <= n <= 2000- 对于
i != 0,满足0 <= parent[i] <= n - 1 parent[0] == -10 <= num <= n - 11 <= user <= 104parent表示一棵合法的树。lock,unlock和upgrade的调用 总共 不超过2000次。
通过代码
高赞题解
简单介绍一下需要的知识点:
- 从根开始DFS遍历树可以得到DFS序列(先序遍历),每个节点的子树对应序列中的以该节点开始,长度为子树大小的区间。
- 树状数组可以分别在对数时间做到:区间加,单点询问;单点加,区间求和,求出前缀和大于等于某个值的最小下标。
维护$2$个树状数组up和down,加锁时:
- 在up中给该节点子树区间$+1$。
- 在down中给该节点$+1$.
考虑upgrade操作:
- 从该节点到根都不能有锁。这等价于up中该节点的值为$0$.
- 子树中有锁,首先区间和不为$0$,可以通过树状数组上二分逐个求出子树中的锁。每找到一个锁需要对数时间,这部分的复杂度依赖于lock操作的次数,因此均摊是对数时间的。
参考代码:
[]struct BIT : vector<int>{ BIT(int n = 0): vector<int>(n){} void add(int p, int x) { for (; p < (int)size(); p += p &- p) at(p) += x; } int sum(int p) { int res = 0; for (; p; p -= p & -p) res += at(p); return res; } int query(int x) { //find the smallest positive integer p such that sum(p) >= x int L = 0, R = size(); while (L + 1 < R) { int m = (L + R) >> 1; if (at(m) < x) { x -= at(m); L = m; } else R = m; } return R; } }; class LockingTree { public: vector<int> size, p, q, mark; BIT down, up; LockingTree(vector<int>& parent): size(parent.size()), p(parent.size()), q(parent.size() + 1), mark(parent.size(), -1), up(parent.size() + 1){ vector<vector<int>> children(parent.size()); for (int i = 1; i < (int)parent.size(); i += 1) children[parent[i]].push_back(i); int timer = 0; function<void(int)> dfs = [&](int u) { size[u] = 1; p[u] = timer += 1; q[timer] = u; for (int v : children[u]) { dfs(v); size[u] += size[v]; } }; dfs(0); int k = 1; while (k <= (int)parent.size()) k <<= 1; down.resize(k); } bool lock(int num, int user) { if (mark[num] != -1) return false; mark[num] = user; down.add(p[num], 1); up.add(p[num], 1); up.add(p[num] + size[num], -1); return true; } bool unlock(int num, int user) { if (mark[num] != user) return false; mark[num] = -1; down.add(p[num], -1); up.add(p[num], -1); up.add(p[num] + size[num], 1); return true; } bool upgrade(int num, int user) { if (up.sum(p[num])) return false; int L = down.sum(p[num] - 1), R = down.sum(p[num] + size[num] - 1); if (L == R) return false; for (int i = 0; i < R - L; i += 1) { int k = down.query(L + 1); mark[q[k]] = -1; down.add(k, -1); up.add(k, -1); up.add(k + size[q[k]], 1); } lock(num, user); return true; } };
统计信息
| 通过次数 | 提交次数 | AC比率 |
|---|---|---|
| 1943 | 5016 | 38.7% |
提交历史
| 提交时间 | 提交结果 | 执行时间 | 内存消耗 | 语言 |
|---|




