原文链接: https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/pyramid-transition-matrix
英文原文
You are stacking blocks to form a pyramid. Each block has a color, which is represented by a single letter. Each row of blocks contains one less block than the row beneath it and is centered on top.
To make the pyramid aesthetically pleasing, there are only specific triangular patterns that are allowed. A triangular pattern consists of a single block stacked on top of two blocks. The patterns are given as a list of three-letter strings allowed, where the first two characters of a pattern represent the left and right bottom blocks respectively, and the third character is the top block.
- For example,
"ABC"represents a triangular pattern with a'C'block stacked on top of an'A'(left) and'B'(right) block. Note that this is different from"BAC"where'B'is on the left bottom and'A'is on the right bottom.
You start with a bottom row of blocks bottom, given as a single string, that you must use as the base of the pyramid.
Given bottom and allowed, return true if you can build the pyramid all the way to the top such that every triangular pattern in the pyramid is in allowed, or false otherwise.
Example 1:
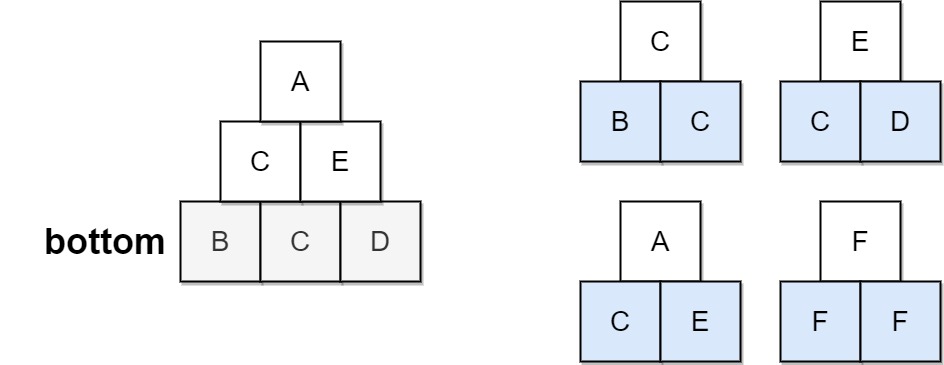
Input: bottom = "BCD", allowed = ["BCC","CDE","CEA","FFF"] Output: true Explanation: The allowed triangular patterns are shown on the right. Starting from the bottom (level 3), we can build "CE" on level 2 and then build "E" on level 1. There are three triangular patterns in the pyramid, which are "BCC", "CDE", and "CEA". All are allowed.
Example 2:
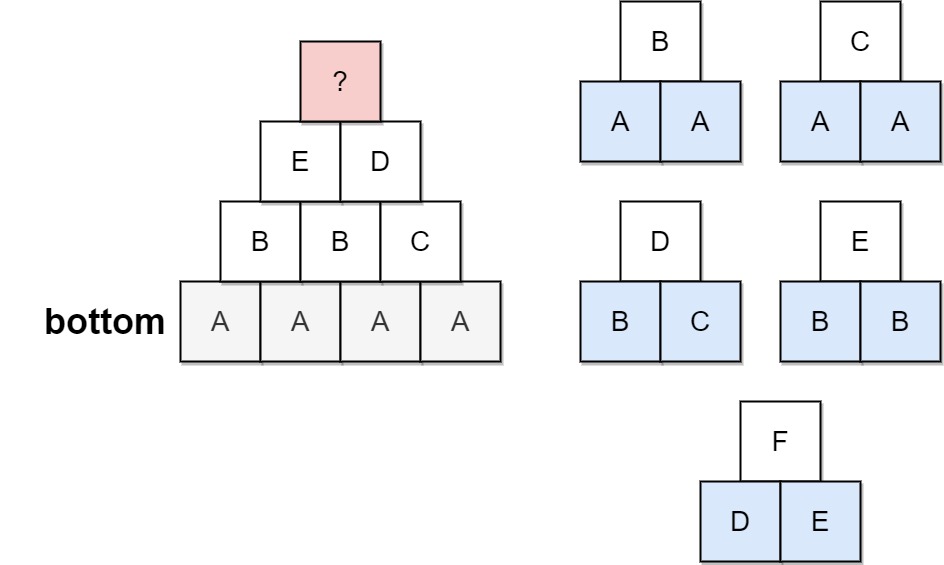
Input: bottom = "AAAA", allowed = ["AAB","AAC","BCD","BBE","DEF"] Output: false Explanation: The allowed triangular patterns are shown on the right. Starting from the bottom (level 4), there are multiple ways to build level 3, but trying all the possibilites, you will get always stuck before building level 1.
Constraints:
2 <= bottom.length <= 60 <= allowed.length <= 216allowed[i].length == 3- The letters in all input strings are from the set
{'A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'E', 'F'}. - All the values of
allowedare unique.
