原文链接: https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/convert-bst-to-greater-tree
英文原文
Given the root of a Binary Search Tree (BST), convert it to a Greater Tree such that every key of the original BST is changed to the original key plus the sum of all keys greater than the original key in BST.
As a reminder, a binary search tree is a tree that satisfies these constraints:
- The left subtree of a node contains only nodes with keys less than the node's key.
- The right subtree of a node contains only nodes with keys greater than the node's key.
- Both the left and right subtrees must also be binary search trees.
Example 1:

Input: root = [4,1,6,0,2,5,7,null,null,null,3,null,null,null,8] Output: [30,36,21,36,35,26,15,null,null,null,33,null,null,null,8]
Example 2:
Input: root = [0,null,1] Output: [1,null,1]
Example 3:
Input: root = [1,0,2] Output: [3,3,2]
Example 4:
Input: root = [3,2,4,1] Output: [7,9,4,10]
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[0, 104]. -104 <= Node.val <= 104- All the values in the tree are unique.
rootis guaranteed to be a valid binary search tree.
Note: This question is the same as 1038: https://leetcode.com/problems/binary-search-tree-to-greater-sum-tree/
中文题目
给出二叉 搜索 树的根节点,该树的节点值各不相同,请你将其转换为累加树(Greater Sum Tree),使每个节点 node 的新值等于原树中大于或等于 node.val 的值之和。
提醒一下,二叉搜索树满足下列约束条件:
- 节点的左子树仅包含键 小于 节点键的节点。
- 节点的右子树仅包含键 大于 节点键的节点。
- 左右子树也必须是二叉搜索树。
注意:本题和 1038: https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/binary-search-tree-to-greater-sum-tree/ 相同
示例 1:
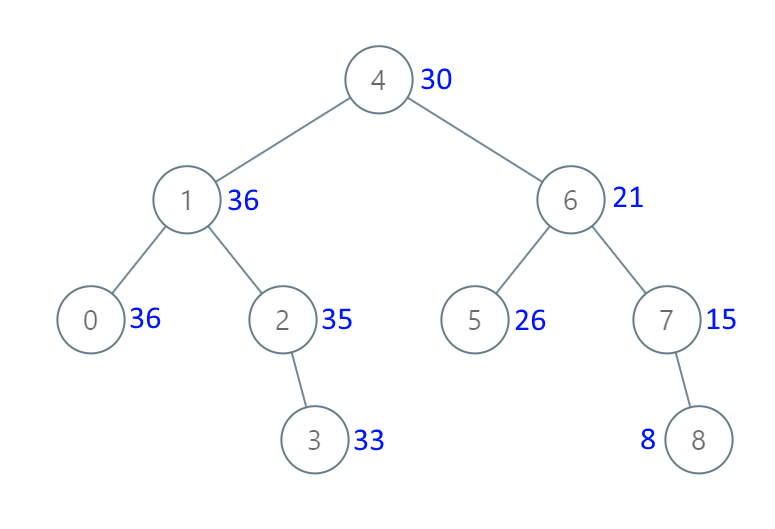
输入:[4,1,6,0,2,5,7,null,null,null,3,null,null,null,8] 输出:[30,36,21,36,35,26,15,null,null,null,33,null,null,null,8]
示例 2:
输入:root = [0,null,1] 输出:[1,null,1]
示例 3:
输入:root = [1,0,2] 输出:[3,3,2]
示例 4:
输入:root = [3,2,4,1] 输出:[7,9,4,10]
提示:
- 树中的节点数介于
0和104之间。 - 每个节点的值介于
-104和104之间。 - 树中的所有值 互不相同 。
- 给定的树为二叉搜索树。
通过代码
高赞题解
本文将带你用树的一种遍历算法解决N个
leetcode相关算法题(算法小渣渣致敬叶师傅)
我不害怕曾經練過一萬種踢法的人,但我害怕一種踢法練過一萬次的人(by 叶师傅的徒弟Bruce Lee)
树的遍历(Traversal)
如下图, 三种遍历方式, 可用同一种递归思想实现
先序遍历(PreOrder, 按照先访问根节点的顺序)
var preorderTraversal = function(root) {
const res = []
function traversal (root) {
if (root !== null) {
res.push(root.val) // 访问根节点的值
traversal(root.left) // 递归遍历左子树
traversal(root.right) // 递归遍历右子树
}
}
traversal(root)
return res
}94 中序遍历(InOrder, 按照根节点在中间访问的顺序)

