英文原文
Given the root of a binary tree, construct a 0-indexed m x n string matrix res that represents a formatted layout of the tree. The formatted layout matrix should be constructed using the following rules:
- The height of the tree is
heightand the number of rowsmshould be equal toheight + 1. - The number of columns
nshould be equal to2height+1 - 1. - Place the root node in the middle of the top row (more formally, at location
res[0][(n-1)/2]). - For each node that has been placed in the matrix at position
res[r][c], place its left child atres[r+1][c-2height-r-1]and its right child atres[r+1][c+2height-r-1]. - Continue this process until all the nodes in the tree have been placed.
- Any empty cells should contain the empty string
"".
Return the constructed matrix res.
Example 1:
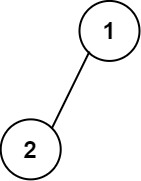
Input: root = [1,2] Output: [["","1",""], ["2","",""]]
Example 2:
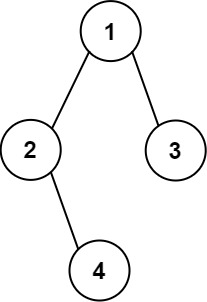
Input: root = [1,2,3,null,4] Output: [["","","","1","","",""], ["","2","","","","3",""], ["","","4","","","",""]]
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[1, 210]. -99 <= Node.val <= 99- The depth of the tree will be in the range
[1, 10].
中文题目
在一个 m*n 的二维字符串数组中输出二叉树,并遵守以下规则:
- 行数
m应当等于给定二叉树的高度。 - 列数
n应当总是奇数。 - 根节点的值(以字符串格式给出)应当放在可放置的第一行正中间。根节点所在的行与列会将剩余空间划分为两部分(左下部分和右下部分)。你应该将左子树输出在左下部分,右子树输出在右下部分。左下和右下部分应当有相同的大小。即使一个子树为空而另一个非空,你不需要为空的子树输出任何东西,但仍需要为另一个子树留出足够的空间。然而,如果两个子树都为空则不需要为它们留出任何空间。
- 每个未使用的空间应包含一个空的字符串
""。 - 使用相同的规则输出子树。
示例 1:
输入:
1
/
2
输出:
[["", "1", ""],
["2", "", ""]]
示例 2:
输入:
1
/ \
2 3
\
4
输出:
[["", "", "", "1", "", "", ""],
["", "2", "", "", "", "3", ""],
["", "", "4", "", "", "", ""]]
示例 3:
输入:
1
/ \
2 5
/
3
/
4
输出:
[["", "", "", "", "", "", "", "1", "", "", "", "", "", "", ""]
["", "", "", "2", "", "", "", "", "", "", "", "5", "", "", ""]
["", "3", "", "", "", "", "", "", "", "", "", "", "", "", ""]
["4", "", "", "", "", "", "", "", "", "", "", "", "", "", ""]]
注意: 二叉树的高度在范围 [1, 10] 中。
通过代码
官方题解
方法一:递归【通过】
创建一个长度为 $height\times(2^{height}-1)$ 的数组 $res$,其中 $height$ 是树的高度。先使用空字符串 "" 填充数组 $res$。然后递归调用 fill(res, root, i, l, r) 将节点的值输出到数组 $res$ 中,其中 $i$ 表示当前节点所在层数,$l$ 和 $r$ 表示当前子树在数组 $res$ 中的左右边界,当前节点被输出到数组 $res$ 第 $i$ 行的第 $l$ 列和第 $r$ 列中间位置上。
在递归方法中,执行以下步骤:
如果到达树的末尾,即
root = null,直接返回。确定当前节点所在的列 $j=(l+r)/2$。将当前节点输出到数组 $res$ 的第 $i$ 行第 $j$ 列,即 $res[i][j]$。
递归调用
fill(res, root.left, i + 1, l, (l + r) / 2),输出 $root$ 的左子树。递归调用
fill(res, root.right, i + 1, (l + r + 1) / 2, r),输出 $root$ 的右子树。
注意:在第三步和第四步的递归调用中需要更新行号,确保子节点可以输出的正确的位置。另外,也要根据 $l$ 和 $r$ 更新子树的左右边界。
另外,创建方法 getHeight(root), 用于计算 $root$ 为根节点的树高度 $height$。递归遍历树的所有分支,从中找出最深的一个分支作为树的高度。
最后,将数组 $res$ 转换成题目要求格式。
