原文链接: https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/logical-or-of-two-binary-grids-represented-as-quad-trees
英文原文
A Binary Matrix is a matrix in which all the elements are either 0 or 1.
Given quadTree1 and quadTree2. quadTree1 represents a n * n binary matrix and quadTree2 represents another n * n binary matrix.
Return a Quad-Tree representing the n * n binary matrix which is the result of logical bitwise OR of the two binary matrixes represented by quadTree1 and quadTree2.
Notice that you can assign the value of a node to True or False when isLeaf is False, and both are accepted in the answer.
A Quad-Tree is a tree data structure in which each internal node has exactly four children. Besides, each node has two attributes:
val: True if the node represents a grid of 1's or False if the node represents a grid of 0's.isLeaf: True if the node is leaf node on the tree or False if the node has the four children.
class Node {
public boolean val;
public boolean isLeaf;
public Node topLeft;
public Node topRight;
public Node bottomLeft;
public Node bottomRight;
}
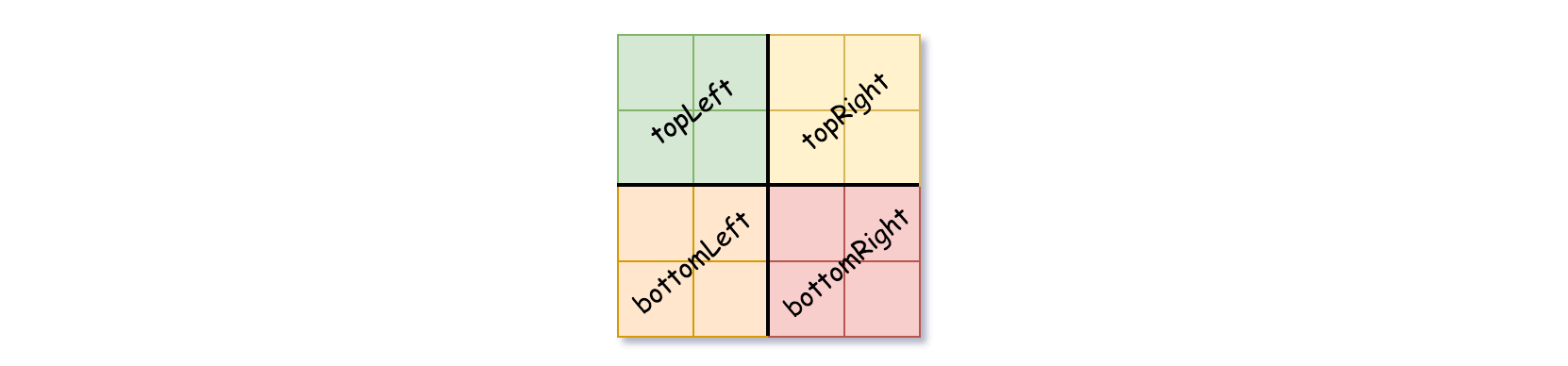
We can construct a Quad-Tree from a two-dimensional area using the following steps:
- If the current grid has the same value (i.e all
1'sor all0's) setisLeafTrue and setvalto the value of the grid and set the four children to Null and stop. - If the current grid has different values, set
isLeafto False and setvalto any value and divide the current grid into four sub-grids as shown in the photo. - Recurse for each of the children with the proper sub-grid.
If you want to know more about the Quad-Tree, you can refer to the wiki.
Quad-Tree format:
The input/output represents the serialized format of a Quad-Tree using level order traversal, where null signifies a path terminator where no node exists below.
It is very similar to the serialization of the binary tree. The only difference is that the node is represented as a list [isLeaf, val].
If the value of isLeaf or val is True we represent it as 1 in the list [isLeaf, val] and if the value of isLeaf or val is False we represent it as 0.
