原文链接: https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/maximum-width-of-binary-tree
英文原文
Given the root of a binary tree, return the maximum width of the given tree.
The maximum width of a tree is the maximum width among all levels.
The width of one level is defined as the length between the end-nodes (the leftmost and rightmost non-null nodes), where the null nodes between the end-nodes are also counted into the length calculation.
It is guaranteed that the answer will in the range of 32-bit signed integer.
Example 1:
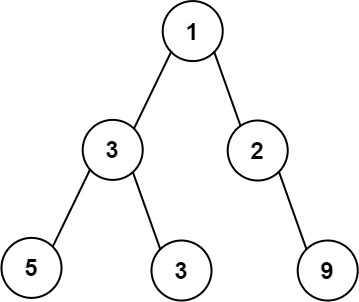
Input: root = [1,3,2,5,3,null,9] Output: 4 Explanation: The maximum width existing in the third level with the length 4 (5,3,null,9).
Example 2:
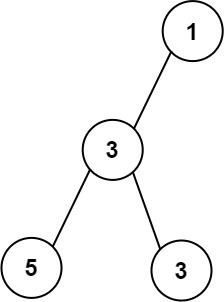
Input: root = [1,3,null,5,3] Output: 2 Explanation: The maximum width existing in the third level with the length 2 (5,3).
Example 3:
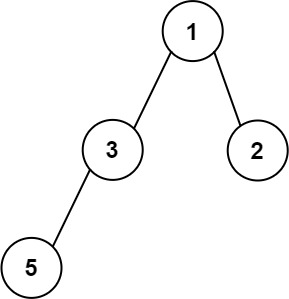
Input: root = [1,3,2,5] Output: 2 Explanation: The maximum width existing in the second level with the length 2 (3,2).
Example 4:
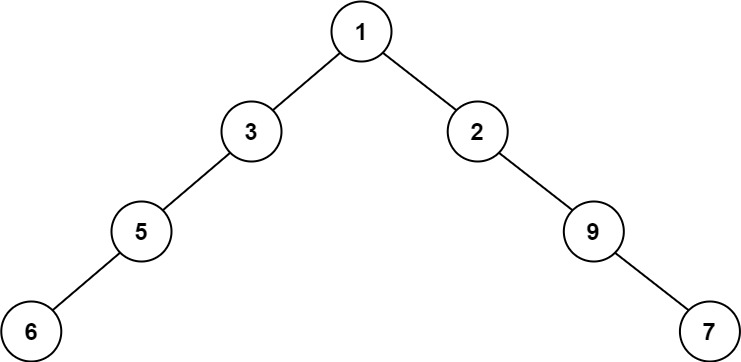
Input: root = [1,3,2,5,null,null,9,6,null,null,7] Output: 8 Explanation: The maximum width existing in the fourth level with the length 8 (6,null,null,null,null,null,null,7).
