英文原文
There are n cities. Some of them are connected, while some are not. If city a is connected directly with city b, and city b is connected directly with city c, then city a is connected indirectly with city c.
A province is a group of directly or indirectly connected cities and no other cities outside of the group.
You are given an n x n matrix isConnected where isConnected[i][j] = 1 if the ith city and the jth city are directly connected, and isConnected[i][j] = 0 otherwise.
Return the total number of provinces.
Example 1:
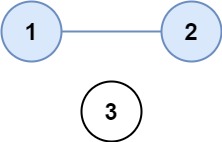
Input: isConnected = [[1,1,0],[1,1,0],[0,0,1]] Output: 2
Example 2:
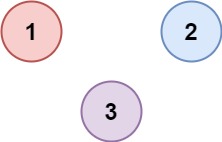
Input: isConnected = [[1,0,0],[0,1,0],[0,0,1]] Output: 3
Constraints:
1 <= n <= 200n == isConnected.lengthn == isConnected[i].lengthisConnected[i][j]is1or0.isConnected[i][i] == 1isConnected[i][j] == isConnected[j][i]
中文题目
有 n 个城市,其中一些彼此相连,另一些没有相连。如果城市 a 与城市 b 直接相连,且城市 b 与城市 c 直接相连,那么城市 a 与城市 c 间接相连。
省份 是一组直接或间接相连的城市,组内不含其他没有相连的城市。
给你一个 n x n 的矩阵 isConnected ,其中 isConnected[i][j] = 1 表示第 i 个城市和第 j 个城市直接相连,而 isConnected[i][j] = 0 表示二者不直接相连。
返回矩阵中 省份 的数量。
示例 1:

输入:isConnected = [[1,1,0],[1,1,0],[0,0,1]] 输出:2
示例 2:

输入:isConnected = [[1,0,0],[0,1,0],[0,0,1]] 输出:3
提示:
1 <= n <= 200n == isConnected.lengthn == isConnected[i].lengthisConnected[i][j]为1或0isConnected[i][i] == 1isConnected[i][j] == isConnected[j][i]
通过代码
高赞题解
前言
连续两天都是并查集的题目,借此题来详细刨析一下
基本概念
并查集是一种数据结构
并查集这三个字,一个字代表一个意思。
并(Union),代表合并
查(Find),代表查找
集(Set),代表这是一个以字典为基础的数据结构,它的基本功能是合并集合中的元素,查找集合中的元素
并查集的典型应用是有关连通分量的问题
并查集解决单个问题(添加,合并,查找)的时间复杂度都是$O(1)$
因此,并查集可以应用到在线算法中
并查集的实现
数据结构
并查集跟树有些类似,只不过她跟树是相反的。在树这个数据结构里面,每个节点会记录它的子节点。在并查集里,每个节点会记录它的父节点。
[]class UnionFind: def __init__(self): """ 记录每个节点的父节点 """ self.father = {}
[]class UnionFind{ private: // 记录父节点 unordered_map<int,int> father; };
[]class UnionFind { private Map<Integer,Integer> father; }

可以看到,如果节点是相互连通的(从一个节点可以到达另一个节点),那么他们在同一棵树里,或者说在同一个集合里,或者说他们的祖先是相同的。
初始化
当把一个新节点添加到并查集中,它的父节点应该为空
[]def add(self,x): """ 添加新节点 """ if x not in self.father: self.father[x] = None
[]void add(int x){ if(!father.count(x)){ father[x] = -1; } }
[]public void add(int x) { if (!father.containsKey(x)) { father.put(x, null); } }
< ,
, >
>
合并两个节点
如果发现两个节点是连通的,那么就要把他们合并,也就是他们的祖先是相同的。这里究竟把谁当做父节点一般是没有区别的。
[]def merge(self,x,y,val): """ 合并两个节点 """ root_x,root_y = self.find(x),self.find(y) if root_x != root_y: self.father[root_x] = root_y
[]void merge(int x,int y){ int root_x = find(x); int root_y = find(y); if(root_x != root_y){ father[root_x] = root_y; } }
[]public void merge(int x, int y) { int rootX = find(x); int rootY = find(y); if (rootX != rootY){ father.put(rootX,rootY); } }
< ,
, ,
, >
>
两节点是否连通
我们判断两个节点是否处于同一个连通分量的时候,就需要判断它们的祖先是否相同
[]def is_connected(self,x,y): """ 判断两节点是否相连 """ return self.find(x) == self.find(y)
[]bool is_connected(int x,int y){ return find(x) == find(y); }
[]public boolean isConnected(int x, int y) { return find(x) == find(y); }
查找祖先
查找祖先的方法是:如果节点的父节点不为空,那就不断迭代。