[solution1-Java]public class Solution { public List<List<String>> printTree(TreeNode root) { int height = getHeight(root); String[][] res = new String[height][(1 << height) - 1]; for(String[] arr:res) Arrays.fill(arr,""); List<List<String>> ans = new ArrayList<>(); fill(res, root, 0, 0, res[0].length); for(String[] arr:res) ans.add(Arrays.asList(arr)); return ans; } public void fill(String[][] res, TreeNode root, int i, int l, int r) { if (root == null) return; res[i][(l + r) / 2] = "" + root.val; fill(res, root.left, i + 1, l, (l + r) / 2); fill(res, root.right, i + 1, (l + r + 1) / 2, r); } public int getHeight(TreeNode root) { if (root == null) return 0; return 1 + Math.max(getHeight(root.left), getHeight(root.right)); } }
复杂度分析
时间复杂度:$O(h*2^h)$,其中 $h$ 是树的高度,填充长度为 $h\times(2^h-1)$ 的数组 $res$。
空间复杂度:$O(h*2^h)$,数组 $res$ 的长度为 $h\times(2^h-1)$。
方法二:使用队列(BFS) 【通过】
算法
也可以使用广度优先搜索解决该问题。使用类 $Params$ 存储树的节点 $node$,类中包含该节点的值,所在层数 $i$,和以该节点为根的子树的左边界 $l$ 和右边界 $r$。
初始化一个与 方法一 用途相同的数组 $res$,将根节点 $root$ 加入到队列 $queue$ 中,然后执行以下步骤。
从队列中移除元素 $p$。
将该元素的值输出到 $res[p.i][(p.l + p.r) / 2]$,其中 $i$ 表示当前节点的所在行,$l$ 和 $r$ 表示当前子树的左右边界。这些值都是在节点加入 $queue$ 之前就已经计算好的。
如果节点 $p$ 有左孩子,则将它的左孩子加入到 $queue$,同时计算左孩子的所在行,和以该节点为根的子树的左右边界。
如果节点 $p$ 有右孩子,则将它的右孩子加入到 $queue$,同时计算右孩子的所在行,和以该节点为根的子树的左右边界。
回复步骤一到四,直到 $queue$ 为空。
最后,将数组 $res$ 转换为题目要求的格式返回。
[solution2-Java]public class Solution /** * Definition for a binary tree node. * public class TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode left; * TreeNode right; * TreeNode(int x) { val = x; } * } */ public class Solution { class Params { Params(TreeNode n, int ii, int ll, int rr) { root = n; i = ii; l = ll; r = rr; } TreeNode root; int i, l, r; } public List < List < String >> printTree(TreeNode root) { int height = getHeight(root); System.out.println(height); String[][] res = new String[height][(1 << height) - 1]; for (String[] arr: res) Arrays.fill(arr, ""); List < List < String >> ans = new ArrayList < > (); fill(res, root, 0, 0, res[0].length); for (String[] arr: res) ans.add(Arrays.asList(arr)); return ans; } public void fill(String[][] res, TreeNode root, int i, int l, int r) { Queue < Params > queue = new LinkedList(); queue.add(new Params(root, 0, 0, res[0].length)); while (!queue.isEmpty()) { Params p = queue.remove(); res[p.i][(p.l + p.r) / 2] = "" + p.root.val; if (p.root.left != null) queue.add(new Params(p.root.left, p.i + 1, p.l, (p.l + p.r) / 2)); if (p.root.right != null) queue.add(new Params(p.root.right, p.i + 1, (p.l + p.r + 1) / 2, p.r)); } } public int getHeight(TreeNode root) { Queue < TreeNode > queue = new LinkedList(); queue.add(root); int height = 0; while (!queue.isEmpty()) { height++; Queue < TreeNode > temp = new LinkedList(); while (!queue.isEmpty()) { TreeNode node = queue.remove(); if (node.left != null) temp.add(node.left); if (node.right != null) temp.add(node.right); } queue = temp; } return height; } }
复杂度分析
时间复杂度:$O(h*2^h)$,其中 $h$ 是树的高度,填充长度为 $h\times(2^h-1)$ 的数组 $res$。
空间复杂度:$O(h*2^h)$,数组 $res$ 的长度为 $h\times(2^h-1)$。
统计信息
| 通过次数 | 提交次数 | AC比率 |
|---|---|---|
| 9927 | 16535 | 60.0% |
提交历史
| 提交时间 | 提交结果 | 执行时间 | 内存消耗 | 语言 |
|---|




