原文链接: https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/recover-binary-search-tree
英文原文
You are given the root of a binary search tree (BST), where the values of exactly two nodes of the tree were swapped by mistake. Recover the tree without changing its structure.
Example 1:
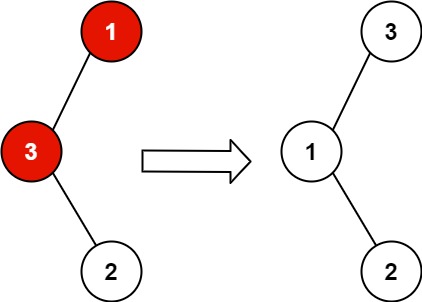
Input: root = [1,3,null,null,2] Output: [3,1,null,null,2] Explanation: 3 cannot be a left child of 1 because 3 > 1. Swapping 1 and 3 makes the BST valid.
Example 2:
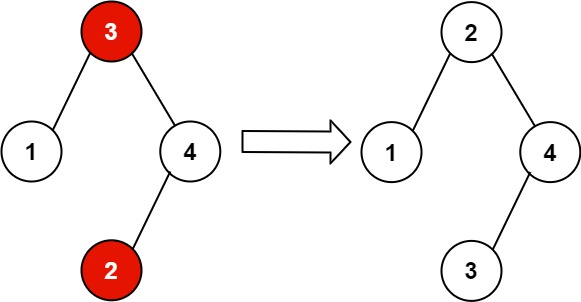
Input: root = [3,1,4,null,null,2] Output: [2,1,4,null,null,3] Explanation: 2 cannot be in the right subtree of 3 because 2 < 3. Swapping 2 and 3 makes the BST valid.
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[2, 1000]. -231 <= Node.val <= 231 - 1
Follow up: A solution using
O(n) space is pretty straight-forward. Could you devise a constant O(1) space solution?中文题目
给你二叉搜索树的根节点 root ,该树中的两个节点被错误地交换。请在不改变其结构的情况下,恢复这棵树。
进阶:使用 O(n) 空间复杂度的解法很容易实现。你能想出一个只使用常数空间的解决方案吗?
示例 1:

输入:root = [1,3,null,null,2] 输出:[3,1,null,null,2] 解释:3 不能是 1 左孩子,因为 3 > 1 。交换 1 和 3 使二叉搜索树有效。
示例 2:

输入:root = [3,1,4,null,null,2] 输出:[2,1,4,null,null,3] 解释:2 不能在 3 的右子树中,因为 2 < 3 。交换 2 和 3 使二叉搜索树有效。
提示:
- 树上节点的数目在范围
[2, 1000]内 -231 <= Node.val <= 231 - 1
通过代码
高赞题解
解法一
注意题目给出的条件,是 二叉搜索树,这就是意味着节点之间是有顺序关系的。
如果我们把整棵树都 遍历 一遍,将遍历的结果保存下来,比如放到一个数组中。
那么这个数组应该是有序的。
既然是有序的那就好办了,我们将这个有序的数组遍历一遍。
如果数组是完全有序的,那么直接返回就可以了。
否则,我们找到顺序不一致的两个下标i和j,将arr[i].val和arr[j].val的值互换一下即可。
 {:width=400}{:align=center}
{:width=400}{:align=center}
代码实现:
[]class Solution { public void recoverTree(TreeNode root) { List<TreeNode> list = new ArrayList<TreeNode>(); dfs(root,list); TreeNode x = null; TreeNode y = null; //扫面遍历的结果,找出可能存在错误交换的节点x和y for(int i=0;i<list.size()-1;++i) { if(list.get(i).val>list.get(i+1).val) { y = list.get(i+1); if(x==null) { x = list.get(i); } } } //如果x和y不为空,则交换这两个节点值,恢复二叉搜索树 if(x!=null && y!=null) { int tmp = x.val; x.val = y.val; y.val = tmp; } } //中序遍历二叉树,并将遍历的结果保存到list中 private void dfs(TreeNode node,List<TreeNode> list) { if(node==null) { return; } dfs(node.left,list); list.add(node); dfs(node.right,list); } }
[]class Solution(object): def recoverTree(self, root): nodes = [] # 中序遍历二叉树,并将遍历的结果保存到list中 def dfs(root): if not root: return dfs(root.left) nodes.append(root) dfs(root.right) dfs(root) x = None y = None pre = nodes[0] # 扫面遍历的结果,找出可能存在错误交换的节点x和y for i in xrange(1,len(nodes)): if pre.val>nodes[i].val: y=nodes[i] if not x: x = pre pre = nodes[i] # 如果x和y不为空,则交换这两个节点值,恢复二叉搜索树 if x and y: x.val,y.val = y.val,x.val
解法二
解法一种,我们利用了额外的数组保存了遍历的结果,如果后面一个数比前面一个数小,那就找到了要交换的节点。
 {:width=400}{:align=center}
{:width=400}{:align=center}
按照同样的思路,用中序遍历的方式遍历这颗二叉搜索树,我们再增加一个辅助的pre指针,记录 上一个 节点的值。
如果 当前节点的值,小于 上一个节点的值,这就找到了需要交换的节点。利用这种方式,就不需要额外的数组空间了。
详细过程请点击查看下面的幻灯片:
< ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, >
>
注意,这种方式仍然使用了外部空间,虽然我们只用了常数个变量,但是递归调用仍然是需要额外空间的,其空间复杂度是 $O(h)$,h 为树的高度。
所以用递归的方式遍历,或者手动模拟栈的方式遍历,都没有达到真正的常数空间。
代码实现 :