Example 1:
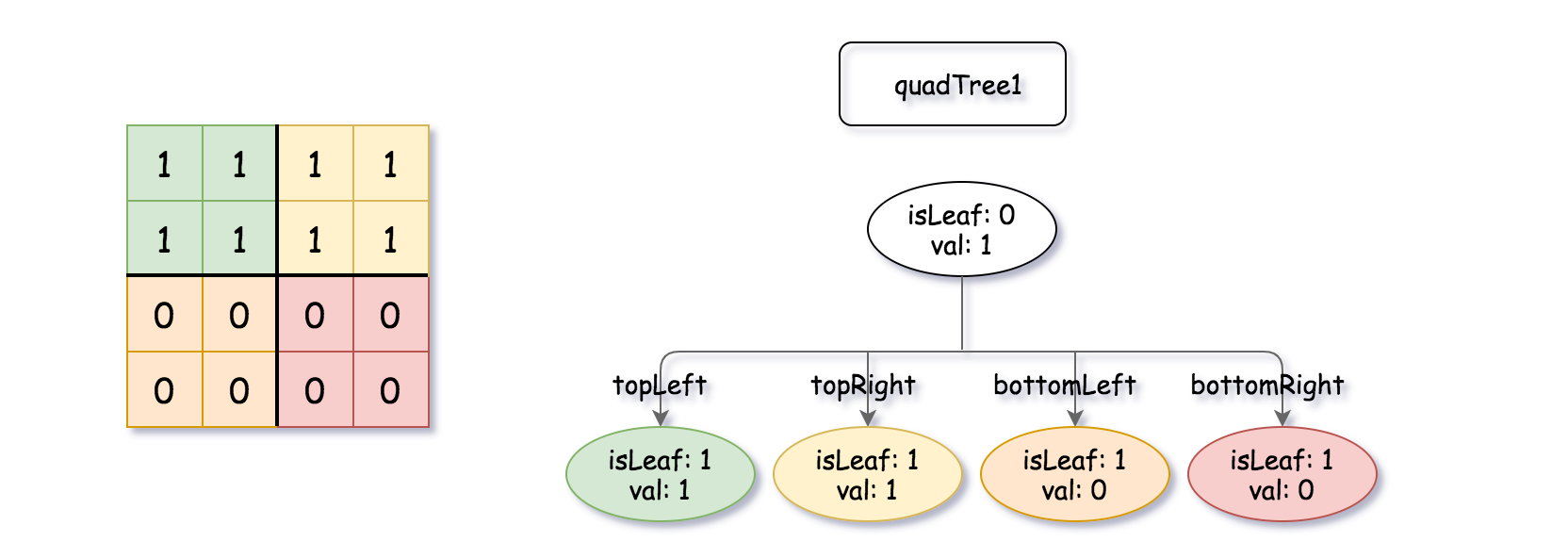
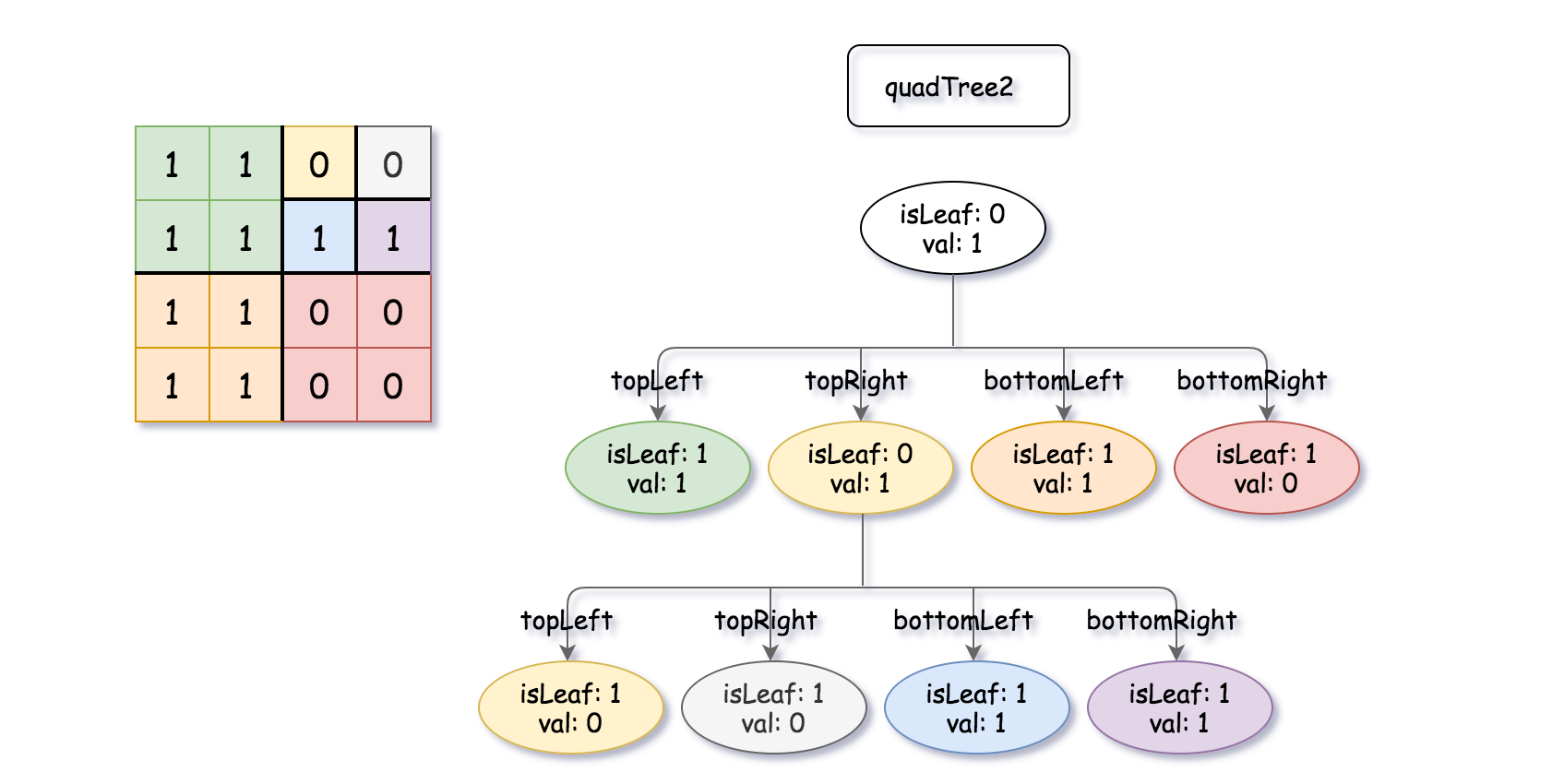
Input: quadTree1 = [[0,1],[1,1],[1,1],[1,0],[1,0]] , quadTree2 = [[0,1],[1,1],[0,1],[1,1],[1,0],null,null,null,null,[1,0],[1,0],[1,1],[1,1]] Output: [[0,0],[1,1],[1,1],[1,1],[1,0]] Explanation: quadTree1 and quadTree2 are shown above. You can see the binary matrix which is represented by each Quad-Tree. If we apply logical bitwise OR on the two binary matrices we get the