var inorderTraversal = function(root) {
const res = []
function traversal (root) {
if (root !== null) {
traversal(root.left)
res.push(root.val)
traversal(root.right)
}
}
traversal(root)
return res
}145 后续遍历(PosterOrder, 按照根节点在后面访问的顺序)

var postorderTraversal = function(root) {
const res = []
function traversal (root) {
if (root !== null) {
traversal(root.left)
traversal(root.right)
res.push(root.val)
}
}
traversal(root)
return res
}100 相同的树

可以利用这种递归思想并发同时爬两棵树
var isSameTree = function(p, q) {
function traversal (root1, root2) {
if (root1 === null && root2 !== null) {
return false
} else if (root1 !== null && root2 === null) {
return false
} else if (root1 === null && root2 === null) {
return true
} else {
return root1.val === root2.val && traversal(root1.left, root2.left) && traversal(root1.right, root2.right)
}
}
return traversal(p, q)
}226 翻转二叉树

这种算法可以帮助Homebrew作者Max Howell解开Google的算法面试题

var invertTree = function(root) {
function traversal (root) {
if (root === null) {
return null
} else {
[root.left, root.right] = [traversal(root.right), traversal(root.left)]
return root
}
}
return traversal(root)
}590 N叉树的后序遍历

我们还可以用此种算法解决N叉树的问题
var postorder = function(root) {
const res = []
function traversal (root) {
if (root !== null) {
root.children.forEach(child => {
traversal(child)
})
res.push(root.val)
}
}
traversal(root)
return res
}如果你已对这种写法审美疲劳, 可以换个写法, 使用匿名函数
var postorder = function(root) {
const res = []
;(function (root) {
if (root !== null) {
root.children.forEach(child => {
arguments.callee(child)
})
res.push(root.val)
}
})(root)
return res
}还可以利用栈来迭代
var postorder = function(root) {
if (root === null) {
return []
}
const res = []
const arr = [root]
while (arr.length) {
const cur = arr.pop()
res.push(cur.val)
for (let i = cur.children.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
arr.push(cur.children[i])
}
}
return res.reverse()
}103 二叉树的锯齿形层次遍历

大白话, 蛇皮走位爬树
var zigzagLevelOrder = function(root) {
if (root === null) {
return []
} else {
let res = []
function traversal (root, depth) {
if (root !== null) {
if (res[depth] === undefined) {
res[depth] = []
}
res[depth].push(root.val)
traversal(root.left, depth + 1)
traversal(root.right, depth + 1)
}
}
traversal(root, 0)
res.forEach((item, index) => {
if (index & 1) {
res[index] = item.reverse()
}
})
return res
}
}优化
var zigzagLevelOrder = function(root) {
if (root === null) {
return []
} else {
let res = []
function traversal (root, depth) {
if (root !== null) {
if (res[depth] === undefined) {
res[depth] = []
}
if (depth & 1) {
res[depth].unshift(root.val)
} else {
res[depth].push(root.val)
}
traversal(root.left, depth + 1)
traversal(root.right, depth + 1)
}
}
traversal(root, 0)
return res
}
}230 二叉搜索树中第K小的元素

var kthSmallest = function (root, k) {
let arr = []
function traversal (node) {
if (node !== null) {
traversal(node.left)
arr.push(node.val)
traversal(node.right)
}
}
traversal(root)
return arr[k - 1]
}优化, 减少遍历次数
var kthSmallest = function (root, k) {
let arr = []
function traversal(node) {
if (node !== null && arr.length < k) {
traversal(node.left)
arr.push(node.val)
traversal(node.right)
}
}
traversal(root)
return arr[k - 1]
}进一步优化, 使用O(1)的额外空间
var kthSmallest = function (root, k) {
let res
let count = 0
function traversal(node) {
if (node !== null) {
if (count < k) {
traversal(node.left)
}
if (++count === k) {
res = node.val
}
if (count < k) {
traversal(node.right)
}
}
}
traversal(root)
return res
}102 二叉树的层序遍历

var levelOrder = function(root) {
const res = []
function traversal (root, depth) {
if (root !== null) {
if (!res[depth]) {
res[depth] = []
}
traversal(root.left, depth + 1)
res[depth].push(root.val)
traversal(root.right, depth + 1)
}
}
traversal(root, 0)
return res
}199 二叉树的右视图

