英文原文
Given a root node reference of a BST and a key, delete the node with the given key in the BST. Return the root node reference (possibly updated) of the BST.
Basically, the deletion can be divided into two stages:
- Search for a node to remove.
- If the node is found, delete the node.
Example 1:
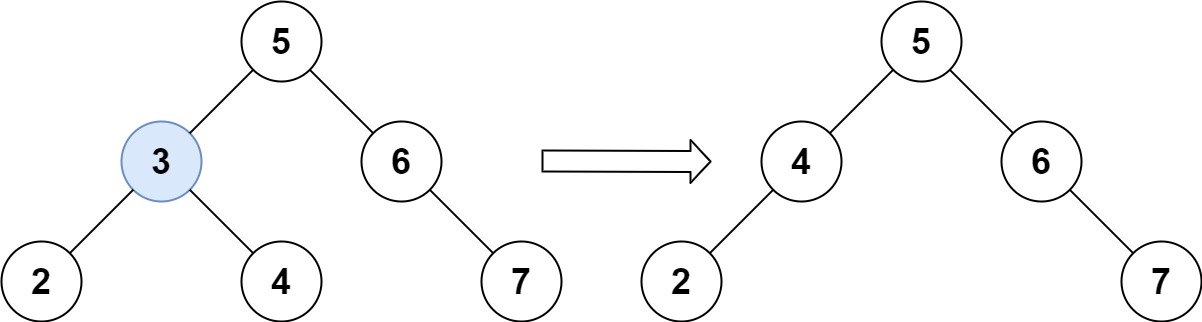
Input: root = [5,3,6,2,4,null,7], key = 3 Output: [5,4,6,2,null,null,7] Explanation: Given key to delete is 3. So we find the node with value 3 and delete it. One valid answer is [5,4,6,2,null,null,7], shown in the above BST. Please notice that another valid answer is [5,2,6,null,4,null,7] and it's also accepted.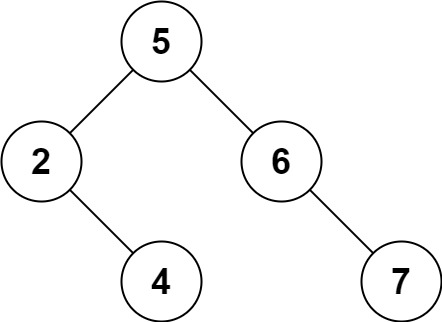
Example 2:
Input: root = [5,3,6,2,4,null,7], key = 0 Output: [5,3,6,2,4,null,7] Explanation: The tree does not contain a node with value = 0.
Example 3:
Input: root = [], key = 0 Output: []
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[0, 104]. -105 <= Node.val <= 105- Each node has a unique value.
rootis a valid binary search tree.-105 <= key <= 105
Follow up: Could you solve it with time complexity O(height of tree)?
中文题目
给定一个二叉搜索树的根节点 root 和一个值 key,删除二叉搜索树中的 key 对应的节点,并保证二叉搜索树的性质不变。返回二叉搜索树(有可能被更新)的根节点的引用。
一般来说,删除节点可分为两个步骤:
- 首先找到需要删除的节点;
- 如果找到了,删除它。
示例 1:

输入:root = [5,3,6,2,4,null,7], key = 3 输出:[5,4,6,2,null,null,7] 解释:给定需要删除的节点值是 3,所以我们首先找到 3 这个节点,然后删除它。 一个正确的答案是 [5,4,6,2,null,null,7], 如下图所示。 另一个正确答案是 [5,2,6,null,4,null,7]。
示例 2:
输入: root = [5,3,6,2,4,null,7], key = 0 输出: [5,3,6,2,4,null,7] 解释: 二叉树不包含值为 0 的节点
示例 3:
输入: root = [], key = 0 输出: []
提示:
- 节点数的范围
[0, 104]. -105 <= Node.val <= 105- 节点值唯一
root是合法的二叉搜索树-105 <= key <= 105
进阶: 要求算法时间复杂度为 O(h),h 为树的高度。
通过代码
官方题解
二叉搜索树的三个特性:
这些性质最好在面试之前了解清楚:
- 二叉搜索树的中序遍历的序列是递增排序的序列。中序遍历的遍历次序:
Left -> Node -> Right。
[Inorder_traversal-Java]public LinkedList<Integer> inorder(TreeNode root, LinkedList<Integer> arr) { if (root == null) return arr; inorder(root.left, arr); arr.add(root.val); inorder(root.right, arr); return arr; }
[Inorder_traversal-Python]def inorder(root): return inorder(root.left) + [root.val] + inorder(root.right) if root else []
 {:width=500}
{:width=500}
Successor代表的是中序遍历序列的下一个节点。即比当前节点大的最小节点,简称后继节点。 先取当前节点的右节点,然后一直取该节点的左节点,直到左节点为空,则最后指向的节点为后继节点。
[Successor-Java]public int successor(TreeNode root) { root = root.right; while (root.left != null) root = root.left; return root; }
[Successor-Python]def successor(root): root = root.right while root.left: root = root.left return root
Predecessor代表的是中序遍历序列的前一个节点。即比当前节点小的最大节点,简称前驱节点。先取当前节点的左节点,然后取该节点的右节点,直到右节点为空,则最后指向的节点为前驱节点。
[Predecessor-Java]public int predecessor(TreeNode root) { root = root.left; while (root.right != null) root = root.right; return root; }
[Predecessor-Python]def predecessor(root): root = root.left while root.right: root = root.right return root
 {:width=500}
{:width=500}
方法:递归
这里有三种可能的情况:
- 要删除的节点为叶子节点,可以直接删除。
 {:width=500}
{:width=500}
- 要删除的节点不是叶子节点且拥有右节点,则该节点可以由该节点的后继节点进行替代,该后继节点位于右子树中较低的位置。然后可以从后继节点的位置递归向下操作以删除后继节点。
 {:width=500}
{:width=500}
