原文链接: https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/complete-binary-tree-inserter
英文原文
A complete binary tree is a binary tree in which every level, except possibly the last, is completely filled, and all nodes are as far left as possible.
Design an algorithm to insert a new node to a complete binary tree keeping it complete after the insertion.
Implement the CBTInserter class:
CBTInserter(TreeNode root)Initializes the data structure with therootof the complete binary tree.int insert(int v)Inserts aTreeNodeinto the tree with valueNode.val == valso that the tree remains complete, and returns the value of the parent of the insertedTreeNode.TreeNode get_root()Returns the root node of the tree.
Example 1:
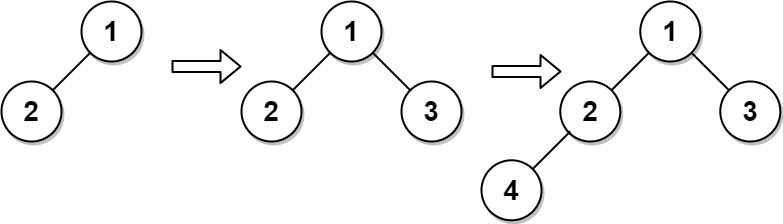
Input ["CBTInserter", "insert", "insert", "get_root"] [[[1, 2]], [3], [4], []] Output [null, 1, 2, [1, 2, 3, 4]]Explanation
CBTInserter cBTInserter = new CBTInserter([1, 2]);
cBTInserter.insert(3); // return 1
cBTInserter.insert(4); // return 2
cBTInserter.get_root(); // return [1, 2, 3, 4]
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree will be in the range
[1, 1000]. 0 <= Node.val <= 5000rootis a complete binary tree.0 <= val <= 5000- At most
104calls will be made toinsertandget_root.
中文题目
完全二叉树是每一层(除最后一层外)都是完全填充(即,节点数达到最大)的,并且所有的节点都尽可能地集中在左侧。
设计一个用完全二叉树初始化的数据结构 CBTInserter,它支持以下几种操作:
CBTInserter(TreeNode root)使用头节点为root的给定树初始化该数据结构;CBTInserter.insert(int v)向树中插入一个新节点,节点类型为TreeNode,值为v。使树保持完全二叉树的状态,并返回插入的新节点的父节点的值;CBTInserter.get_root()将返回树的头节点。
示例 1:
输入:inputs = ["CBTInserter","insert","get_root"], inputs = [[[1]],[2],[]] 输出:[null,1,[1,2]]
示例 2:
输入:inputs = ["CBTInserter","insert","insert","get_root"], inputs = [[[1,2,3,4,5,6]],[7],[8],[]] 输出:[null,3,4,[1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8]]
提示:
- 最初给定的树是完全二叉树,且包含
1到1000个节点。 - 每个测试用例最多调用
CBTInserter.insert操作10000次。 - 给定节点或插入节点的每个值都在
0到5000之间。
通过代码
官方题解
方法 1:双端队列
想法
将所有节点编号,按照从上到下从左到右的顺序。
在每个插入步骤中,我们希望插入到一个编号最小的节点(这样有 0 或者 1 个孩子)。
通过维护一个 deque (双端队列),保存这些节点的编号,我们可以解决这个问题。插入一个节点之后,将成为最高编号的节点,并且没有孩子,所以插入到队列的后端。为了找到最小数字的节点,我们从队列前端弹出元素。
算法
首先,通过广度优先搜索将 deque 中插入含有 0 个或者 1 个孩子的节点编号。
然后插入节点,父亲是 deque 的第一个元素,我们将新节点加入我们的 deque。
[]class CBTInserter { TreeNode root; Deque<TreeNode> deque; public CBTInserter(TreeNode root) { this.root = root; deque = new LinkedList(); Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList(); queue.offer(root); // BFS to populate deque while (!queue.isEmpty()) { TreeNode node = queue.poll(); if (node.left == null || node.right == null) deque.offerLast(node); if (node.left != null) queue.offer(node.left); if (node.right != null) queue.offer(node.right); } } public int insert(int v) { TreeNode node = deque.peekFirst(); deque.offerLast(new TreeNode(v)); if (node.left == null) node.left = deque.peekLast(); else { node.right = deque.peekLast(); deque.pollFirst(); } return node.val; } public TreeNode get_root() { return root; } }
[]class CBTInserter(object): def __init__(self, root): self.deque = collections.deque() self.root = root q = collections.deque([root]) while q: node = q.popleft() if not node.left or not node.right: self.deque.append(node) if node.left: q.append(node.left) if node.right: q.append(node.right) def insert(self, v): node = self.deque[0] self.deque.append(TreeNode(v)) if not node.left: node.left = self.deque[-1] else: node.right = self.deque[-1] self.deque.popleft() return node.val def get_root(self): return self.root
复杂度分析
- 时间复杂度:预处理 $O(N)$,其中 $N$ 是树上节点编号。每个插入步骤是 $O(1)$。
- 空间复杂度:$O(N_\text{cur})$,其中当前插入操作树的大小为 $N_{\text{cur}}$。
统计信息
| 通过次数 | 提交次数 | AC比率 |
|---|---|---|
| 5907 | 9185 | 64.3% |
提交历史
| 提交时间 | 提交结果 | 执行时间 | 内存消耗 | 语言 |
|---|