[]class Solution { //用两个变量x,y来记录需要交换的节点 private TreeNode x = null; private TreeNode y = null; private TreeNode pre = null; public void recoverTree(TreeNode root) { dfs(root); //如果x和y都不为空,说明二叉搜索树出现错误的节点,将其交换 if(x!=null && y!=null) { int tmp = x.val; x.val = y.val; y.val = tmp; } } //中序遍历二叉树,并比较上一个节点(pre)和当前节点的值,如果pre的值大于当前节点值,则记录下这两个节点 private void dfs(TreeNode node) { if(node==null) { return; } dfs(node.left); if(pre==null) { pre = node; } else { if(pre.val>node.val) { y = node; if(x==null) { x = pre; } } pre = node; } dfs(node.right); } }
[]class Solution(object): def recoverTree(self, root): # 用两个变量x,y来记录需要交换的节点 self.x = None self.y = None self.pre = None # 中序遍历二叉树,并比较上一个节点(pre)和当前节点的值,如果pre的值大于当前节点值,则记录下这两个节点 def dfs(root): if not root: return dfs(root.left) if not self.pre: self.pre = root else: if self.pre.val>root.val: self.y = root if not self.x: self.x = self.pre self.pre = root dfs(root.right) dfs(root) # 如果x和y都不为空,说明二叉搜索树出现错误的节点,将其交换 if self.x and self.y: self.x.val,self.y.val = self.y.val,self.x.val
解法三
解法二还不是真正的常数空间复杂度,想要达到常数空间,我们可以用 莫里斯遍历,这种方式可以做到 $O(1)$ 的空间复杂度去遍历一棵树。
我们先看看莫里斯遍历到底是咋回事
 {:width=400}{:align=center}
{:width=400}{:align=center}
回想一下中序遍历的递归版本是
dfs(root.left)
打印节点 root
dfs(root.right)也就是一路往左走到底,左边走不通了,再往右边走。对于上图来说,就是4->3->1这个过程,一路往左,走不通了再往右,也就是遍历2。
当然如果2的右边还有节点那么还会继续遍历下去。
现在2的右边已经是空了,对于递归来说操作系统自动出栈,然后会访问3这个节点。
既然2是叶子节点,左右子树都是空,我们可以利用这个空闲出来的信息,将2的右子树指向3,这样当2遍历完后,再往右走,就会自动走到3这个节点了。
同理,将3的右子树指向4,将6的右子树指向7。
这样的话,我们就可以省去额外的栈空间了。利用叶子节点的右子树这个特点,将其重新赋予指向关系 ,就是莫里斯遍历的核心了。
不过光是这样还不行,再回看上面那张图,其实已经不是一棵树了,而是变成图了。因为出现了循环。
所以,我们还需要将新加这个指向关系给去掉。
 {:width=400}{:align=center}
{:width=400}{:align=center}
对于上图来说,假设我们已经遍历到4 这个节点了,那就意味着4在左子树都遍历完了,对应的就是1,2,3都遍历完了。
从上图中也可以看出,所谓新加的指向关系,就是找到根节点左子树的最右子树,然后将最右子树的```right```指向根节点。
完整执行过程请点击下面幻灯片查看:
<,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,>
仔细看上图,```3```->```1```->```2```,这几个节点会走两遍。
第一遍的时候,```3```的左子树的最右节点是```2```,于是将```2.right```指向```3```。
之后等```1```,```2```两个节点都遍历完后,当前节点走到了```3```这里,又会触发一遍 根节点的左子树的最右节点这个循环查找逻辑,此时可以判断出最右的节点```2.right```是等于root的,所以就将2.right重新设置为空,即还原回去。
代码实现:
```Java []
class Solution {
public void recoverTree(TreeNode root) {
if(root==null) {
return;
}
TreeNode x = null;
TreeNode y = null;
TreeNode pre = null;
TreeNode tmp = null;
while(root!=null) {
if(root.left!=null) {
tmp = root.left;
while(tmp.right!=null && tmp.right!=root) {
tmp = tmp.right;
}
if(tmp.right==null) {
tmp.right = root;
root = root.left;
}
else {
if(pre!=null && pre.val>root.val) {
y = root;
if(x==null) {
x = pre;
}
}
pre = root;
tmp.right = null;
root = root.right;
}
}
else {
if(pre!=null && pre.val>root.val) {
y = root;
if(x==null) {
x = pre;
}
}
pre = root;
root = root.right;
}
}
if(x!=null && y!=null) {
int t = x.val;
x.val = y.val;
y.val = t;
}
}
}[]class Solution(object): def recoverTree(self, root): x = None y = None pre = None tmp = None while root: if root.left: tmp = root.left while tmp.right and tmp.right!=root: tmp = tmp.right if tmp.right is None: tmp.right = root root = root.left else: if pre and pre.val>root.val: y = root if not x: x = pre pre = root tmp.right = None root = root.right else: if pre and pre.val>root.val: y = root if not x: x = pre pre = root root = root.right if x and y: x.val,y.val = y.val,x.val
统计信息
| 通过次数 | 提交次数 | AC比率 |
|---|---|---|
| 78273 | 128511 | 60.9% |
提交历史
| 提交时间 | 提交结果 | 执行时间 | 内存消耗 | 语言 |
|---|