[]def find(self,x): """ 查找根节点 """ root = x while self.father[root] != None: root = self.father[root] return root
[]int find(int x){ int root = x; while(father[root] != -1){ root = father[root]; } return root; }
[]public int find(int x) { int root = x; while(father.get(root) != null){ root = father.get(root); } return root; }
< ,
, ,
, ,
, >
>
这里有一个优化的点:如果我们树很深,比如说退化成链表,那么每次查询的效率都会非常低。所以我们要做一下路径压缩。也就是把树的深度固定为二。
这么做可行的原因是,并查集只是记录了节点之间的连通关系,而节点相互连通只需要有一个相同的祖先就可以了。
路径压缩可以用递归,也可以迭代。这里用迭代的方法。
< ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, >
>
[]def find(self,x): """ 查找根节点 路径压缩 """ root = x while self.father[root] != None: root = self.father[root] # 路径压缩 while x != root: original_father = self.father[x] self.father[x] = root x = original_father return root
[]int find(int x){ int root = x; while(father[root] != -1){ root = father[root]; } // 路径压缩 while(x != root){ int original_father = father[x]; father[x] = root; x = original_father; } return root; }
[]public int find(int x) { int root = x; while(father.get(root) != null){ root = father.get(root); } while(x != root){ int original_father = father.get(x); father.put(x,root); x = original_father; } return root; }
路径压缩的时间复杂度为$O(\log^*n)$
$\log^*n$ 表示 n 取多少次$\log_2n$并向下取整以后 变成 1
可以认为$O(\log^n) = O(1)$,因为$\log^2^{65536} = 5$,而$2^{65536}$是一个天文数字。这个时间复杂度当成结论记下就可以。
完整模板
[]class UnionFind: def __init__(self): """ 记录每个节点的父节点 """ self.father = {} def find(self,x): """ 查找根节点 路径压缩 """ root = x while self.father[root] != None: root = self.father[root] # 路径压缩 while x != root: original_father = self.father[x] self.father[x] = root x = original_father return root def merge(self,x,y,val): """ 合并两个节点 """ root_x,root_y = self.find(x),self.find(y) if root_x != root_y: self.father[root_x] = root_y def is_connected(self,x,y): """ 判断两节点是否相连 """ return self.find(x) == self.find(y) def add(self,x): """ 添加新节点 """ if x not in self.father: self.father[x] = None
[]class UnionFind{ public: int find(int x){ int root = x; while(father[root] != -1){ root = father[root]; } while(x != root){ int original_father = father[x]; father[x] = root; x = original_father; } return root; } bool is_connected(int x,int y){ return find(x) == find(y); } void merge(int x,int y){ int root_x = find(x); int root_y = find(y); if(root_x != root_y){ father[root_x] = root_y; } } void add(int x){ if(!father.count(x)){ father[x] = -1; } } private: // 记录父节点 unordered_map<int,int> father; };
[]class UnionFind { private Map<Integer,Integer> father; public UnionFind() { father = new HashMap<Integer,Integer>(); } public void add(int x) { if (!father.containsKey(x)) { father.put(x, null); } } public void merge(int x, int y) { int rootX = find(x); int rootY = find(y); if (rootX != rootY){ father.put(rootX,rootY); } } public int find(int x) { int root = x; while(father.get(root) != null){ root = father.get(root); } while(x != root){ int original_father = father.get(x); father.put(x,root); x = original_father; } return root; } public boolean isConnected(int x, int y) { return find(x) == find(y); } }
