原文链接: https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/minimum-area-rectangle-ii
英文原文
You are given an array of points in the X-Y plane points where points[i] = [xi, yi].
Return the minimum area of any rectangle formed from these points, with sides not necessarily parallel to the X and Y axes. If there is not any such rectangle, return 0.
Answers within 10-5 of the actual answer will be accepted.
Example 1:

Input: points = [[1,2],[2,1],[1,0],[0,1]] Output: 2.00000 Explanation: The minimum area rectangle occurs at [1,2],[2,1],[1,0],[0,1], with an area of 2.
Example 2:

Input: points = [[0,1],[2,1],[1,1],[1,0],[2,0]] Output: 1.00000 Explanation: The minimum area rectangle occurs at [1,0],[1,1],[2,1],[2,0], with an area of 1.
Example 3:

Input: points = [[0,3],[1,2],[3,1],[1,3],[2,1]] Output: 0 Explanation: There is no possible rectangle to form from these points.
Example 4:

Input: points = [[3,1],[1,1],[0,1],[2,1],[3,3],[3,2],[0,2],[2,3]] Output: 2.00000 Explanation: The minimum area rectangle occurs at [2,1],[2,3],[3,3],[3,1], with an area of 2.
Constraints:
1 <= points.length <= 50points[i].length == 20 <= xi, yi <= 4 * 104- All the given points are unique.
中文题目
给定在 xy 平面上的一组点,确定由这些点组成的任何矩形的最小面积,其中矩形的边不一定平行于 x 轴和 y 轴。
如果没有任何矩形,就返回 0。
示例 1:
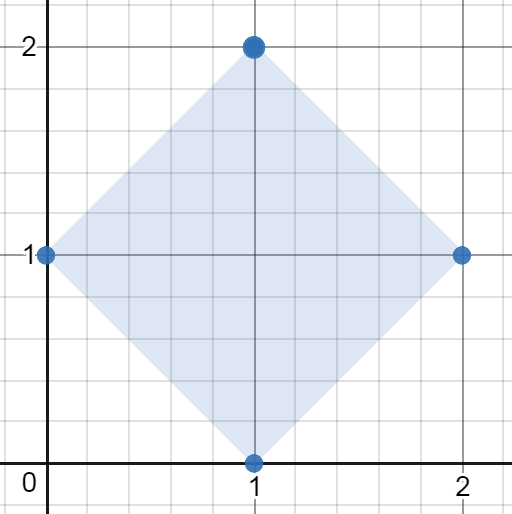
输入:[[1,2],[2,1],[1,0],[0,1]] 输出:2.00000 解释:最小面积的矩形出现在 [1,2],[2,1],[1,0],[0,1] 处,面积为 2。
示例 2:
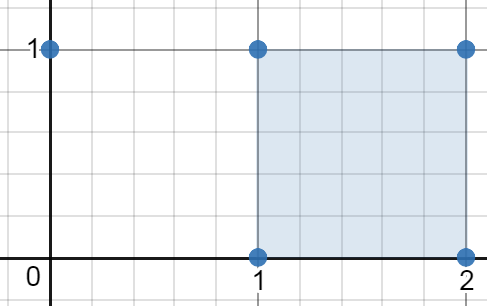
输入:[[0,1],[2,1],[1,1],[1,0],[2,0]] 输出:1.00000 解释:最小面积的矩形出现在 [1,0],[1,1],[2,1],[2,0] 处,面积为 1。
示例 3:
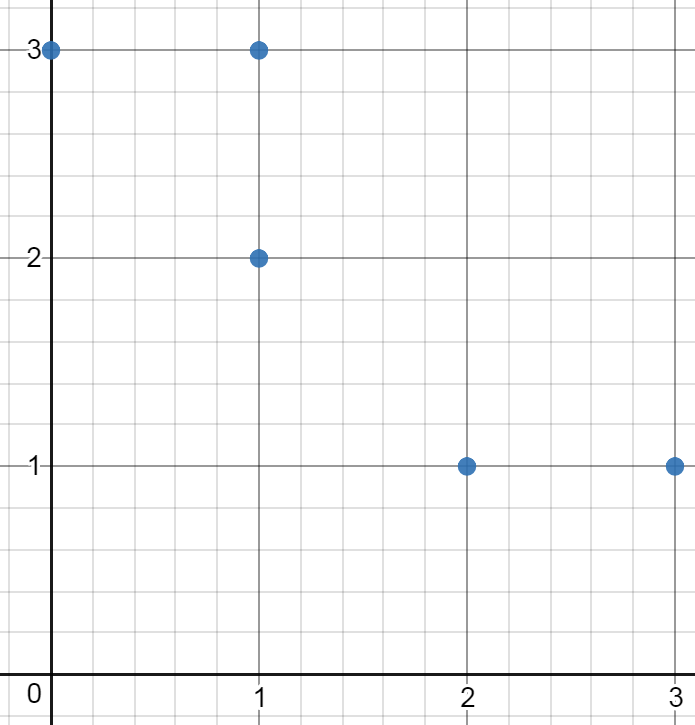
输入:[[0,3],[1,2],[3,1],[1,3],[2,1]] 输出:0 解释:没法从这些点中组成任何矩形。
示例 4:
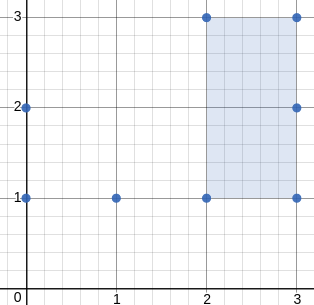
输入:[[3,1],[1,1],[0,1],[2,1],[3,3],[3,2],[0,2],[2,3]] 输出:2.00000 解释:最小面积的矩形出现在 [2,1],[2,3],[3,3],[3,1] 处,面积为 2。
提示:
1 <= points.length <= 500 <= points[i][0] <= 400000 <= points[i][1] <= 40000- 所有的点都是不同的。
- 与真实值误差不超过
10^-5的答案将视为正确结果。
通过代码
官方题解
方法一:枚举三角形
思路
对于每一个三角形,我们尝试寻找第四个点并判定它们是否能形成一个矩形。
算法
假设前三个点分别是 p1, p2, p3,并且 p2 与 p3 在最终的矩形中处于对角位置。那么第四个点一定是 p4 = p2 + p3 - p1(向量计算),因为 p1, p2, p4, p3 一定形成一个平行四边形,满足 p1 + (p2 - p1) + (p3 - p1) = p4。
