英文原文
Given the root of a binary tree and two integers val and depth, add a row of nodes with value val at the given depth depth.
Note that the root node is at depth 1.
The adding rule is:
- Given the integer
depth, for each not null tree nodecurat the depthdepth - 1, create two tree nodes with valuevalascur's left subtree root and right subtree root. cur's original left subtree should be the left subtree of the new left subtree root.cur's original right subtree should be the right subtree of the new right subtree root.- If
depth == 1that means there is no depthdepth - 1at all, then create a tree node with valuevalas the new root of the whole original tree, and the original tree is the new root's left subtree.
Example 1:
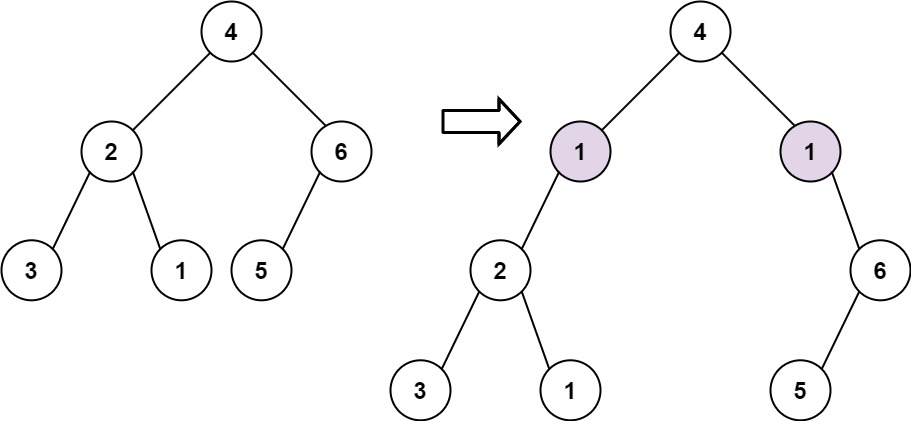
Input: root = [4,2,6,3,1,5], val = 1, depth = 2 Output: [4,1,1,2,null,null,6,3,1,5]
Example 2:
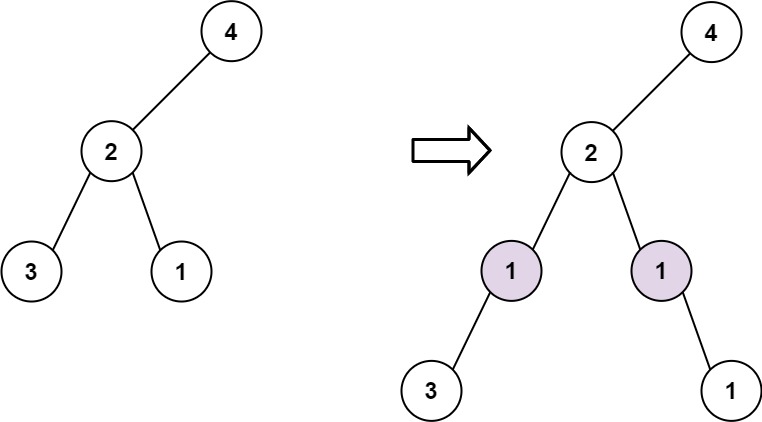
Input: root = [4,2,null,3,1], val = 1, depth = 3 Output: [4,2,null,1,1,3,null,null,1]
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[1, 104]. - The depth of the tree is in the range
[1, 104]. -100 <= Node.val <= 100-105 <= val <= 1051 <= depth <= the depth of tree + 1
中文题目
给定一个二叉树,根节点为第1层,深度为 1。在其第 d 层追加一行值为 v 的节点。
添加规则:给定一个深度值 d (正整数),针对深度为 d-1 层的每一非空节点 N,为 N 创建两个值为 v 的左子树和右子树。
将 N 原先的左子树,连接为新节点 v 的左子树;将 N 原先的右子树,连接为新节点 v 的右子树。
如果 d 的值为 1,深度 d - 1 不存在,则创建一个新的根节点 v,原先的整棵树将作为 v 的左子树。
示例 1:
输入:
二叉树如下所示:
4
/ \
2 6
/ \ /
3 1 5
v = 1
d = 2
输出:
4
/ \
1 1
/ \
2 6
/ \ /
3 1 5
示例 2:
输入:
二叉树如下所示:
4
/
2
/ \
3 1
v = 1
d = 3
输出:
4
/
2
/ \
1 1
/ \
3 1
注意:
- 输入的深度值 d 的范围是:[1,二叉树最大深度 + 1]。
- 输入的二叉树至少有一个节点。
通过代码
官方题解
方法一:深度优先搜索(递归)
如果 d 的值为 1,我们就添加一个节点,并将整棵树作为新节点的左子树。否则我们可以使用深度优先搜索找出所有 d 层的节点并进行操作。在搜索时,我们需要记录当前节点的深度 depth,如果此时 depth == d - 1,那么我们需要在当前节点的左右孩子各增加一个节点。如果当前节点的左右孩子已经有节点,我们就将这些节点存储到临时变量中,在增加新节点后再把左右孩子作为新节点的左子树或右子树,并结束递归。如果 depth != d - 1,我们就需要对当前节点的子节点进行递归搜索。
< ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, >
>
[sol1]/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * public class TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode left; * TreeNode right; * TreeNode(int x) { val = x; } * } */ public class Solution { public TreeNode addOneRow(TreeNode t, int v, int d) { if (d == 1) { TreeNode n = new TreeNode(v); n.left = t; return n; } insert(v, t, 1, d); return t; } public void insert(int val, TreeNode node, int depth, int n) { if (node == null) return; if (depth == n - 1) { TreeNode t = node.left; node.left = new TreeNode(val); node.left.left = t; t = node.right; node.right = new TreeNode(val); node.right.right = t; } else { insert(val, node.left, depth + 1, n); insert(val, node.right, depth + 1, n); } } }