基本思路: 先序遍历, 记录每一层深度下的节点的值, 并先记录左节点再记录右节点, 则最后记录的值即为该层深度的右视图看到的值
var rightSideView = function(root) {
const arr = []
function traversal (root, depth) {
if (root) {
if (arr[depth] === undefined) {
arr[depth] = []
}
arr[depth].push(root.val)
traversal(root.left, depth + 1)
traversal(root.right, depth + 1)
}
}
traversal(root, 0)
const res = []
for (let i = 0; i < arr.length; ++i) {
res.push(arr[i][arr[i].length - 1])
}
return res
};104 二叉树的最大深度

var maxDepth = function (root) {
let res = 0
function traversal (root, depth) {
if (root !== null) {
if (depth > res) {
res = depth
}
if (root.left) {
traversal(root.left, depth + 1)
}
if (root.right) {
traversal(root.right, depth + 1)
}
}
}
traversal(root, 1)
return res
}107 二叉树的层次遍历 II

var levelOrderBottom = function(root) {
if (root === null) {
return []
}
let res = []
function traversal (root, depth) {
if (root !== null) {
if (!res[depth]) {
res[depth] = []
}
traversal(root.left, depth + 1)
res[depth].push(root.val)
traversal(root.right, depth + 1)
}
}
traversal(root, 0)
return res.reverse()
}671 二叉树中第二小的节点

var findSecondMinimumValue = function(root) {
let arr = []
;(function traversal (root) {
if (root !== null) {
traversal(root.left)
arr.push(root.val)
traversal(root.right)
}
})(root)
let _arr = [...new Set(arr)].sort()
return _arr[1] ? _arr[1] : -1
}1038 从二叉搜索树到更大和树

var bstToGst = function(root) {
let sum = 0
function traversal (root) {
if (root !== null) {
traversal(root.right)
root.val += sum
sum = root.val
traversal(root.left)
}
}
traversal(root)
return root
}538 把二叉搜索树转换为累加树

var convertBST = function(root) {
let sum = 0
function traversal (root) {
if (root !== null) {
traversal(root.right)
sum += root.val
root.val = sum
traversal(root.left)
}
}
traversal(root)
return root
}700 二叉搜索树中的搜索

var searchBST = function(root, val) {
function traversal (root) {
if (root !== null) {
if (root.val === val) {
return root
} else if (root.val < val) {
return traversal(root.right)
} else {
return traversal(root.left)
}
} else {
return root
}
}
return traversal(root)
}559 N叉树的最大深度

var maxDepth = function(root) {
if (root === null) {
return 0
} else {
let depth = 1
function traversal (root, curDepth) {
if (root !== null) {
if (curDepth > depth) {
depth = curDepth
}
root.children.forEach(child => traversal(child, curDepth + 1))
}
}
traversal(root, 1)
return depth
}
}589 N叉树的前序遍历

var preorder = function(root) {
const res = []
function traversal (root) {
if (root !== null) {
res.push(root.val)
root.children.forEach(child => traversal(child))
}
}
traversal(root)
return res
}897 递增顺序查找树

var increasingBST = function(root) {
const arr = []
function traversal (root) {
if (root !== null) {
traversal(root.left)
arr.push(root.val)
traversal(root.right)
}
}
traversal(root)
const res = new TreeNode(arr[0])
let currentNode = res
for (let i = 0; i < arr.length - 1; i++) {
currentNode.left = null
currentNode.right = new TreeNode(arr[i + 1])
currentNode = currentNode.right
}
return res
}原文在掘金: https://juejin.im/post/5e1c4e46f265da3e140fa54d
欢迎点赞👍、关注和来撩三连😎
统计信息
| 通过次数 | 提交次数 | AC比率 |
|---|---|---|
| 117140 | 165442 | 70.8% |
提交历史
| 提交时间 | 提交结果 | 执行时间 | 内存消耗 | 语言 |
|---|