如果计算得到的第四个点存在于给定的点集中(我们可以使用一个 HashSet 来判定是否存在),那么接下来我们应该判定平行四边形的某一个角的度数是否为 90 度。最简单的判定方法就是计算向量 (p2 - p1) 与 (p3 - p1) 的点积。(另一种方法是我们把它们都规范化成长度为 1 的向量,然后检查其中一个是否与另一个旋转 90 度相等)
[hEzYRLSC-Java]import java.awt.Point; class Solution { public double minAreaFreeRect(int[][] points) { int N = points.length; Point[] A = new Point[N]; Set<Point> pointSet = new HashSet(); for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i) { A[i] = new Point(points[i][0], points[i][1]); pointSet.add(A[i]); } double ans = Double.MAX_VALUE; for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i) { Point p1 = A[i]; for (int j = 0; j < N; ++j) if (j != i) { Point p2 = A[j]; for (int k = j+1; k < N; ++k) if (k != i) { Point p3 = A[k]; Point p4 = new Point(p2.x + p3.x - p1.x, p2.y + p3.y - p1.y); if (pointSet.contains(p4)) { int dot = ((p2.x - p1.x) * (p3.x - p1.x) + (p2.y - p1.y) * (p3.y - p1.y)); if (dot == 0) { double area = p1.distance(p2) * p1.distance(p3); if (area < ans) ans = area; } } } } } return ans < Double.MAX_VALUE ? ans : 0; } }
[hEzYRLSC-Python]class Solution(object): def minAreaFreeRect(self, points): EPS = 1e-7 points = set(map(tuple, points)) ans = float('inf') for p1, p2, p3 in itertools.permutations(points, 3): p4 = p2[0] + p3[0] - p1[0], p2[1] + p3[1] - p1[1] if p4 in points: v21 = complex(p2[0] - p1[0], p2[1] - p1[1]) v31 = complex(p3[0] - p1[0], p3[1] - p1[1]) if abs(v21.real * v31.real + v21.imag * v31.imag) < EPS: area = abs(v21) * abs(v31) if area < ans: ans = area return ans if ans < float('inf') else 0
复杂度分析
时间复杂度:$O(N^3)$,其中 $N$ 是点集
points的大小。空间复杂度:$O(N)$。
方法二:枚举中心
思路
我们可以考虑一个矩形 ABCD 的对角线 AC 与 BD。它们共享同一个中点 O,并且中点到顶点的长度均相同 dist(O, A) == dist(O, B) == dist(O, C) == dist(O, D)。 注意到形成一个矩形的充分必要条件是两条对角线的中点相同且端点到中点距离也相同。
由此得到启发,让我们可以将点对 PQ 按照它们的中点 C 与距中点距离 r = dist(P, C) 分类。我们的策略就是暴力枚举属于相同分类的点对。
算法
对于每一个点对,按照它们的 中点 与 中点距 进行分类。我们只需要记录其中一个点 P 就可以了,因为另一个点可以计算得出 P' = 2 * center - P(向量计算)。
对于每对 中点 与 中点距,我们检查每一个可行的矩形(假设两个点对分别为 P, P', Q, Q')。这个矩形的面积 dist(P, Q) * dist(P, Q') 可作为一个候选答案。