以上就是并查集的基本模板,根据不同的题目要求进行对应的添加即可。
今天的题目
今天的题目就是在考察连通分量的数目,所以我们要在模板中额外添加一个变量去跟踪集合的数量(有多少棵树)。
初始化的时候把集合数量加一
合并的时候让集合数量减一
[]class UnionFind: def __init__(self): self.father = {} # 额外记录集合的数量 self.num_of_sets = 0 def find(self,x): root = x while self.father[root] != None: root = self.father[root] while x != root: original_father = self.father[x] self.father[x] = root x = original_father return root def merge(self,x,y): root_x,root_y = self.find(x),self.find(y) if root_x != root_y: self.father[root_x] = root_y # 集合的数量-1 self.num_of_sets -= 1 def add(self,x): if x not in self.father: self.father[x] = None # 集合的数量+1 self.num_of_sets += 1 class Solution: def findCircleNum(self, M: List[List[int]]) -> int: uf = UnionFind() for i in range(len(M)): uf.add(i) for j in range(i): if M[i][j]: uf.merge(i,j) return uf.num_of_sets
[]class UnionFind{ public: int find(int x){ int root = x; while(father[root] != -1){ root = father[root]; } while(x != root){ int original_father = father[x]; father[x] = root; x = original_father; } return root; } bool is_connected(int x,int y){ return find(x) == find(y); } void merge(int x,int y){ int root_x = find(x); int root_y = find(y); if(root_x != root_y){ father[root_x] = root_y; num_of_sets--; } } void add(int x){ if(!father.count(x)){ father[x] = -1; num_of_sets++; } } int get_num_of_sets(){ return num_of_sets; } private: // 记录父节点 unordered_map<int,int> father; // 记录集合数量 int num_of_sets = 0; }; class Solution { public: int findCircleNum(vector<vector<int>>& isConnected) { UnionFind uf; for(int i = 0;i < isConnected.size();i++){ uf.add(i); for(int j = 0;j < i;j++){ if(isConnected[i][j]){ uf.merge(i,j); } } } return uf.get_num_of_sets(); } };
[]class UnionFind { // 记录父节点 private Map<Integer,Integer> father; // 记录集合的数量 private int numOfSets = 0; public UnionFind() { father = new HashMap<Integer,Integer>(); numOfSets = 0; } public void add(int x) { if (!father.containsKey(x)) { father.put(x, null); numOfSets++; } } public void merge(int x, int y) { int rootX = find(x); int rootY = find(y); if (rootX != rootY){ father.put(rootX,rootY); numOfSets--; } } public int find(int x) { int root = x; while(father.get(root) != null){ root = father.get(root); } while(x != root){ int original_father = father.get(x); father.put(x,root); x = original_father; } return root; } public boolean isConnected(int x, int y) { return find(x) == find(y); } public int getNumOfSets() { return numOfSets; } } class Solution { public int findCircleNum(int[][] isConnected) { UnionFind uf = new UnionFind(); for(int i = 0;i < isConnected.length;i++){ uf.add(i); for(int j = 0;j < i;j++){ if(isConnected[i][j] == 1){ uf.merge(i,j); } } } return uf.getNumOfSets(); } }
相关题目
模板题:
在线算法:
其他:
统计信息
| 通过次数 | 提交次数 | AC比率 |
|---|---|---|
| 173475 | 280350 | 61.9% |
提交历史
| 提交时间 | 提交结果 | 执行时间 | 内存消耗 | 语言 |
|---|
相似题目
| 题目 | 难度 |
|---|---|
| 无向图中连通分量的数目 | 中等 |
| 机器人能否返回原点 | 简单 |
| 句子相似性 | 简单 |
| 句子相似性 II | 中等 |
| 彼此熟识的最早时间 | 中等 |