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[1, 3000]. -100 <= Node.val <= 100
中文题目
给定一个二叉树,编写一个函数来获取这个树的最大宽度。树的宽度是所有层中的最大宽度。这个二叉树与满二叉树(full binary tree)结构相同,但一些节点为空。
每一层的宽度被定义为两个端点(该层最左和最右的非空节点,两端点间的null节点也计入长度)之间的长度。
示例 1:
输入:
1
/ \
3 2
/ \ \
5 3 9
输出: 4
解释: 最大值出现在树的第 3 层,宽度为 4 (5,3,null,9)。
示例 2:
输入:
1
/
3
/ \
5 3
输出: 2
解释: 最大值出现在树的第 3 层,宽度为 2 (5,3)。
示例 3:
输入:
1
/ \
3 2
/
5
输出: 2
解释: 最大值出现在树的第 2 层,宽度为 2 (3,2)。
示例 4:
输入:
1
/ \
3 2
/ \
5 9
/ \
6 7
输出: 8
解释: 最大值出现在树的第 4 层,宽度为 8 (6,null,null,null,null,null,null,7)。
注意: 答案在32位有符号整数的表示范围内。
通过代码
官方题解
方法框架
解释
由于我们需要将给定树中的每个节点都访问一遍,我们需要遍历树。我们可以用深度优先搜索或者宽度优先搜索将树遍历。
这个问题中的主要想法是给每个节点一个 position 值,如果我们走向左子树,那么 position -> position * 2,如果我们走向右子树,那么 position -> positon * 2 + 1。当我们在看同一层深度的位置值 L 和 R 的时候,宽度就是 R - L + 1。
方法 1:宽度优先搜索 [Accepted]
想法和算法
宽度优先搜索顺序遍历每个节点的过程中,我们记录节点的 position 信息,对于每一个深度,第一个遇到的节点是最左边的节点,最后一个到达的节点是最右边的节点。
[]def widthOfBinaryTree(self, root): queue = [(root, 0, 0)] cur_depth = left = ans = 0 for node, depth, pos in queue: if node: queue.append((node.left, depth+1, pos*2)) queue.append((node.right, depth+1, pos*2 + 1)) if cur_depth != depth: cur_depth = depth left = pos ans = max(pos - left + 1, ans) return ans
[]class Solution { public int widthOfBinaryTree(TreeNode root) { Queue<AnnotatedNode> queue = new LinkedList(); queue.add(new AnnotatedNode(root, 0, 0)); int curDepth = 0, left = 0, ans = 0; while (!queue.isEmpty()) { AnnotatedNode a = queue.poll(); if (a.node != null) { queue.add(new AnnotatedNode(a.node.left, a.depth + 1, a.pos * 2)); queue.add(new AnnotatedNode(a.node.right, a.depth + 1, a.pos * 2 + 1)); if (curDepth != a.depth) { curDepth = a.depth; left = a.pos; } ans = Math.max(ans, a.pos - left + 1); } } return ans; } } class AnnotatedNode { TreeNode node; int depth, pos; AnnotatedNode(TreeNode n, int d, int p) { node = n; depth = d; pos = p; } }
复杂度分析
时间复杂度: $O(N)$,其中 $N$ 是输入树的节点数目,我们遍历每个节点一遍。
空间复杂度: $O(N)$,这是
queue的大小。
方法 2:深度优先搜索 [Accepted]
想法和算法
按照深度优先的顺序,我们记录每个节点的 position 。对于每一个深度,第一个到达的位置会被记录在 left[depth] 中。
然后对于每一个节点,它对应这一层的可能宽度是 pos - left[depth] + 1 。我们将每一层这些可能的宽度去一个最大值就是答案。
[]class Solution(object): def widthOfBinaryTree(self, root): self.ans = 0 left = {} def dfs(node, depth = 0, pos = 0): if node: left.setdefault(depth, pos) self.ans = max(self.ans, pos - left[depth] + 1) dfs(node.left, depth + 1, pos * 2) dfs(node.right, depth + 1, pos * 2 + 1) dfs(root) return self.ans
[]class Solution { int ans; Map<Integer, Integer> left; public int widthOfBinaryTree(TreeNode root) { ans = 0; left = new HashMap(); dfs(root, 0, 0); return ans; } public void dfs(TreeNode root, int depth, int pos) { if (root == null) return; left.computeIfAbsent(depth, x-> pos); ans = Math.max(ans, pos - left.get(depth) + 1); dfs(root.left, depth + 1, 2 * pos); dfs(root.right, depth + 1, 2 * pos + 1); } }
复杂度分析
时间复杂度: $O(N)$ ,其中 $N$ 是树中节点的数目,我们需要遍历每个节点。
空间复杂度: $O(N)$ ,这部分空间是因为我们 DFS 递归过程中有 $N$ 层的栈。
此分析方法由 @awice 提供。
统计信息
| 通过次数 | 提交次数 | AC比率 |
|---|---|---|
| 31426 | 76903 | 40.9% |
提交历史
| 提交时间 | 提交结果 | 执行时间 | 内存消耗 | 语言 |
|---|




