原文链接: https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/trim-a-binary-search-tree
英文原文
Given the root of a binary search tree and the lowest and highest boundaries as low and high, trim the tree so that all its elements lies in [low, high]. Trimming the tree should not change the relative structure of the elements that will remain in the tree (i.e., any node's descendant should remain a descendant). It can be proven that there is a unique answer.
Return the root of the trimmed binary search tree. Note that the root may change depending on the given bounds.
Example 1:
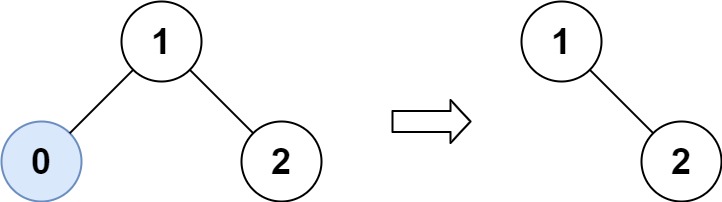
Input: root = [1,0,2], low = 1, high = 2 Output: [1,null,2]
Example 2:
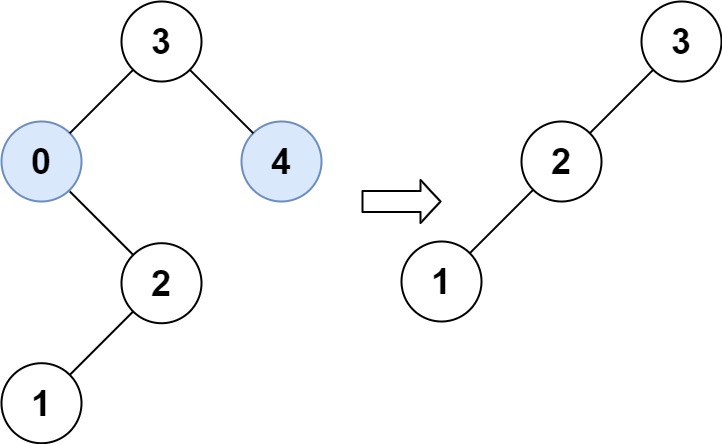
Input: root = [3,0,4,null,2,null,null,1], low = 1, high = 3 Output: [3,2,null,1]
Example 3:
Input: root = [1], low = 1, high = 2 Output: [1]
Example 4:
Input: root = [1,null,2], low = 1, high = 3 Output: [1,null,2]
Example 5:
Input: root = [1,null,2], low = 2, high = 4 Output: [2]
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree in the range
[1, 104]. 0 <= Node.val <= 104- The value of each node in the tree is unique.
rootis guaranteed to be a valid binary search tree.0 <= low <= high <= 104
中文题目
给你二叉搜索树的根节点 root ,同时给定最小边界low 和最大边界 high。通过修剪二叉搜索树,使得所有节点的值在[low, high]中。修剪树不应该改变保留在树中的元素的相对结构(即,如果没有被移除,原有的父代子代关系都应当保留)。 可以证明,存在唯一的答案。
所以结果应当返回修剪好的二叉搜索树的新的根节点。注意,根节点可能会根据给定的边界发生改变。
示例 1:

输入:root = [1,0,2], low = 1, high = 2 输出:[1,null,2]
示例 2:

输入:root = [3,0,4,null,2,null,null,1], low = 1, high = 3 输出:[3,2,null,1]
示例 3:
输入:root = [1], low = 1, high = 2 输出:[1]
示例 4:
输入:root = [1,null,2], low = 1, high = 3 输出:[1,null,2]
示例 5:
输入:root = [1,null,2], low = 2, high = 4 输出:[2]
提示:
- 树中节点数在范围
[1, 104]内 0 <= Node.val <= 104- 树中每个节点的值都是唯一的
- 题目数据保证输入是一棵有效的二叉搜索树
0 <= low <= high <= 104
通过代码
官方题解
方法:递归
思路
令 trim(node) 作为该节点上的子树的理想答案。我们可以递归地构建该答案。
算法
当 $\text{node.val > R}$,那么修剪后的二叉树必定出现在节点的左边。
类似地,当 $\text{node.val < L}$,那么修剪后的二叉树出现在节点的右边。否则,我们将会修剪树的两边。
[GoXj8r6W-Java]class Solution { public TreeNode trimBST(TreeNode root, int L, int R) { if (root == null) return root; if (root.val > R) return trimBST(root.left, L, R); if (root.val < L) return trimBST(root.right, L, R); root.left = trimBST(root.left, L, R); root.right = trimBST(root.right, L, R); return root; } }
[GoXj8r6W-Python]class Solution(object): def trimBST(self, root, L, R): def trim(node): if not node: return None elif node.val > R: return trim(node.left) elif node.val < L: return trim(node.right) else: node.left = trim(node.left) node.right = trim(node.right) return node return trim(root)
复杂度分析
时间复杂度:$O(N)$,其中 $N$ 是给定的树的全部节点。我们最多访问每个节点一次。
空间复杂度:$O(N)$,即使我们没有明确使用任何额外的内存,在最糟糕的情况下,我们递归调用的栈可能与节点数一样大。
统计信息
| 通过次数 | 提交次数 | AC比率 |
|---|---|---|
| 39748 | 59779 | 66.5% |
提交历史
| 提交时间 | 提交结果 | 执行时间 | 内存消耗 | 语言 |
|---|