binary matrix below which is represented by the result Quad-Tree. Notice that the binary matrices shown are only for illustration, you don't have to construct the binary matrix to get the result tree.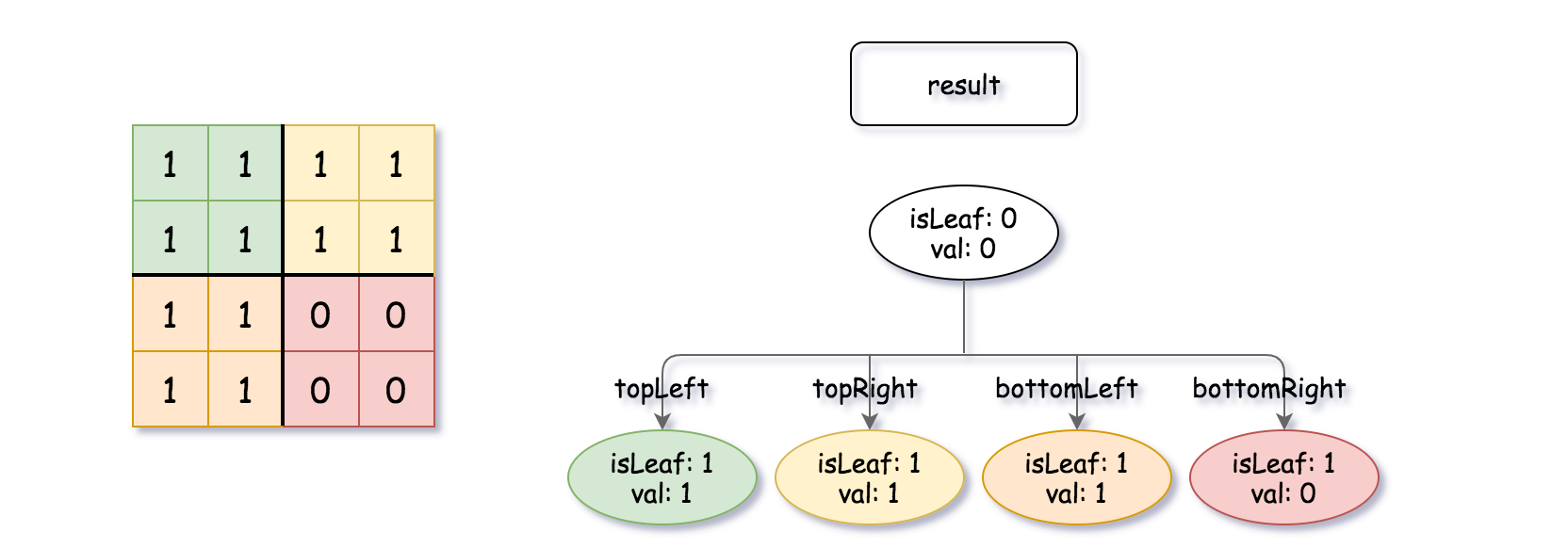
Example 2:
Input: quadTree1 = [[1,0]] , quadTree2 = [[1,0]] Output: [[1,0]] Explanation: Each tree represents a binary matrix of size 1*1. Each matrix contains only zero. The resulting matrix is of size 1*1 with also zero.