复杂度分析
时间复杂度:$O(N)$,其中 $N$ 是二叉树的节点个数。我们最多会遍历 $N$ 个节点。
空间复杂度:$O(N)$。在最坏情况下,需要递归 $N$ 层,用到 $O(N)$ 的栈空间。
方法二:深度优先搜索(非递归)
我们可以直接用栈来模拟递归,实现深度优先搜索的非递归版本。
我们首先将根节点入栈,随后每次栈顶的元素即为当前搜索到的结点,我们取出这个节点,根据 depth 和 d - 1 的关系为当前节点增加新的子节点,或者将当前节点的子节点全部入栈,继续搜索。
< ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, >
>
[sol2]/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * public class TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode left; * TreeNode right; * TreeNode(int x) { val = x; } * } */ public class Solution { class Node{ Node(TreeNode n,int d){ node=n; depth=d; } TreeNode node; int depth; } public TreeNode addOneRow(TreeNode t, int v, int d) { if (d == 1) { TreeNode n = new TreeNode(v); n.left = t; return n; } Stack<Node> stack=new Stack<>(); stack.push(new Node(t,1)); while(!stack.isEmpty()) { Node n=stack.pop(); if(n.node==null) continue; if (n.depth == d - 1 ) { TreeNode temp = n.node.left; n.node.left = new TreeNode(v); n.node.left.left = temp; temp = n.node.right; n.node.right = new TreeNode(v); n.node.right.right = temp; } else{ stack.push(new Node(n.node.left, n.depth + 1)); stack.push(new Node(n.node.right, n.depth + 1)); } } return t; } }
复杂度分析
时间复杂度:$O(N)$,其中 $N$ 是二叉树的节点个数。我们最多会遍历 $N$ 个节点。
空间复杂度:$O(N)$。
方法三:广度优先搜索
我们同样可以使用广度优先搜索解决这个问题,并且广度优先搜索是最容易理解且最直观的一种方法。
我们将根节点放入队列 queue。在每一轮搜索中,如果 queue 中节点的深度为 d - 1(显然 queue 中所有的节点都在同一深度),我们就退出搜索,并为 queue 中所有节点添加新的子节点;否则我们将 queue 中所有节点的子节点放入新的队列 temp 中,再用 temp 替代 queue。
< ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, >
>
[sol3]/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * public class TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode left; * TreeNode right; * TreeNode(int x) { val = x; } * } */ public class Solution { public TreeNode addOneRow(TreeNode t, int v, int d) { if (d == 1) { TreeNode n = new TreeNode(v); n.left = t; return n; } Queue < TreeNode > queue = new LinkedList < > (); queue.add(t); int depth = 1; while (depth < d - 1) { Queue < TreeNode > temp = new LinkedList < > (); while (!queue.isEmpty()) { TreeNode node = queue.remove(); if (node.left != null) temp.add(node.left); if (node.right != null) temp.add(node.right); } queue = temp; depth++; } while (!queue.isEmpty()) { TreeNode node = queue.remove(); TreeNode temp = node.left; node.left = new TreeNode(v); node.left.left = temp; temp = node.right; node.right = new TreeNode(v); node.right.right = temp; } return t; } }
复杂度分析s
时间复杂度:$O(N)$,其中 $N$ 是二叉树的节点个数。我们最多会遍历 $N$ 个节点。
空间复杂度:$O(N)$。
统计信息
| 通过次数 | 提交次数 | AC比率 |
|---|---|---|
| 11688 | 21420 | 54.6% |
提交历史
| 提交时间 | 提交结果 | 执行时间 | 内存消耗 | 语言 |
|---|




