原文链接: https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/smallest-subtree-with-all-the-deepest-nodes
英文原文
Given the root of a binary tree, the depth of each node is the shortest distance to the root.
Return the smallest subtree such that it contains all the deepest nodes in the original tree.
A node is called the deepest if it has the largest depth possible among any node in the entire tree.
The subtree of a node is a tree consisting of that node, plus the set of all descendants of that node.
Example 1:
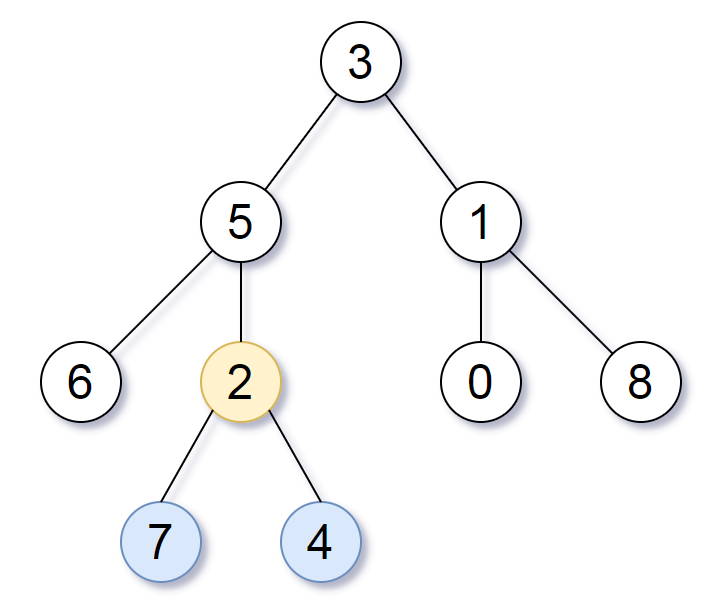
Input: root = [3,5,1,6,2,0,8,null,null,7,4] Output: [2,7,4] Explanation: We return the node with value 2, colored in yellow in the diagram. The nodes coloured in blue are the deepest nodes of the tree. Notice that nodes 5, 3 and 2 contain the deepest nodes in the tree but node 2 is the smallest subtree among them, so we return it.
Example 2:
Input: root = [1] Output: [1] Explanation: The root is the deepest node in the tree.
Example 3:
Input: root = [0,1,3,null,2] Output: [2] Explanation: The deepest node in the tree is 2, the valid subtrees are the subtrees of nodes 2, 1 and 0 but the subtree of node 2 is the smallest.
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree will be in the range
[1, 500]. 0 <= Node.val <= 500- The values of the nodes in the tree are unique.
Note: This question is the same as 1123: https://leetcode.com/problems/lowest-common-ancestor-of-deepest-leaves/
中文题目
给定一个根为 root 的二叉树,每个节点的深度是 该节点到根的最短距离 。
如果一个节点在 整个树 的任意节点之间具有最大的深度,则该节点是 最深的 。
一个节点的 子树 是该节点加上它的所有后代的集合。
返回能满足 以该节点为根的子树中包含所有最深的节点 这一条件的具有最大深度的节点。
注意:本题与力扣 1123 重复:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/lowest-common-ancestor-of-deepest-leaves/
示例 1:

输入:root = [3,5,1,6,2,0,8,null,null,7,4] 输出:[2,7,4] 解释: 我们返回值为 2 的节点,在图中用黄色标记。 在图中用蓝色标记的是树的最深的节点。 注意,节点 5、3 和 2 包含树中最深的节点,但节点 2 的子树最小,因此我们返回它。
示例 2:
输入:root = [1] 输出:[1] 解释:根节点是树中最深的节点。
示例 3:
输入:root = [0,1,3,null,2] 输出:[2] 解释:树中最深的节点为 2 ,有效子树为节点 2、1 和 0 的子树,但节点 2 的子树最小。
提示:
- 树中节点的数量介于 1 和 500 之间。
0 <= Node.val <= 500- 每个节点的值都是独一无二的。
通过代码
官方题解
方法一: 两次深度优先搜索
思路
最直白的做法,先做一次深度优先搜索标记所有节点的深度来找到最深的节点,再做一次深度优先搜索用回溯法找最小子树。定义第二次深度优先搜索方法为 answer(node),每次递归有以下四种情况需要处理:
如果
node没有左右子树,返回node。如果
node左右子树的后代中都有最深节点,返回node。如果只有左子树或右子树中有且拥有所有的最深节点,返回这棵子树的根节点(即
node的左/右孩子)。否则,当前子树中不存在答案。
算法
先做一次深度优先搜索标记所有节点的深度,再做一次深度优先搜索找到最终答案。
[solution1-Java]class Solution { Map<TreeNode, Integer> depth; int max_depth; public TreeNode subtreeWithAllDeepest(TreeNode root) { depth = new HashMap(); depth.put(null, -1); dfs(root, null); max_depth = -1; for (Integer d: depth.values()) max_depth = Math.max(max_depth, d); return answer(root); } public void dfs(TreeNode node, TreeNode parent) { if (node != null) { depth.put(node, depth.get(parent) + 1); dfs(node.left, node); dfs(node.right, node); } } public TreeNode answer(TreeNode node) { if (node == null || depth.get(node) == max_depth) return node; TreeNode L = answer(node.left), R = answer(node.right); if (L != null && R != null) return node; if (L != null) return L; if (R != null) return R; return null; } }
