原文链接: https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/interval-list-intersections
英文原文
You are given two lists of closed intervals, firstList and secondList, where firstList[i] = [starti, endi] and secondList[j] = [startj, endj]. Each list of intervals is pairwise disjoint and in sorted order.
Return the intersection of these two interval lists.
A closed interval [a, b] (with a <= b) denotes the set of real numbers x with a <= x <= b.
The intersection of two closed intervals is a set of real numbers that are either empty or represented as a closed interval. For example, the intersection of [1, 3] and [2, 4] is [2, 3].
Example 1:
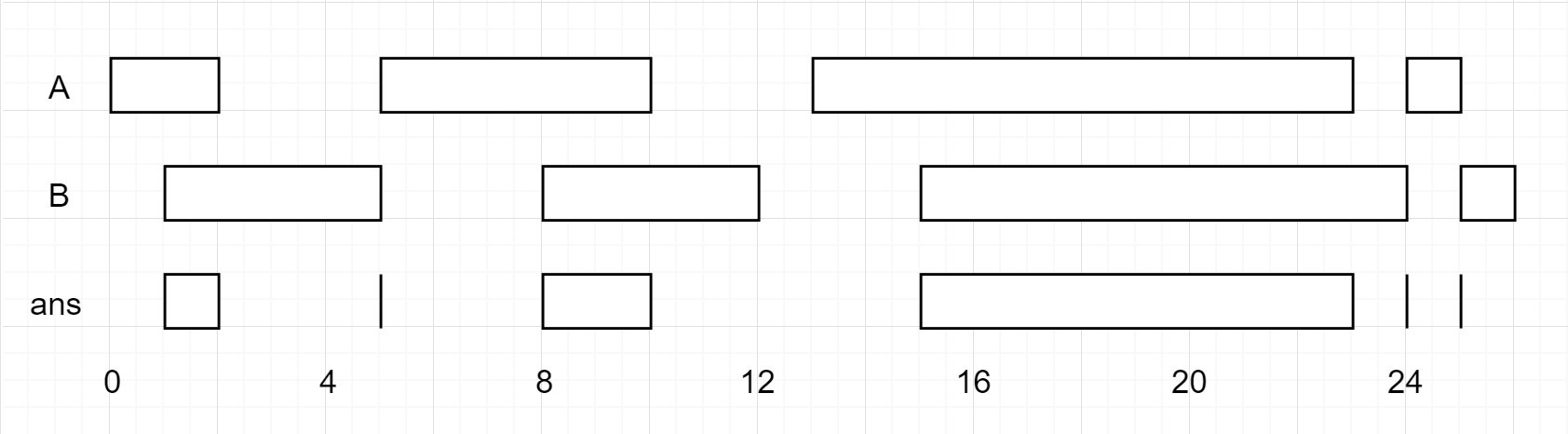
Input: firstList = [[0,2],[5,10],[13,23],[24,25]], secondList = [[1,5],[8,12],[15,24],[25,26]] Output: [[1,2],[5,5],[8,10],[15,23],[24,24],[25,25]]
Example 2:
Input: firstList = [[1,3],[5,9]], secondList = [] Output: []
Example 3:
Input: firstList = [], secondList = [[4,8],[10,12]] Output: []
Example 4:
Input: firstList = [[1,7]], secondList = [[3,10]] Output: [[3,7]]
Constraints:
0 <= firstList.length, secondList.length <= 1000firstList.length + secondList.length >= 10 <= starti < endi <= 109endi < starti+10 <= startj < endj <= 109endj < startj+1
中文题目
给定两个由一些 闭区间 组成的列表,firstList 和 secondList ,其中 firstList[i] = [starti, endi] 而 secondList[j] = [startj, endj] 。每个区间列表都是成对 不相交 的,并且 已经排序 。
返回这 两个区间列表的交集 。
形式上,闭区间 [a, b](其中 a <= b)表示实数 x 的集合,而 a <= x <= b 。
两个闭区间的 交集 是一组实数,要么为空集,要么为闭区间。例如,[1, 3] 和 [2, 4] 的交集为 [2, 3] 。
示例 1:

输入:firstList = [[0,2],[5,10],[13,23],[24,25]], secondList = [[1,5],[8,12],[15,24],[25,26]] 输出:[[1,2],[5,5],[8,10],[15,23],[24,24],[25,25]]
示例 2:
输入:firstList = [[1,3],[5,9]], secondList = [] 输出:[]
示例 3:
输入:firstList = [], secondList = [[4,8],[10,12]] 输出:[]
示例 4:
输入:firstList = [[1,7]], secondList = [[3,10]] 输出:[[3,7]]
提示:
0 <= firstList.length, secondList.length <= 1000firstList.length + secondList.length >= 10 <= starti < endi <= 109endi < starti+10 <= startj < endj <= 109endj < startj+1
通过代码
官方题解
方法:归并区间
思路
我们称 b 为区间 [a, b] 的末端点。
在两个数组给定的所有区间中,假设拥有最小末端点的区间是 A[0]。(为了不失一般性,该区间出现在数组 A 中)
然后,在数组 B 的区间中, A[0] 只可能与数组 B 中的至多一个区间相交。(如果 B 中存在两个区间均与 A[0] 相交,那么它们将共同包含 A[0] 的末端点,但是 B 中的区间应该是不相交的,所以存在矛盾)
算法
如果 A[0] 拥有最小的末端点,那么它只可能与 B[0] 相交。然后我们就可以删除区间 A[0],因为它不能与其他任何区间再相交了。
相似的,如果 B[0] 拥有最小的末端点,那么它只可能与区间 A[0] 相交,然后我们就可以将 B[0] 删除,因为它无法再与其他区间相交了。
我们用两个指针 i 与 j 来模拟完成删除 A[0] 或 B[0] 的操作。
[solution-Java]class Solution { public int[][] intervalIntersection(int[][] A, int[][] B) { List<int[]> ans = new ArrayList(); int i = 0, j = 0; while (i < A.length && j < B.length) { // Let's check if A[i] intersects B[j]. // lo - the startpoint of the intersection // hi - the endpoint of the intersection int lo = Math.max(A[i][0], B[j][0]); int hi = Math.min(A[i][1], B[j][1]); if (lo <= hi) ans.add(new int[]{lo, hi}); // Remove the interval with the smallest endpoint if (A[i][1] < B[j][1]) i++; else j++; } return ans.toArray(new int[ans.size()][]); } }
[solution-python]class Solution: def intervalIntersection(self, A: List[List[int]], B: List[List[int]]) -> List[List[int]]: ans = [] i = j = 0 while i < len(A) and j < len(B): # Let's check if A[i] intersects B[j]. # lo - the startpoint of the intersection # hi - the endpoint of the intersection lo = max(A[i][0], B[j][0]) hi = min(A[i][1], B[j][1]) if lo <= hi: ans.append([lo, hi]) # Remove the interval with the smallest endpoint if A[i][1] < B[j][1]: i += 1 else: j += 1 return ans
复杂度分析
时间复杂度:$O(M + N)$,其中 $M, N$ 分别是数组
A和B的长度。空间复杂度:$O(M + N)$,答案中区间数量的上限。
统计信息
| 通过次数 | 提交次数 | AC比率 |
|---|---|---|
| 29376 | 43133 | 68.1% |
提交历史
| 提交时间 | 提交结果 | 执行时间 | 内存消耗 | 语言 |
|---|
相似题目
| 题目 | 难度 |
|---|---|
| 合并区间 | 中等 |
| 合并两个有序数组 | 简单 |
| 员工空闲时间 | 困难 |