Example 3:
Input: quadTree1 = [[0,0],[1,0],[1,0],[1,1],[1,1]] , quadTree2 = [[0,0],[1,1],[1,1],[1,0],[1,1]] Output: [[1,1]]
Example 4:
Input: quadTree1 = [[0,0],[1,1],[1,0],[1,1],[1,1]] , quadTree2 = [[0,0],[1,1],[0,1],[1,1],[1,1],null,null,null,null,[1,1],[1,0],[1,0],[1,1]] Output: [[0,0],[1,1],[0,1],[1,1],[1,1],null,null,null,null,[1,1],[1,0],[1,0],[1,1]]
Example 5:
Input: quadTree1 = [[0,1],[1,0],[0,1],[1,1],[1,0],null,null,null,null,[1,0],[1,0],[1,1],[1,1]] , quadTree2 = [[0,1],[0,1],[1,0],[1,1],[1,0],[1,0],[1,0],[1,1],[1,1]] Output: [[0,0],[0,1],[0,1],[1,1],[1,0],[1,0],[1,0],[1,1],[1,1],[1,0],[1,0],[1,1],[1,1]]
Constraints:
quadTree1andquadTree2are both valid Quad-Trees each representing an * ngrid.n == 2^xwhere0 <= x <= 9.
中文题目
二进制矩阵中的所有元素不是 0 就是 1 。
给你两个四叉树,quadTree1 和 quadTree2。其中 quadTree1 表示一个 n * n 二进制矩阵,而 quadTree2 表示另一个 n * n 二进制矩阵。
请你返回一个表示 n * n 二进制矩阵的四叉树,它是 quadTree1 和 quadTree2 所表示的两个二进制矩阵进行 按位逻辑或运算 的结果。
注意,当 isLeaf 为 False 时,你可以把 True 或者 False 赋值给节点,两种值都会被判题机制 接受 。
四叉树数据结构中,每个内部节点只有四个子节点。此外,每个节点都有两个属性:
val:储存叶子结点所代表的区域的值。1 对应 True,0 对应 False;isLeaf: 当这个节点是一个叶子结点时为 True,如果它有 4 个子节点则为 False 。
class Node {
public boolean val;
public boolean isLeaf;
public Node topLeft;
public Node topRight;
public Node bottomLeft;
public Node bottomRight;
}
我们可以按以下步骤为二维区域构建四叉树:
- 如果当前网格的值相同(即,全为
0或者全为1),将isLeaf设为 True ,将val设为网格相应的值,并将四个子节点都设为 Null 然后停止。 - 如果当前网格的值不同,将
isLeaf设为 False, 将val设为任意值,然后如下图所示,将当前网格划分为四个子网格。 - 使用适当的子网格递归每个子节点。

如果你想了解更多关于四叉树的内容,可以参考 wiki 。
四叉树格式:
输出为使用层序遍历后四叉树的序列化形式,其中 null 表示路径终止符,其下面不存在节点。
它与二叉树的序列化非常相似。唯一的区别是节点以列表形式表示 [isLeaf, val] 。
如果 isLeaf 或者 val 的值为 True ,则表示它在列表 [isLeaf, val] 中的值为 1 ;如果 isLeaf 或者 val 的值为 False ,则表示值为 0 。
示例 1:


输入:quadTree1 = [[0,1],[1,1],[1,1],[1,0],[1,0]] , quadTree2 = [[0,1],[1,1],[0,1],[1,1],[1,0],null,null,null,null,[1,0],[1,0],[1,1],[1,1]] 输出:[[0,0],[1,1],[1,1],[1,1],[1,0]] 解释:quadTree1 和 quadTree2 如上所示。由四叉树所表示的二进制矩阵也已经给出。 如果我们对这两个矩阵进行按位逻辑或运算,则可以得到下面的二进制矩阵,由一个作为结果的四叉树表示。 注意,我们展示的二进制矩阵仅仅是为了更好地说明题意,你无需构造二进制矩阵来获得结果四叉树。
示例 2:
输入:quadTree1 = [[1,0]] , quadTree2 = [[1,0]] 输出:[[1,0]] 解释:两个数所表示的矩阵大小都为 1*1,值全为 0 结果矩阵大小为 1*1,值全为 0 。
示例 3:
输入:quadTree1 = [[0,0],[1,0],[1,0],[1,1],[1,1]] , quadTree2 = [[0,0],[1,1],[1,1],[1,0],[1,1]] 输出:[[1,1]]
示例 4:
输入:quadTree1 = [[0,0],[1,1],[1,0],[1,1],[1,1]] , quadTree2 = [[0,0],[1,1],[0,1],[1,1],[1,1],null,null,null,null,[1,1],[1,0],[1,0],[1,1]] 输出:[[0,0],[1,1],[0,1],[1,1],[1,1],null,null,null,null,[1,1],[1,0],[1,0],[1,1]]
示例 5:
输入:quadTree1 = [[0,1],[1,0],[0,1],[1,1],[1,0],null,null,null,null,[1,0],[1,0],[1,1],[1,1]] , quadTree2 = [[0,1],[0,1],[1,0],[1,1],[1,0],[1,0],[1,0],[1,1],[1,1]] 输出:[[0,0],[0,1],[0,1],[1,1],[1,0],[1,0],[1,0],[1,1],[1,1],[1,0],[1,0],[1,1],[1,1]]
提示:
quadTree1和quadTree2都是符合题目要求的四叉树,每个都代表一个n * n的矩阵。n == 2^x,其中0 <= x <= 9.
通过代码
高赞题解
A || B 的意思是指
- 如果A为叶子节点,并且A的值等于true, 这时直接返回true, 不用管B
- 如果A为叶子节点,但是A的值等于false, 这时直接返回B就可以了(*注意 即使B不是一个叶子节点,也要直接返回, 可以参照后面的图片)
- 如果A不为叶子节点, 原理一样,这时看B, 如果B为叶子节点,并且B的值为true, 则直接返回true, 不用管A
- 如果A不为叶子节点, B为叶子节点,并且B的值为false, 这时直接返回A
- 如果A和B都不为叶子节点, 这时分别再讲A, B的四个子节点传入下一次递归计算结果
- 最后, 如果A和B的四个子节点的值都会true的话, 这时需要进行合并为一个节点。

代码示例
class Solution {
public:
Node* intersect(Node* quadTree1, Node* quadTree2) {
if (quadTree1->isLeaf) { // 1.如果A是叶子节点
if (quadTree1->val) { // 2.如果A的值为true则直接返回A树
return quadTree1;
}
else {
return quadTree2; // 3.A为叶子但A的值为false, 则返回B树
}
}
if (quadTree2->isLeaf) { // 4.如果B是叶子节点
if (quadTree2->val) { // 5.如果B的值为true则直接返回B树
return quadTree2;
}
else {
return quadTree1; // 6.B为叶子节点,但B的值为false,则返回A树
}
}
// 7.A和B都不为叶子节点的情况下,分别递归获取四个方向的子节点
Node* topLeft = intersect(quadTree1->topLeft, quadTree2->topLeft);
Node* topRight = intersect(quadTree1->topRight, quadTree2->topRight);
Node* bottomLeft = intersect(quadTree1->bottomLeft, quadTree2->bottomLeft);
Node* bottomRight = intersect(quadTree1->bottomRight, quadTree2->bottomRight);
// 8.如果四个节点同时为叶子节点。并且值为true时,则返回的节点进行合并,合并为一个值为true的叶子节点
if (topLeft->isLeaf && topRight->isLeaf && bottomLeft->isLeaf && bottomRight->isLeaf &&
topLeft->val && topRight->val && bottomLeft->val && bottomRight->val) {
return new Node(true, true, NULL, NULL, NULL, NULL);
}
// 9. 通过第7步获取得四个方位的节点,构造出一个新的节点树
return new Node(false, false, topLeft, topRight, bottomLeft, bottomRight);
}
};统计信息
| 通过次数 | 提交次数 | AC比率 |
|---|---|---|
| 3053 | 6055 | 50.4% |
提交历史
| 提交时间 | 提交结果 | 执行时间 | 内存消耗 | 语言 |
|---|