- 要删除的节点不是叶子节点,且没有右节点但是有左节点。这意味着它的后继节点在它的上面,但是我们并不想返回。我们可以使用它的前驱节点进行替代,然后再递归的向下删除前驱节点。
 {:width=500}
{:width=500}
算法:
- 如果
key > root.val,说明要删除的节点在右子树,root.right = deleteNode(root.right, key)。 - 如果
key < root.val,说明要删除的节点在左子树,root.left = deleteNode(root.left, key)。 - 如果
key == root.val,则该节点就是我们要删除的节点,则:- 如果该节点是叶子节点,则直接删除它:
root = null。 - 如果该节点不是叶子节点且有右节点,则用它的后继节点的值替代
root.val = successor.val,然后删除后继节点。 - 如果该节点不是叶子节点且只有左节点,则用它的前驱节点的值替代
root.val = predecessor.val,然后删除前驱节点。
- 如果该节点是叶子节点,则直接删除它:
- 返回
root。
 {:width=500}
{:width=500}
[solution1-Java]class Solution { /* One step right and then always left */ public int successor(TreeNode root) { root = root.right; while (root.left != null) root = root.left; return root.val; } /* One step left and then always right */ public int predecessor(TreeNode root) { root = root.left; while (root.right != null) root = root.right; return root.val; } public TreeNode deleteNode(TreeNode root, int key) { if (root == null) return null; // delete from the right subtree if (key > root.val) root.right = deleteNode(root.right, key); // delete from the left subtree else if (key < root.val) root.left = deleteNode(root.left, key); // delete the current node else { // the node is a leaf if (root.left == null && root.right == null) root = null; // the node is not a leaf and has a right child else if (root.right != null) { root.val = successor(root); root.right = deleteNode(root.right, root.val); } // the node is not a leaf, has no right child, and has a left child else { root.val = predecessor(root); root.left = deleteNode(root.left, root.val); } } return root; } }
[solution1-Python]class Solution: def successor(self, root): """ One step right and then always left """ root = root.right while root.left: root = root.left return root.val def predecessor(self, root): """ One step left and then always right """ root = root.left while root.right: root = root.right return root.val def deleteNode(self, root: TreeNode, key: int) -> TreeNode: if not root: return None # delete from the right subtree if key > root.val: root.right = self.deleteNode(root.right, key) # delete from the left subtree elif key < root.val: root.left = self.deleteNode(root.left, key) # delete the current node else: # the node is a leaf if not (root.left or root.right): root = None # the node is not a leaf and has a right child elif root.right: root.val = self.successor(root) root.right = self.deleteNode(root.right, root.val) # the node is not a leaf, has no right child, and has a left child else: root.val = self.predecessor(root) root.left = self.deleteNode(root.left, root.val) return root
复杂度分析
- 时间复杂度:$\mathcal{O}(\log N)$。在算法的执行过程中,我们一直在树上向左或向右移动。首先先用 $\mathcal{O}(H_1)$ 的时间找到要删除的节点,$H_1$ 值得是从根节点到要删除节点的高度。然后删除节点需要 $\mathcal{O}(H_2)$ 的时间,$H_2$ 指的是从要删除节点到替换节点的高度。由于 $\mathcal{O}(H_1 + H_2) = \mathcal{O}(H)$,$H$ 值得是树的高度,若树是一个平衡树则 $H$ = $\log N$。
- 空间复杂度:$\mathcal{O}(H)$,递归时堆栈使用的空间,$H$ 是树的高度。
统计信息
| 通过次数 | 提交次数 | AC比率 |
|---|---|---|
| 69181 | 141185 | 49.0% |
提交历史
| 提交时间 | 提交结果 | 执行时间 | 内存消耗 | 语言 |
|---|
相似题目
| 题目 | 难度 |
|---|---|
| 拆分二叉搜索树 | 中等 |