[DYbWiAKp-Java]import java.awt.Point; class Solution { public double minAreaFreeRect(int[][] points) { int N = points.length; Point[] A = new Point[N]; for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i) A[i] = new Point(points[i][0], points[i][1]); Map<Integer, Map<Point, List<Point>>> seen = new HashMap(); for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i) for (int j = i+1; j < N; ++j) { // center is twice actual to keep integer precision Point center = new Point(A[i].x + A[j].x, A[i].y + A[j].y); int r2 = (A[i].x - A[j].x) * (A[i].x - A[j].x); r2 += (A[i].y - A[j].y) * (A[i].y - A[j].y); if (!seen.containsKey(r2)) seen.put(r2, new HashMap<Point, List<Point>>()); if (!seen.get(r2).containsKey(center)) seen.get(r2).put(center, new ArrayList<Point>()); seen.get(r2).get(center).add(A[i]); } double ans = Double.MAX_VALUE; for (Map<Point, List<Point>> info: seen.values()) { for (Point center: info.keySet()) { // center is twice actual List<Point> candidates = info.get(center); int clen = candidates.size(); for (int i = 0; i < clen; ++i) for (int j = i+1; j < clen; ++j) { Point P = candidates.get(i); Point Q = candidates.get(j); Point Q2 = new Point(center); Q2.translate(-Q.x, -Q.y); double area = P.distance(Q) * P.distance(Q2); if (area < ans) ans = area; } } } return ans < Double.MAX_VALUE ? ans : 0; } }
[DYbWiAKp-Python]class Solution(object): def minAreaFreeRect(self, points): points = [complex(*z) for z in points] seen = collections.defaultdict(list) for P, Q in itertools.combinations(points, 2): center = (P + Q) / 2 radius = abs(center - P) seen[center, radius].append(P) ans = float("inf") for (center, radius), candidates in seen.iteritems(): for P, Q in itertools.combinations(candidates, 2): ans = min(ans, abs(P - Q) * abs(P - (2*center - Q))) return ans if ans < float("inf") else 0
复杂度分析
时间复杂度:$O(N^2 \log N)$,其中 $N$ 是点集
points的大小。可以证明,被分到同一类的点对数量的上界为 $\log N$ - 点击链接查看更多。空间复杂度:$O(N^2)$。
统计信息
| 通过次数 | 提交次数 | AC比率 |
|---|---|---|
| 2655 | 5212 | 50.9% |
提交历史
| 提交时间 | 提交结果 | 执行时间 | 内存消耗 | 语言 |
|---|




