原文链接: https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/kth-smallest-element-in-a-bst
英文原文
Given the root of a binary search tree, and an integer k, return the kth smallest value (1-indexed) of all the values of the nodes in the tree.
Example 1:
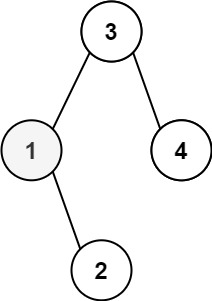
Input: root = [3,1,4,null,2], k = 1 Output: 1
Example 2:
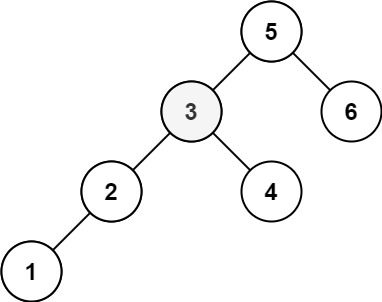
Input: root = [5,3,6,2,4,null,null,1], k = 3 Output: 3
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is
n. 1 <= k <= n <= 1040 <= Node.val <= 104
Follow up: If the BST is modified often (i.e., we can do insert and delete operations) and you need to find the kth smallest frequently, how would you optimize?
中文题目
给定一个二叉搜索树的根节点 root ,和一个整数 k ,请你设计一个算法查找其中第 k 个最小元素(从 1 开始计数)。
示例 1:

输入:root = [3,1,4,null,2], k = 1 输出:1
示例 2:

输入:root = [5,3,6,2,4,null,null,1], k = 3 输出:3
提示:
- 树中的节点数为
n。 1 <= k <= n <= 1040 <= Node.val <= 104
进阶:如果二叉搜索树经常被修改(插入/删除操作)并且你需要频繁地查找第 k 小的值,你将如何优化算法?
通过代码
高赞题解
树的遍历 + 排序
朴素的做法是先对二叉树进行一次完整遍历,将所有节点存入列表中,最后对列表排序后返回目标值。
树的遍历可以使用 DFS 或 BFS。
代码:
[]class Solution { List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>(); public int kthSmallest(TreeNode root, int k) { dfs(root); Collections.sort(list); return list.get(k - 1); } void dfs(TreeNode root) { if (root == null) return ; list.add(root.val); dfs(root.left); dfs(root.right); } }
- 时间复杂度:树的遍历时间复杂度为 $O(n)$;排序的复杂度为 $O(n\log{n})$。整体复杂度为 $O(n\log{n})$
- 空间复杂度:$O(n)$
树的遍历 + 优先队列(堆)
相比于先直接拿到所有节点再排序的解法一,另外一种做法是使用「优先队列(堆)」来做。
由于我们返回的是第 $k$ 小的数,因此我们可以构建一个容量为 $k$ 的大根堆。
根据大根堆的元素个数和当前节点与堆顶元素的关系来分情况讨论:
- 大根堆元素不足 $k$ 个:直接将当前节点值放入大根堆;
- 大根堆元素为 $k$ 个,根据堆顶元素和当前节点值的大小关系进一步分情况讨论:
- 如果当前节点值元素大于堆顶元素,说明当前节点值不可能在第 $k$ 小的范围内,直接丢弃;
- 如果当前节点值元素小于堆顶元素,说明当前节点值可能在第 $k$ 小的范围内,先
poll一个再add进去。
树的遍历可以使用 DFS 或 BFS。
代码:
[]class Solution { public int kthSmallest(TreeNode root, int k) { PriorityQueue<Integer> q = new PriorityQueue<>((a,b)->b-a); Deque<TreeNode> d = new ArrayDeque<>(); d.addLast(root); while (!d.isEmpty()) { TreeNode node = d.pollFirst(); if (q.size() < k) { q.add(node.val); } else if (q.peek() > node.val) { q.poll(); q.add(node.val); } if (node.left != null) d.addLast(node.left); if (node.right != null) d.addLast(node.right); } return q.peek(); } }
- 时间复杂度:树的遍历时间复杂度为 $O(n)$;使用优先队列(堆)复杂度为 $O(n\log{k})$。整体复杂度为 $O(n\log{k})$
- 空间复杂度:空间多少取决于
d和q使用的容量,q最多不超过 $k$ 个元素,复杂度为 $O(k)$,d最多不超过二叉树的一层,复杂度为 $O(n)$。整体复杂度为 $O(n + k)$
中序遍历
上述两种节点,都没有利用该树为二叉搜索树的特性。
而我们知道,二叉搜索树的中序遍历是有序的,因此我们只需要对二叉搜索树执行中序遍历,并返回第 $k$ 小的值即可。
不熟悉二叉树的中序遍历的同学,可以看看 (题解)783. 二叉搜索树节点最小距离。
中序遍历有「迭代」和「递归」两种写法。
代码:
[]class Solution { public int kthSmallest(TreeNode root, int k) { Deque<TreeNode> d = new ArrayDeque<>(); while (root != null || !d.isEmpty()) { while (root != null) { d.addLast(root); root = root.left; } root = d.pollLast(); if (--k == 0) return root.val; root = root.right; } return -1; // never } }
[]class Solution { int k, ans; public int kthSmallest(TreeNode root, int _k) { k = _k; dfs(root); return ans; } void dfs(TreeNode root) { if (root == null || k <= 0) return ; dfs(root.left); if (--k == 0) ans = root.val; dfs(root.right); } }
- 时间复杂度:令 $h$ 为树高,先到达叶子位置(最小节点位置),复杂度为 $O(h)$,然后找到第 $k$ 小的元素,复杂度为 $O(k)$。整体复杂度为 $O(h + k)$
- 空间复杂度:令 $h$ 为树高,复杂度为 $O(h)$
最后
如果有帮助到你,请给题解点个赞和收藏,让更多的人看到 ~ (“▔□▔)/
也欢迎你 关注我(公主号后台回复「送书」即可参与长期看题解学算法送实体书活动)或 加入「组队打卡」小群 ,提供写「证明」&「思路」的高质量题解。
所有题解已经加入 刷题指南,欢迎 star 哦 ~
统计信息
| 通过次数 | 提交次数 | AC比率 |
|---|---|---|
| 170179 | 226241 | 75.2% |
提交历史
| 提交时间 | 提交结果 | 执行时间 | 内存消耗 | 语言 |
|---|
相似题目
| 题目 | 难度 |
|---|---|
| 二叉树的中序遍历 | 简单 |
| 二叉树中第二小的节点 | 简单 |




