原文链接: https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/find-and-replace-in-string
英文原文
You are given a 0-indexed string s that you must perform k replacement operations on. The replacement operations are given as three 0-indexed parallel arrays, indices, sources, and targets, all of length k.
To complete the ith replacement operation:
- Check if the substring
sources[i]occurs at indexindices[i]in the original strings. - If it does not occur, do nothing.
- Otherwise if it does occur, replace that substring with
targets[i].
For example, if s = "abcd", indices[i] = 0, sources[i] = "ab", and targets[i] = "eee", then the result of this replacement will be "eeecd".
All replacement operations must occur simultaneously, meaning the replacement operations should not affect the indexing of each other. The testcases will be generated such that the replacements will not overlap.
- For example, a testcase with
s = "abc",indices = [0, 1], andsources = ["ab","bc"]will not be generated because the"ab"and"bc"replacements overlap.
Return the resulting string after performing all replacement operations on s.
A substring is a contiguous sequence of characters in a string.
Example 1:

Input: s = "abcd", indices = [0, 2], sources = ["a", "cd"], targets = ["eee", "ffff"] Output: "eeebffff" Explanation: "a" occurs at index 0 in s, so we replace it with "eee". "cd" occurs at index 2 in s, so we replace it with "ffff".
Example 2:
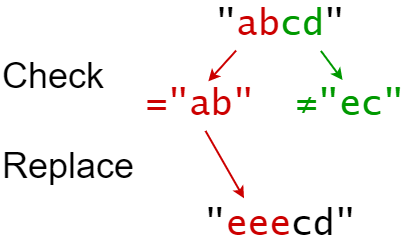
Input: s = "abcd", indices = [0, 2], sources = ["ab","ec"], targets = ["eee","ffff"] Output: "eeecd" Explanation: "ab" occurs at index 0 in s, so we replace it with "eee". "ec" does not occur at index 2 in s, so we do nothing.
Constraints:
1 <= s.length <= 1000k == indices.length == sources.length == targets.length1 <= k <= 1000 <= indexes[i] < s.length1 <= sources[i].length, targets[i].length <= 50sconsists of only lowercase English letters.sources[i]andtargets[i]consist of only lowercase English letters.
中文题目
某个字符串 S 需要执行一些替换操作,用新的字母组替换原有的字母组(不一定大小相同)。
每个替换操作具有 3 个参数:起始索引 i,源字 x 和目标字 y。规则是:如果 x 从原始字符串 S 中的位置 i 开始,那么就用 y 替换出现的 x。如果没有,则什么都不做。
举个例子,如果 S = “abcd” 并且替换操作 i = 2,x = “cd”,y = “ffff”,那么因为 “cd” 从原始字符串 S 中的位置 2 开始,所以用 “ffff” 替换它。
再来看 S = “abcd” 上的另一个例子,如果一个替换操作 i = 0,x = “ab”,y = “eee”,以及另一个替换操作 i = 2,x = “ec”,y = “ffff”,那么第二个操作将不会执行,因为原始字符串中 S[2] = 'c',与 x[0] = 'e' 不匹配。
所有这些操作同时发生。保证在替换时不会有任何重叠: S = "abc", indexes = [0, 1], sources = ["ab","bc"] 不是有效的测试用例。
示例 1:
输入:S = "abcd", indexes = [0,2], sources = ["a","cd"], targets = ["eee","ffff"] 输出:"eeebffff" 解释: "a" 从 S 中的索引 0 开始,所以它被替换为 "eee"。 "cd" 从 S 中的索引 2 开始,所以它被替换为 "ffff"。
示例 2:
输入:S = "abcd", indexes = [0,2], sources = ["ab","ec"], targets = ["eee","ffff"] 输出:"eeecd" 解释: "ab" 从 S 中的索引 0 开始,所以它被替换为 "eee"。 "ec" 没有从原始的 S 中的索引 2 开始,所以它没有被替换。
提示:
0 <= S.length <= 1000S仅由小写英文字母组成0 <= indexes.length <= 1000 <= indexes[i] < S.lengthsources.length == indexes.lengthtargets.length == indexes.length1 <= sources[i].length, targets[i].length <= 50sources[i]和targets[i]仅由小写英文字母组成
通过代码
官方题解
方法一:模拟
我们介绍两种不同的模拟方法。在这两种方法中,我们都通过最初给定的字符串 S 和替换操作,找出其中无效的那些,并保留有效的,以此得到最终的答案 ans。
在 Java 的代码中,我们根据替换操作得到数组 match,其中 match[ix] = j 表示字符串 S 从第 ix 位开始和 sources[j] 匹配,并且会被替换成 target[j],也就是说 sources[j] 是字符串 S[ix:] 的前缀。在得到 match 数组后,我们对 S 从左到右进行扫描,对于每个位置 ix,如果 match[ix] 有值 j,那么在 ans 尾部添加字符串 targets[j],并将 ix 增加 sources[j].length();否则在 ans 尾部添加字符 S[ix],并将 ix 增加 1。
在 Python 代码中,我们将所有的替换操作根据 indexes 值进行降序排序,这样我们依次执行替换操作时,前面的替换操作并不会改变后面替换操作的 indexes 值的位置。对于每个替换操作 i,我们直接判断 S 中对应的子串是否和 sources[i] 相等,如果相等,则替换为 targets[i]。
[sol1]class Solution { public String findReplaceString(String S, int[] indexes, String[] sources, String[] targets) { int N = S.length(); int[] match = new int[N]; Arrays.fill(match, -1); for (int i = 0; i < indexes.length; ++i) { int ix = indexes[i]; if (S.substring(ix, ix + sources[i].length()).equals(sources[i])) match[ix] = i; } StringBuilder ans = new StringBuilder(); int ix = 0; while (ix < N) { if (match[ix] >= 0) { ans.append(targets[match[ix]]); ix += sources[match[ix]].length(); } else { ans.append(S.charAt(ix++)); } } return ans.toString(); } }
[sol1]class Solution(object): def findReplaceString(self, S, indexes, sources, targets): S = list(S) for i, x, y in sorted(zip(indexes, sources, targets), reverse = True): if all(i+k < len(S) and S[i+k] == x[k] for k in xrange(len(x))): S[i:i+len(x)] = list(y) return "".join(S)
复杂度分析
时间复杂度:$O(NQ)$,其中 $N$ 是字符串
S的长度,$Q$ 是替换操作的数量。空间复杂度:$O(N)$,我们认为
sources和targets中的字符串长度均为常数。
统计信息
| 通过次数 | 提交次数 | AC比率 |
|---|---|---|
| 5496 | 12626 | 43.5% |
提交历史
| 提交时间 | 提交结果 | 执行时间 | 内存消耗 | 语言 |
|---|




