英文原文
Given the head of a linked list, rotate the list to the right by k places.
Example 1:
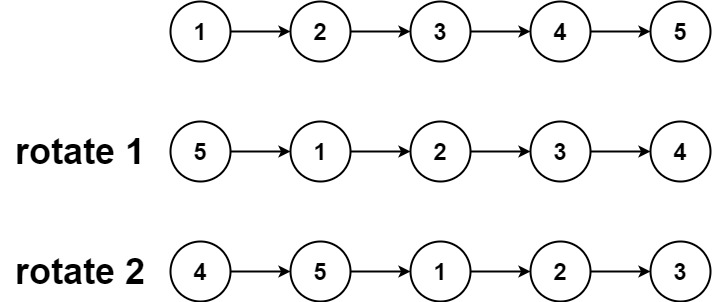
Input: head = [1,2,3,4,5], k = 2 Output: [4,5,1,2,3]
Example 2:
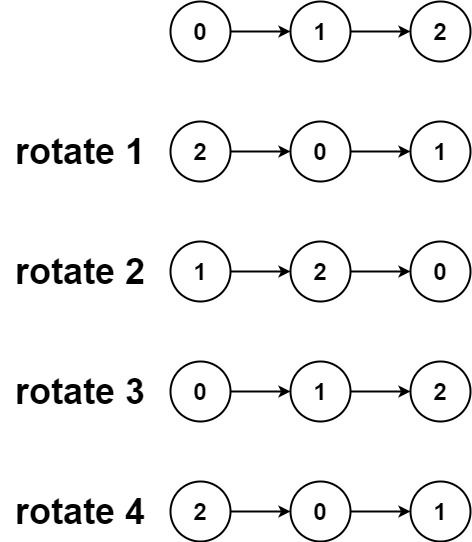
Input: head = [0,1,2], k = 4 Output: [2,0,1]
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the list is in the range
[0, 500]. -100 <= Node.val <= 1000 <= k <= 2 * 109
中文题目
给你一个链表的头节点 head ,旋转链表,将链表每个节点向右移动 k 个位置。
示例 1:

输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5], k = 2 输出:[4,5,1,2,3]
示例 2:

输入:head = [0,1,2], k = 4 输出:[2,0,1]
提示:
- 链表中节点的数目在范围
[0, 500]内 -100 <= Node.val <= 1000 <= k <= 2 * 109
通过代码
高赞题解
方法一:闭合为环
思路及算法
记给定链表的长度为 $n$,注意到当向右移动的次数 $k \geq n$ 时,我们仅需要向右移动 $k \bmod n$ 次即可。因为每 $n$ 次移动都会让链表变为原状。这样我们可以知道,新链表的最后一个节点为原链表的第 $(n - 1) - (k \bmod n)$ 个节点(从 $0$ 开始计数)。
这样,我们可以先将给定的链表连接成环,然后将指定位置断开。
具体代码中,我们首先计算出链表的长度 $n$,并找到该链表的末尾节点,将其与头节点相连。这样就得到了闭合为环的链表。然后我们找到新链表的最后一个节点(即原链表的第 $(n - 1) - (k \bmod n)$ 个节点),将当前闭合为环的链表断开,即可得到我们所需要的结果。
特别地,当链表长度不大于 $1$,或者 $k$ 为 $n$ 的倍数时,新链表将与原链表相同,我们无需进行任何处理。
代码
[sol1-C++]class Solution { public: ListNode* rotateRight(ListNode* head, int k) { if (k == 0 || head == nullptr || head->next == nullptr) { return head; } int n = 1; ListNode* iter = head; while (iter->next != nullptr) { iter = iter->next; n++; } int add = n - k % n; if (add == n) { return head; } iter->next = head; while (add--) { iter = iter->next; } ListNode* ret = iter->next; iter->next = nullptr; return ret; } };
[sol1-Java]class Solution { public ListNode rotateRight(ListNode head, int k) { if (k == 0 || head == null || head.next == null) { return head; } int n = 1; ListNode iter = head; while (iter.next != null) { iter = iter.next; n++; } int add = n - k % n; if (add == n) { return head; } iter.next = head; while (add-- > 0) { iter = iter.next; } ListNode ret = iter.next; iter.next = null; return ret; } }
[sol1-Python3]class Solution: def rotateRight(self, head: ListNode, k: int) -> ListNode: if k == 0 or not head or not head.next: return head n = 1 cur = head while cur.next: cur = cur.next n += 1 if (add := n - k % n) == n: return head cur.next = head while add: cur = cur.next add -= 1 ret = cur.next cur.next = None return ret
[sol1-JavaScript]var rotateRight = function(head, k) { if (k === 0 || !head || !head.next) { return head; } let n = 1; let cur = head; while (cur.next) { cur = cur.next; n++; } let add = n - k % n; if (add === n) { return head; } cur.next = head; while (add) { cur = cur.next; add--; } const ret = cur.next; cur.next = null; return ret; };
[sol1-Golang]func rotateRight(head *ListNode, k int) *ListNode { if k == 0 || head == nil || head.Next == nil { return head } n := 1 iter := head for iter.Next != nil { iter = iter.Next n++ } add := n - k%n if add == n { return head } iter.Next = head for add > 0 { iter = iter.Next add-- } ret := iter.Next iter.Next = nil return ret }
[sol1-C]struct ListNode* rotateRight(struct ListNode* head, int k) { if (k == 0 || head == NULL || head->next == NULL) { return head; } int n = 1; struct ListNode* iter = head; while (iter->next != NULL) { iter = iter->next; n++; } int add = n - k % n; if (add == n) { return head; } iter->next = head; while (add--) { iter = iter->next; } struct ListNode* ret = iter->next; iter->next = NULL; return ret; }
复杂度分析
时间复杂度:$O(n)$,最坏情况下,我们需要遍历该链表两次。
空间复杂度:$O(1)$,我们只需要常数的空间存储若干变量。
统计信息
| 通过次数 | 提交次数 | AC比率 |
|---|---|---|
| 209466 | 501529 | 41.8% |
提交历史
| 提交时间 | 提交结果 | 执行时间 | 内存消耗 | 语言 |
|---|
相似题目
| 题目 | 难度 |
|---|---|
| 轮转数组 | 中等 |
| 分隔链表 | 中等 |