[solution1-Python]class Solution(object): def subtreeWithAllDeepest(self, root): # Tag each node with it's depth. depth = {None: -1} def dfs(node, parent = None): if node: depth[node] = depth[parent] + 1 dfs(node.left, node) dfs(node.right, node) dfs(root) max_depth = max(depth.itervalues()) def answer(node): # Return the answer for the subtree at node. if not node or depth.get(node, None) == max_depth: return node L, R = answer(node.left), answer(node.right) return node if L and R else L or R return answer(root)
复杂度分析
时间复杂度: $O(N)$,其中 $N$ 为树的大小。
空间复杂度: $O(N)$。
方法二: 一次深度优先搜索
思路
可以把 方法一 中两次深度优先搜索合并成一次,定义方法 dfs(node),与方法一中不同的是 dfs(node) 返回两个值,子树中的答案和 node 节点到最深节点的距离。
算法
dfs(node) 返回的结果有两个部分:
Result.node:包含所有最深节点的最小子树的根节点。Result.dist:node到最深节点的距离。
分别计算 dfs(node) 的两个返回结果:
对于
Result.node:如果只有一个
childResult具有最深节点,返回childResult.node。如果两个孩子都有最深节点,返回
node。
Result.dist为childResult.dist加1。
[solution2-Java]class Solution { public TreeNode subtreeWithAllDeepest(TreeNode root) { return dfs(root).node; } // Return the result of the subtree at this node. public Result dfs(TreeNode node) { if (node == null) return new Result(null, 0); Result L = dfs(node.left), R = dfs(node.right); if (L.dist > R.dist) return new Result(L.node, L.dist + 1); if (L.dist < R.dist) return new Result(R.node, R.dist + 1); return new Result(node, L.dist + 1); } } /** * The result of a subtree is: * Result.node: the largest depth node that is equal to or * an ancestor of all the deepest nodes of this subtree. * Result.dist: the number of nodes in the path from the root * of this subtree, to the deepest node in this subtree. */ class Result { TreeNode node; int dist; Result(TreeNode n, int d) { node = n; dist = d; } }
[solution2-Python]class Solution(object): def subtreeWithAllDeepest(self, root): # The result of a subtree is: # Result.node: the largest depth node that is equal to or # an ancestor of all the deepest nodes of this subtree. # Result.dist: the number of nodes in the path from the root # of this subtree, to the deepest node in this subtree. Result = collections.namedtuple("Result", ("node", "dist")) def dfs(node): # Return the result of the subtree at this node. if not node: return Result(None, 0) L, R = dfs(node.left), dfs(node.right) if L.dist > R.dist: return Result(L.node, L.dist + 1) if L.dist < R.dist: return Result(R.node, R.dist + 1) return Result(node, L.dist + 1) return dfs(root).node
复杂度分析
时间复杂度: $O(N)$,其中 $N$ 为树的大小。
空间复杂度: $O(N)$。
统计信息
| 通过次数 | 提交次数 | AC比率 |
|---|---|---|
| 9655 | 14552 | 66.3% |
提交历史
| 提交时间 | 提交结果 | 执行时间 | 内存消耗 | 语言 |
|---|