中文题目
现在,我们用一些方块来堆砌一个金字塔。 每个方块用仅包含一个字母的字符串表示。
使用三元组表示金字塔的堆砌规则如下:
对于三元组 ABC ,C 为顶层方块,方块 A 、B 分别作为方块 C 下一层的的左、右子块。当且仅当 ABC 是被允许的三元组,我们才可以将其堆砌上。
初始时,给定金字塔的基层 bottom,用一个字符串表示。一个允许的三元组列表 allowed,每个三元组用一个长度为 3 的字符串表示。
如果可以由基层一直堆到塔尖就返回 true ,否则返回 false 。
示例 1:
输入:bottom = "BCD", allowed = ["BCG", "CDE", "GEA", "FFF"]
输出:true
解释:
可以堆砌成这样的金字塔:
A
/ \
G E
/ \ / \
B C D
因为符合 BCG、CDE 和 GEA 三种规则。
示例 2:
输入:bottom = "AABA", allowed = ["AAA", "AAB", "ABA", "ABB", "BAC"] 输出:false 解释: 无法一直堆到塔尖。 注意, 允许存在像 ABC 和 ABD 这样的三元组,其中 C != D。
提示:
bottom的长度范围在[2, 8]。allowed的长度范围在[0, 200]。- 方块的标记字母范围为
{'A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'E', 'F', 'G'}。
通过代码
官方题解
方法一:状态转换
算法:
我们模拟方块可以处于的状态。每个状态都是一个二进制数,如果第 k 类型的方块是可能的,则设置第 k 位。然后,我们创建一个转换映射 T[state1][state2] -> state。它接受左状态和右状态并输出所有可能的父状态。
最后,应用这些转换非常简单。但是,这种方法不正确,因为转换不是独立的。例如,如果我们在一行 A, {B or C}, A,并且 allowed 中的元组是 (A, B, D), (C, A, D)。那么无论选择 {B or C},我们都不能创建金字塔的下一行。
[solution1-Python]class Solution(object): def pyramidTransition(self, bottom, allowed): T = [[0] * (1 << 7) for _ in xrange(1 << 7)] for triple in allowed: u, v, w = (1 << (ord(x) - ord('A')) for x in triple) for b1 in xrange(1 << 7): if u & b1: for b2 in xrange(1 << 7): if v & b2: T[b1][b2] |= w state = [1 << (ord(x) - ord('A')) for x in bottom] while len(state) > 1: for i in xrange(len(state) - 1): state[i] = T[state[i]][state[i+1]] state.pop() return bool(state[0])
[solution1-Java]class Solution { public boolean pyramidTransition(String bottom, List<String> allowed) { int[][] T = new int[1 << 7][1 << 7]; for (String triple: allowed) { int u = 1 << (triple.charAt(0) - 'A'); int v = 1 << (triple.charAt(1) - 'A'); int w = 1 << (triple.charAt(2) - 'A'); for (int b1 = 0; b1 < (1 << 7); ++b1) if ((u & b1) > 0) for (int b2 = 0; b2 < (1 << 7); ++b2) if ((v & b2) > 0) T[b1][b2] |= w; } int[] state = new int[bottom.length()]; int t = 0; for (char c: bottom.toCharArray()) state[t++] = 1 << (c - 'A'); while (t-- > 1) for (int i = 0; i < t; ++i) state[i] = T[state[i]][state[i+1]]; return state[0] > 0; } }
复杂度分析
- 时间复杂度:$O(2^{2\mathcal{A}}A + N^2)$。其中 $N$ 指的是
bottom的长度,$A$ 指的是allowed的长度,且 $\mathcal{A}$ 指的是字母的大小。 - 空间复杂度:$O(2^{2\mathcal{A}})$。
方法二:深度优先搜索
我们详尽的尝试每个方块的组合。
算法:
我们需要从三元组列表中创建一个转换映射 T。这个映射 T[x][y] = {set of z} 将是左孩子 x 和右孩子 y 所有可能的父块。
然后,为了求解下一行,我们生成下一行所有的可能组合并求解它们。如果这些组合中有任一一行是可解的,则返回 True,反之返回 False。
[solution1-Python]class Solution(object): def pyramidTransition(self, bottom, allowed): T = collections.defaultdict(set) for u, v, w in allowed: T[u, v].add(w) #Comments can be used to cache intermediate results #seen = set() def solve(A): if len(A) == 1: return True #if A in seen: return False #seen.add(A) return any(solve(cand) for cand in build(A, [])) def build(A, ans, i = 0): if i + 1 == len(A): yield "".join(ans) else: for w in T[A[i], A[i+1]]: ans.append(w) for result in build(A, ans, i+1): yield result ans.pop() return solve(bottom)
[solution1-Java]class Solution { int[][] T; Set<Long> seen; public boolean pyramidTransition(String bottom, List<String> allowed) { T = new int[7][7]; for (String a: allowed) T[a.charAt(0) - 'A'][a.charAt(1) - 'A'] |= 1 << (a.charAt(2) - 'A'); seen = new HashSet(); int N = bottom.length(); int[][] A = new int[N][N]; int t = 0; for (char c: bottom.toCharArray()) A[N-1][t++] = c - 'A'; return solve(A, 0, N-1, 0); } //A[i] - the ith row of the pyramid //R - integer representing the current row of the pyramid //N - length of current row we are calculating //i - index of how far in the current row we are calculating //Returns true iff pyramid can be built public boolean solve(int[][] A, long R, int N, int i) { if (N == 1 && i == 1) { // If successfully placed entire pyramid return true; } else if (i == N) { if (seen.contains(R)) return false; // If we've already tried this row, give up seen.add(R); // Add row to cache return solve(A, 0, N-1, 0); // Calculate next row } else { // w's jth bit is true iff block #j could be // a parent of A[N][i] and A[N][i+1] int w = T[A[N][i]][A[N][i+1]]; // for each set bit in w... for (int b = 0; b < 7; ++b) if (((w >> b) & 1) != 0) { A[N-1][i] = b; //set parent to be equal to block #b //If rest of pyramid can be built, return true //R represents current row, now with ith bit set to b+1 // in base 8. if (solve(A, R * 8 + (b+1), N, i+1)) return true; } return false; } } }
复杂度分析
- 时间复杂度:$O(\mathcal{A}^{N})$,其中 $N$ 指的是
bottom的长度,$\mathcal{A}$ 指的是字母的大小。 - 空间复杂度:$O(N^2)$。
统计信息
| 通过次数 | 提交次数 | AC比率 |
|---|---|---|
| 4811 | 8593 | 56.0% |
提交历史
| 提交时间 | 提交结果 | 执行时间 | 内存消耗 | 语言 |
|---|




